La sensación de inestabilidad es un síntoma frecuente tras un latigazo cervical (LC), existiendo alteraciones objetivas del control postural en fases crónicas. El objetivo fundamental de nuestro estudio fue evaluar las alteraciones objetivas del control postural, así como la presencia o ausencia de alteraciones oculomotoras en las fases agudas tras un LC.
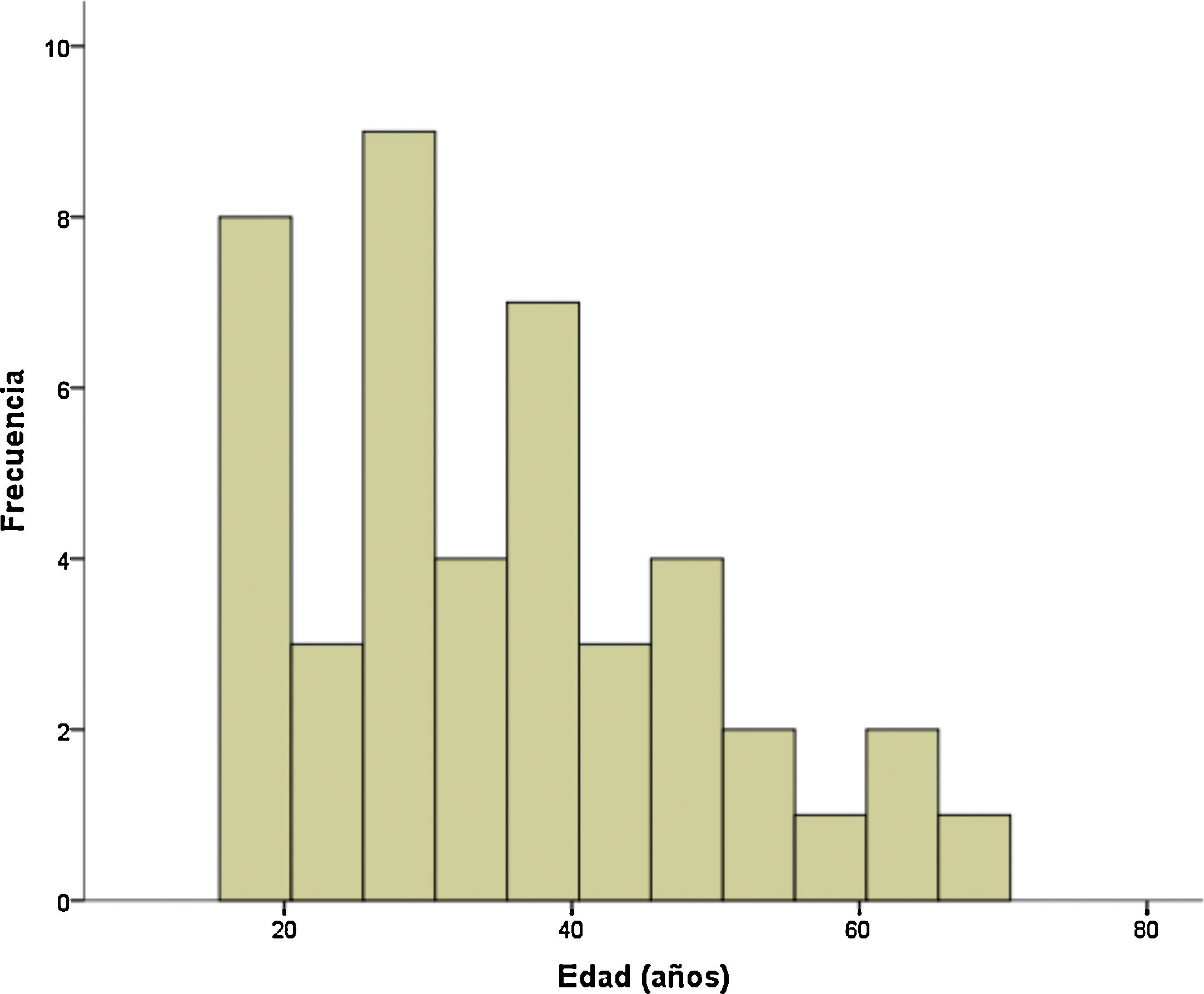
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio posturográfico mediante sistema NedSVE/IBV y una valoración oculomotora en una muestra de 44 sujetos afectos de LC en las primeras 24h tras el accidente.
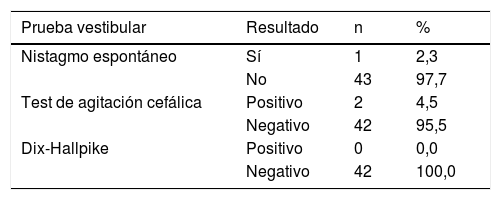
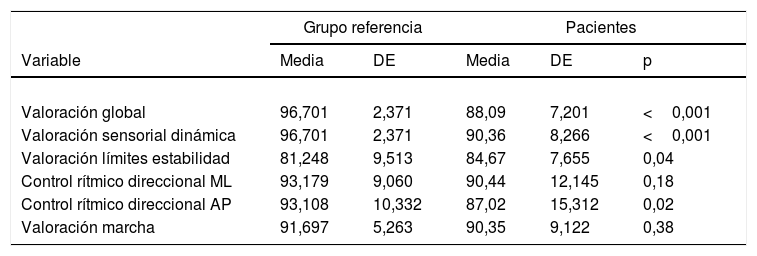
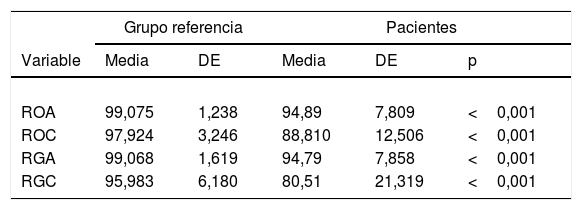
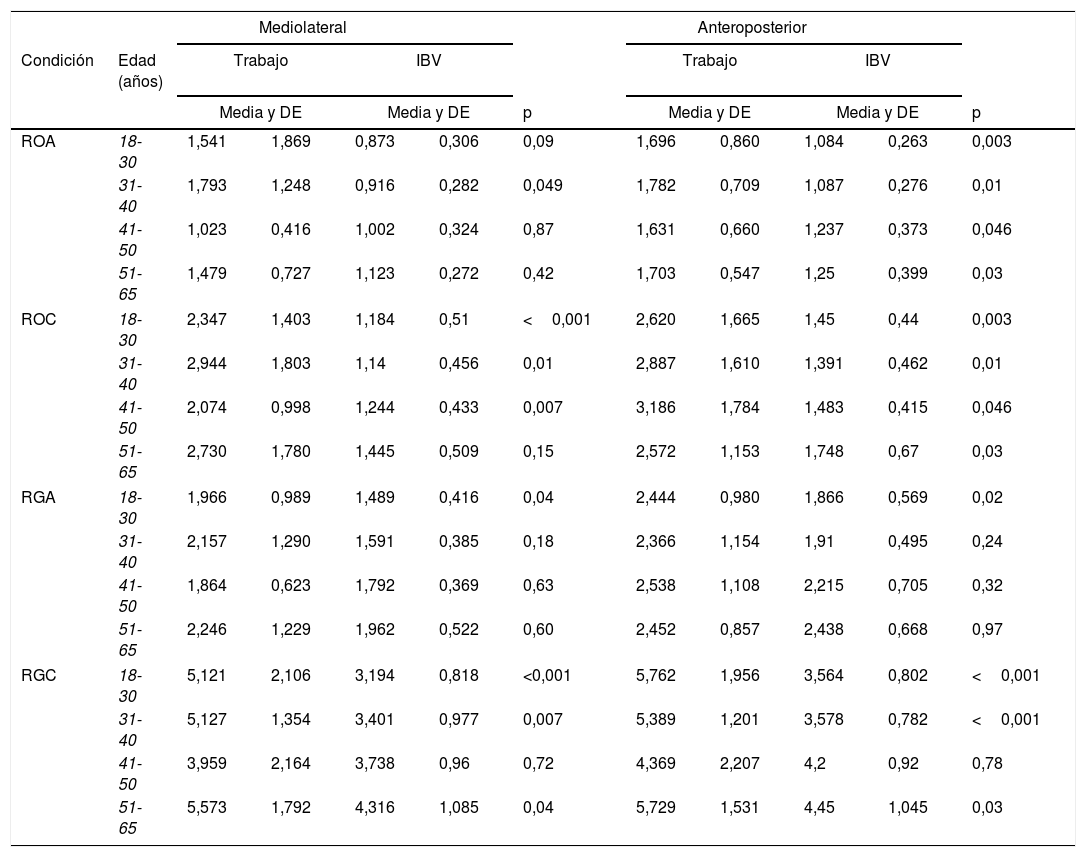
ResultadosMás de la mitad de los pacientes estudiados presentaron una valoración global por debajo de la normalidad. El patrón sensorial predominante fue el denominado patrón vestibular. Los parámetros fundamentales del test de Romberg (desplazamiento total, área de barrido, velocidad media, desplazamientos anteroposterior y mediolateral y fuerza anteroposterior) aumentaron siguiendo la secuencia Romberg ojos abiertos, Romberg gomaespuma ojos abiertos, Romberg ojos cerrados y Romberg gomaespuma ojos cerrados. En cuanto a la comparación con la normalidad y utilizando los valores de referencia del Instituto de Biomecánica de Valencia, los datos de los pacientes de LC muestran diferencias significativas en todos los parámetros analizados, salvo en la valoración de la marcha y el control rítmico direccional mediolateral.
ConclusionesNuestros datos confirman que los pacientes en fase aguda del LC presentan un peor control postural desde las primeras horas tras el accidente. Los resultados evidencian que los pacientes con LC tienen una mayor dependencia visual. Solo una minoría de los pacientes presentan alteraciones oculomotoras durante la exploración temprana.
Instability is a frequent symptom after whiplash (WL) with alterations in postural control in chronic phases. The main objective of our study was to evaluate if there were objective alterations in postural control in the acute phases after a WL, as well as to determine the presence or absence of oculomotor alterations in early phases.
Material and methodsA posturographic study was carried out using the NedSVE/IBV system, as well as an oculomotor assessment, in a sample of 44 patients with WL in the first 24h after the accident.
ResultsMore than half of the patients had a global assessment below normal. The predominant sensory pattern was vestibular. The main parameters of the Romberg test (total displacement, swept area, average speed, anteroposterior and mediolateral displacement and anteroposterior force) increased following the sequence Romberg open eyes, Romberg foam rubber open eyes, Romberg closed eyes, and Romberg foam rubber closed eyes. Concerning the comparison with normality and using the reference values of the Institute of Biomechanics of Valencia, the data from the WL patients showed significant differences in all the parameters analysed, except for gait assessment and the mediolateral directional rhythmic control.
ConclusionsOur data confirm that patients in the acute phase of WL have worse postural control than non-injured persons. The results suggest that patients with WL have greater visual dependence. Only a minority of patients had oculomotor abnormalities during early examination.