The study evaluated the effect of task-oriented training (TOT) on the motor function (MF) and balance of ambulant children with cerebral palsy (CP).
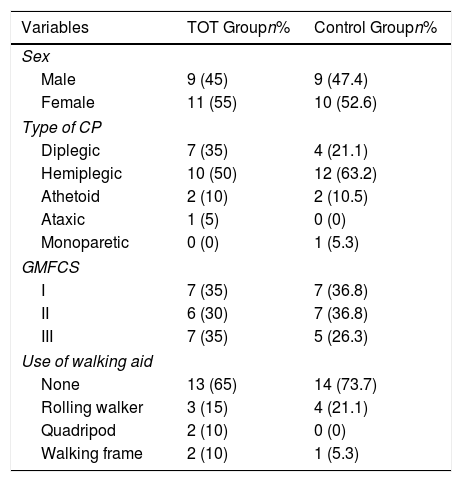
Materials and methodsA total of 46 children were randomised into TOT group (n=23) and Control Group (CG [n=23]), but 39 children complete the study. Balance and MF were assessed at baseline, 6th and 12th weeks and 6 weeks post-intervention. Data were analysed with repeated measures ANOVA, Friedman's, Mann–Whitney U, Student's-t and post hoc tests at α≤0.05.
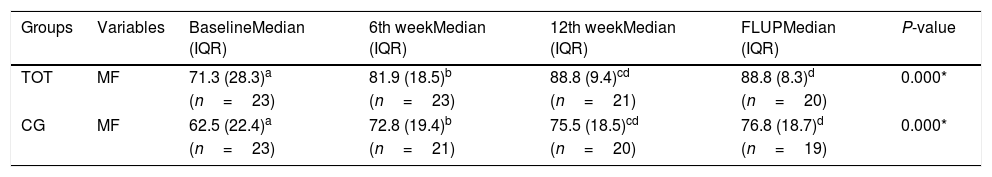
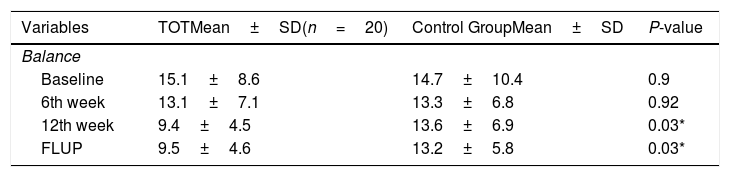
ResultsThe two groups were comparable in all baseline scores (P>0.05). At the 6th week, significant between-group difference was observed in MF only [TOT=81.9 (18.5); CG=72.8 (19.4)] (P<0.05). There were significant between-group differences in MF [TOT=88.8 (9.4); CG=75.5 (18.5); P<0.05] and balance (TOT=9.4±4.5; CG=13.6±6.9; P<0.05) at the 12th week (P<0.05) and 6 weeks post-intervention (P<0.05).
ConclusionTOT improved the balance and MF of ambulant children with CP.
El estudio evaluó el efecto de la formación orientada al cumplimiento de tareas (TOT) de la función motora (FM) y del equilibrio de los niños con parálisis cerebral (PC) capaces de caminar.
Materiales y métodosUn total de 46 niños fueron distribuidos al azar entre el grupo TOT (n=23) y el grupo de control (GC [n=23]), pero solo 39 niños finalizaron el estudio. El equilibrio y la FM se evaluaron al inicio del estudio, en las semanas 6 y 12 y 6 semanas después de la intervención. Los datos se analizaron con medidas repetidas ANOVA, Friedman, la U de Mann-Whitney, la t de Student y pruebas post hoc a α≤0,05.
ResultadosLos 2 grupos fueron comparables en todas las puntuaciones iniciales (p>0,05). En la sexta semana se observó una diferencia considerable entre los grupos de la FM sola (TOT=81,9 [18,5]; GC=72,8 [19,4]) (p<0,05). Hubo diferencias considerables entre los grupos de la FM (TOT=88,8 [9,4]; GC=75,5 [18,5]; p<0,05) y equilibrio (TOT=9,4±4,5; GC=13,6±6,9; p<0,05) a las 12 semanas (p<0,05) y 6 semanas después de la intervención (p<0,05).
ConclusiónLa formación TOT mejoró el equilibrio y la FM de los niños con PC capaces de caminar.