Existe gran disponibilidad de pruebas funcionales y escalas para evaluar distintos aspectos en la adaptación de personas amputadas, pero aún no hay consenso respecto a las más apropiadas.
ObjetivosDescribir las medidas de correlación y asociación entre tres pruebas funcionales para amputados de miembros inferiores y definir cuál es la más adecuada. Evaluar la satisfacción general de los usuarios de prótesis de miembro inferior y su asociación con las pruebas funcionales.
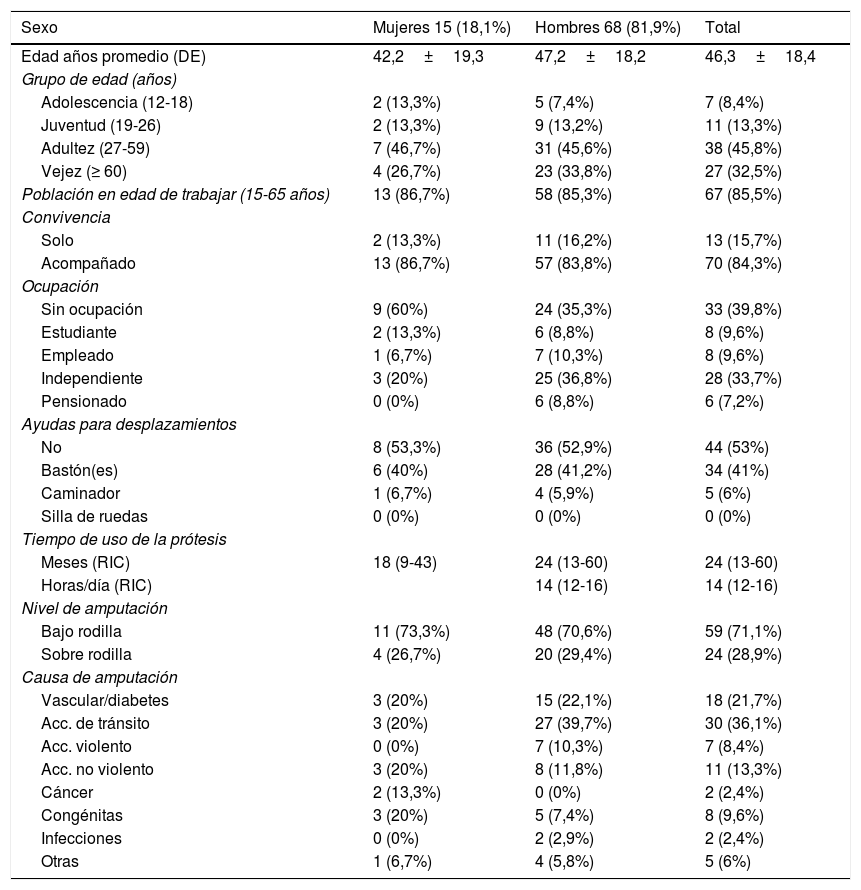
MétodosSe incluyeron 83 personas con amputación unilateral de miembro inferior, usuarios de prótesis exomodulares de bajo costo. Instrumentos: escala de Houghton, la subescala de movilidad del cuestionario de evaluación protésica y la prueba de marcha de 2 minutos (2MWT). El análisis estadístico se realizó mediante la prueba chi cuadrado y el coeficiente de correlación de Spearman.
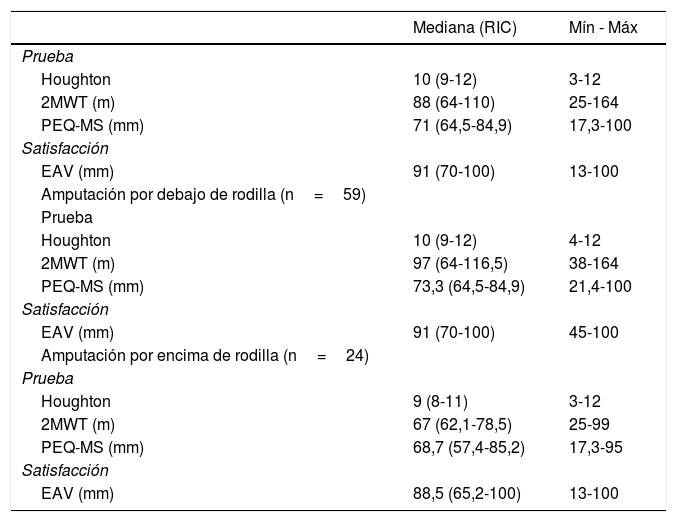
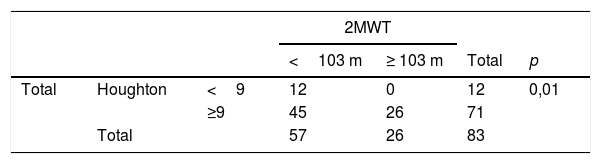
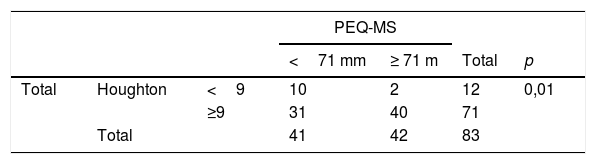
ResultadosLas pruebas funcionales tuvieron una correlación y asociación aceptable entre sí, la correlación entre la escala de Houghton y el 2MWT fue de mayor magnitud (r=0,56 para la muestra total; r=0,53 para amputados debajo de rodilla). Las medidas de asociación no lograron resultados estadísticamente significativos para amputados por encima de la rodilla, ni para la satisfacción general.
ConclusionesLa escala de Houghton y el 2MWT mostraron una buena correlación y asociación entre sí por lo que pueden ser considerados como instrumentos de primera línea para el seguimiento de los usuarios de prótesis exomodulares de miembro inferior. Para la satisfacción general no se identificó asociación importante con los instrumentos evaluados.
There is a wide variety of functional tests and scales for the assessment of different aspects in the adaptation of amputees, but there is still no consensus on which are the most appropriate.
ObjectivesTo describe the measures of correlation and association among three functional tests for lower-limb amputees and to define the most appropriate for this assessment. To assess general satisfaction in lower-limb prostheses users and its association with the functional tests.
MethodsWe included 83 unilateral lower-limb amputees who were users of low-cost exoskeletal prostheses. The instruments employed were the Houghton scale, the Prosthesis Evaluation Questionnaire - Mobility Scale (PEQ-MS) and the 2-minute walk test (2MWT). The statistical analysis was performed using the chi-square test and Spearman's correlation coefficient.
ResultsThe functional tests evaluated had an acceptable correlation and association with each other, but the Spearman correlation between the Houghton scale and the 2MWT was of greater significance (whole sample: r=0.56; below-knee amputees: r=0.53). The association measures did not achieve statistically significant results for above-knee amputees or for general satisfaction.
ConclusionsThe Houghton Scale and the 2MWT showed a good correlation and association with each other, becoming possible first-line instruments for the follow-up of exoskeletal lower limb prosthesis users. No significant association was identified between satisfaction and the instruments measured.