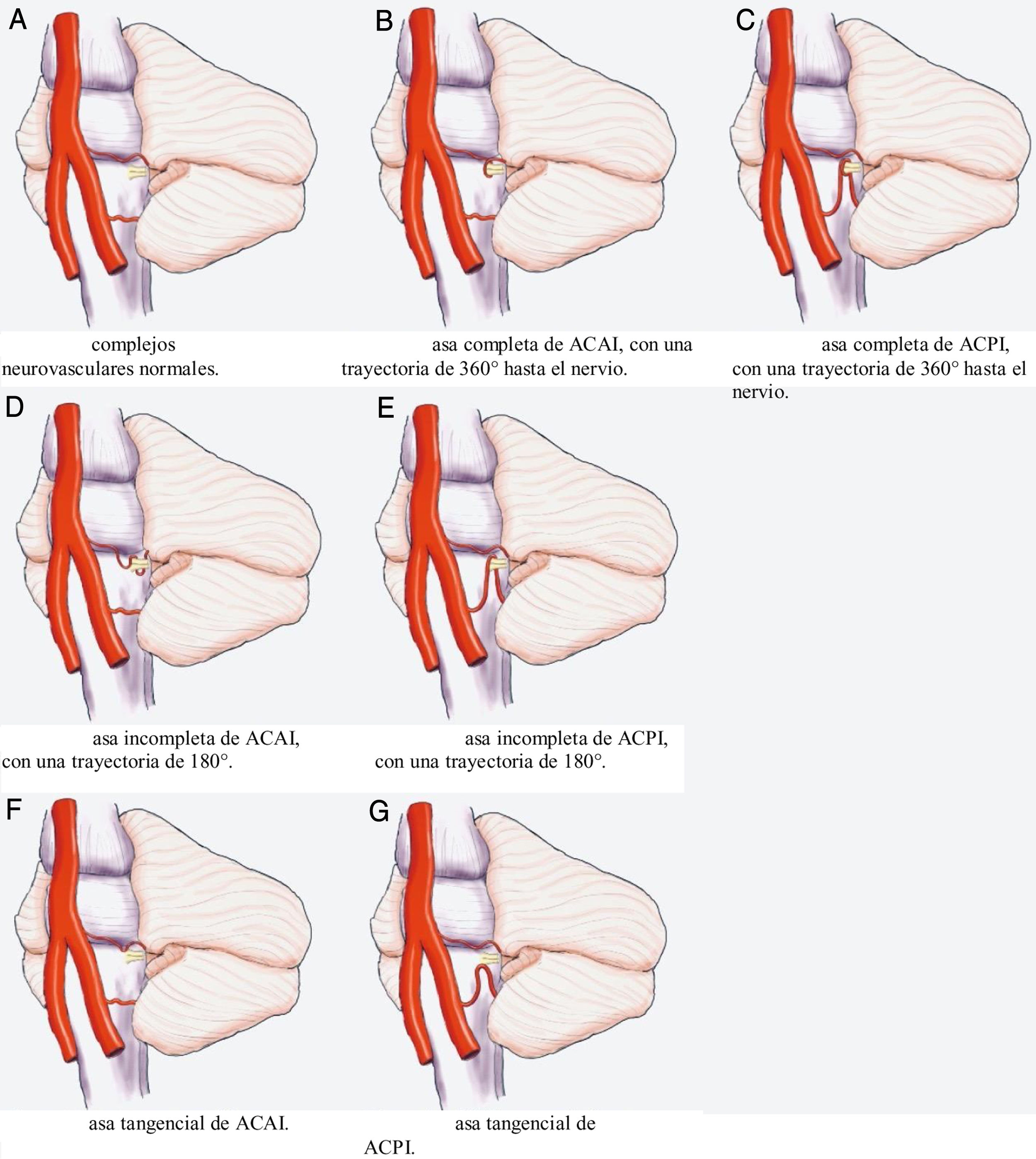
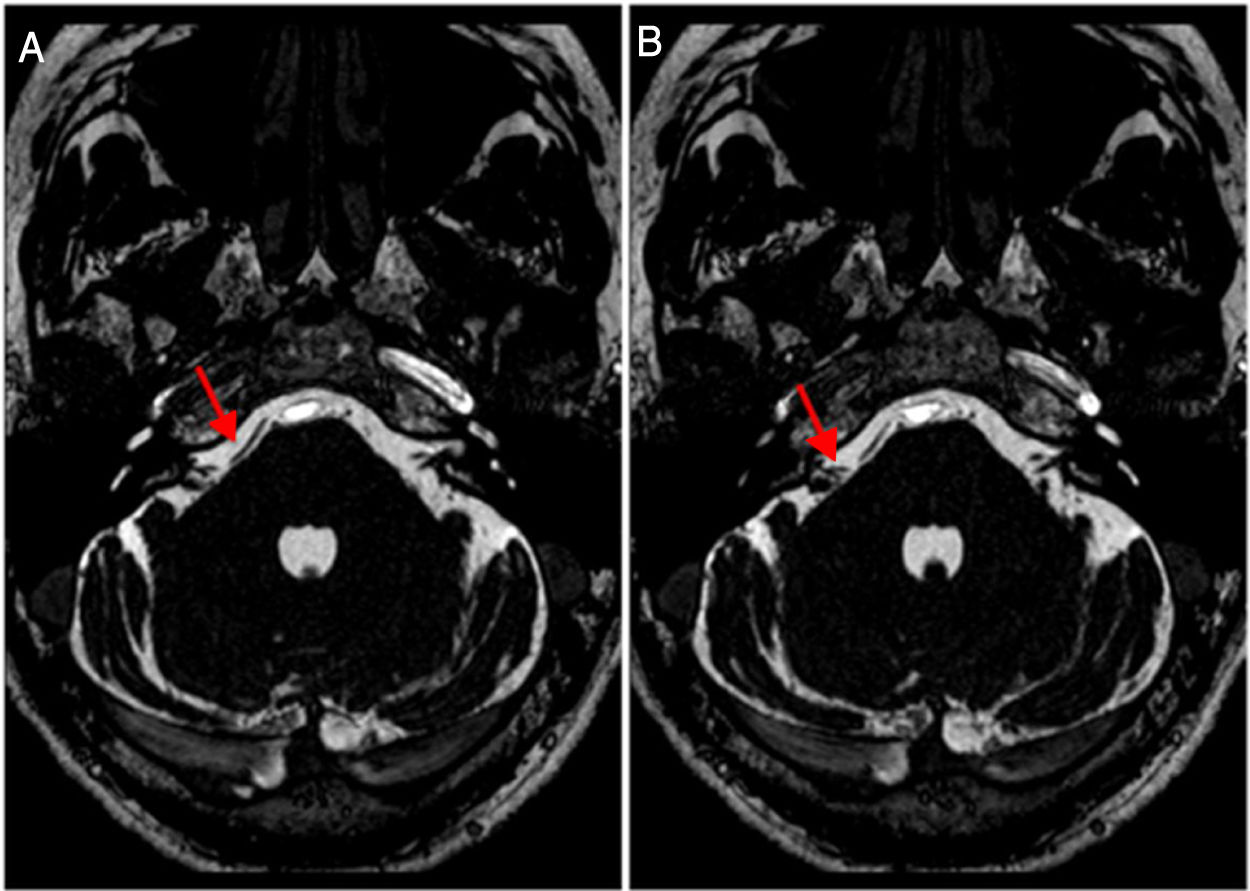
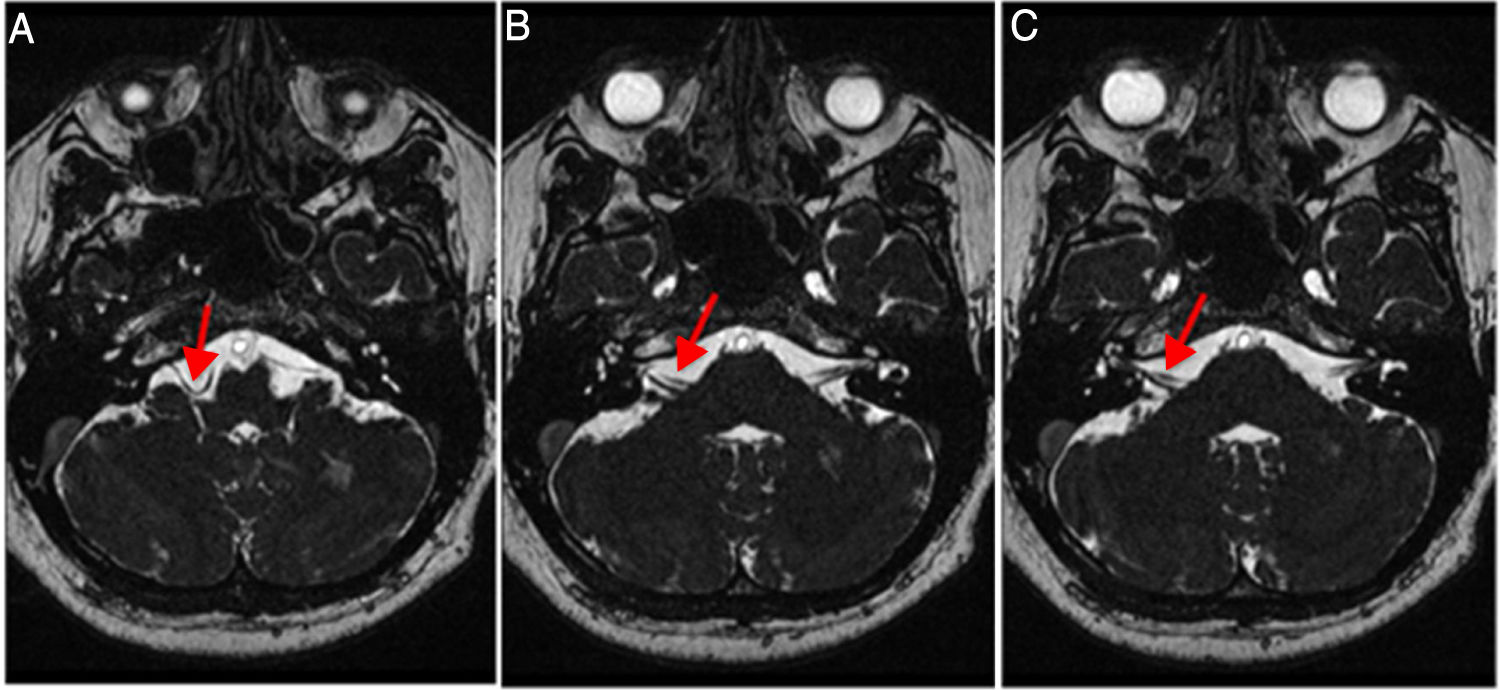
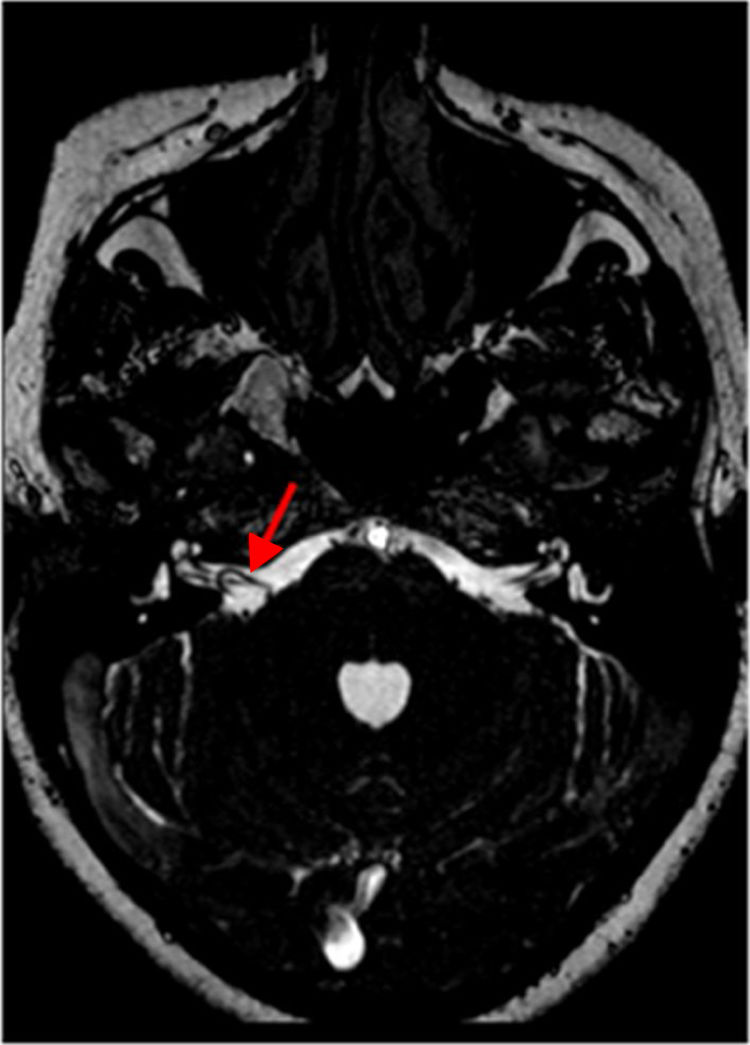
El tronco encefálico, situado en la fosa posterior, conecta el cerebro con la médula espinal. Debido a su ubicación, sus componentes nerviosos guardan una estrecha relación con estructuras vasculares.
ObjetivosDescribir una relación clínico-radiológica del asa vascular del ángulo pontocerebeloso en pacientes con síntomas indicativos de afectación vestibulococlear mediante evaluación por neuroimagen.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo y descriptivo. Se incluyeron todos los pacientes evaluados entre 2011 y 2017 con indicios de asa vascular del ángulo pontocerebeloso e historial clínico y estudios de diagnóstico por imagen disponibles.
Resultados102 pacientes (63 mujeres y 39 hombres) presentaban afectación vestibulococlear. La indicación clínica más frecuente fue mareos (41,18%). Se halló asa vascular unilateral en 43 pacientes (derecho: 21,57%, izquierdo: 20,59%) y bilateral en 59 pacientes (57,84%). El tipo de asa vascular más frecuente fue el tipo II (derecho: 69,14%; izquierdo: 58,75%). El origen más frecuente fue la arteria cerebelosa anteroinferior (ACAI) (derecha: 66,67%, izquierda: 65,00%). No se observó ninguna asociación entre asas vasculares y pérdida de audición neurosensitiva, nistagmo o vértigo. Se halló una asociación con acúfenos.
Conclusiones y significaciónLa presencia de asas vasculares no se asocia a la mayoría de los síntomas auditivos. No obstante, deben notificarse todos los hallazgos de los estudios por imagen. La interpretación de los hallazgos de los estudios por imagen debe correlacionarse con los síntomas clínicos después de excluir otras causas más frecuentes que puedan explicar la sintomatología.
The brainstem, situated in the posterior fossa, connects the brain to the spinal cord. Owing to its location, the nerves of the brainstem are closely related with vascular structures.
ObjectivesTo correlate the finding of vascular loops in the cerebellopontine angle on imaging with symptoms indicative of vestibulocochlear involvement.
Materials and methodsThis retrospective descriptive study included all patients evaluated between 2011 and 2017 with findings suggestive of vascular loops in the cerebellopontine angle for whom the clinical history and imaging studies were available.
ResultsA total of 102 patients (63 women and 39 men) had vestibulocochlear involvement. The most common clinical indication was dizziness (41.18%). A unilateral vascular loop was found in 43 patients (right: 21.57%, left: 20.59%) and bilateral loops were found in 59 (57.84%) patients. The most common type of vascular loop was type II (right: 69.14%; left: 58.75%). The most common origin of vascular loops was the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (right: 66.67%, left: 65.00%). No associations were observed between vascular loops and sensorineural hearing, nystagmus, or vertigo. There was an association with tinnitus.
Conclusions and significanceThe presence of vascular loops is not associated with most auditory symptoms. Nevertheless, all findings on imaging studies must be reported. The interpretation of the findings of imaging studies must be correlated with the clinical symptoms after other more common causes that can explain the symptoms have been ruled out.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora