Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation programmes can reduce mortality but their effects on readmission rates are unclear. The primary aim was to evaluate the efficacy of a supervised exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation programme on cardiac readmissions in patients with acute coronary syndrome at five years.
MethodsWe conducted an open, controlled, randomized, hospital-based clinical trial. Patients were assigned either to the control group (CG) who received standard care or to the intervention group (IG) who participated in a supervised exercise programme (3h per week of supervised exercise training for 10 weeks). Patients were evaluated at 5 years.
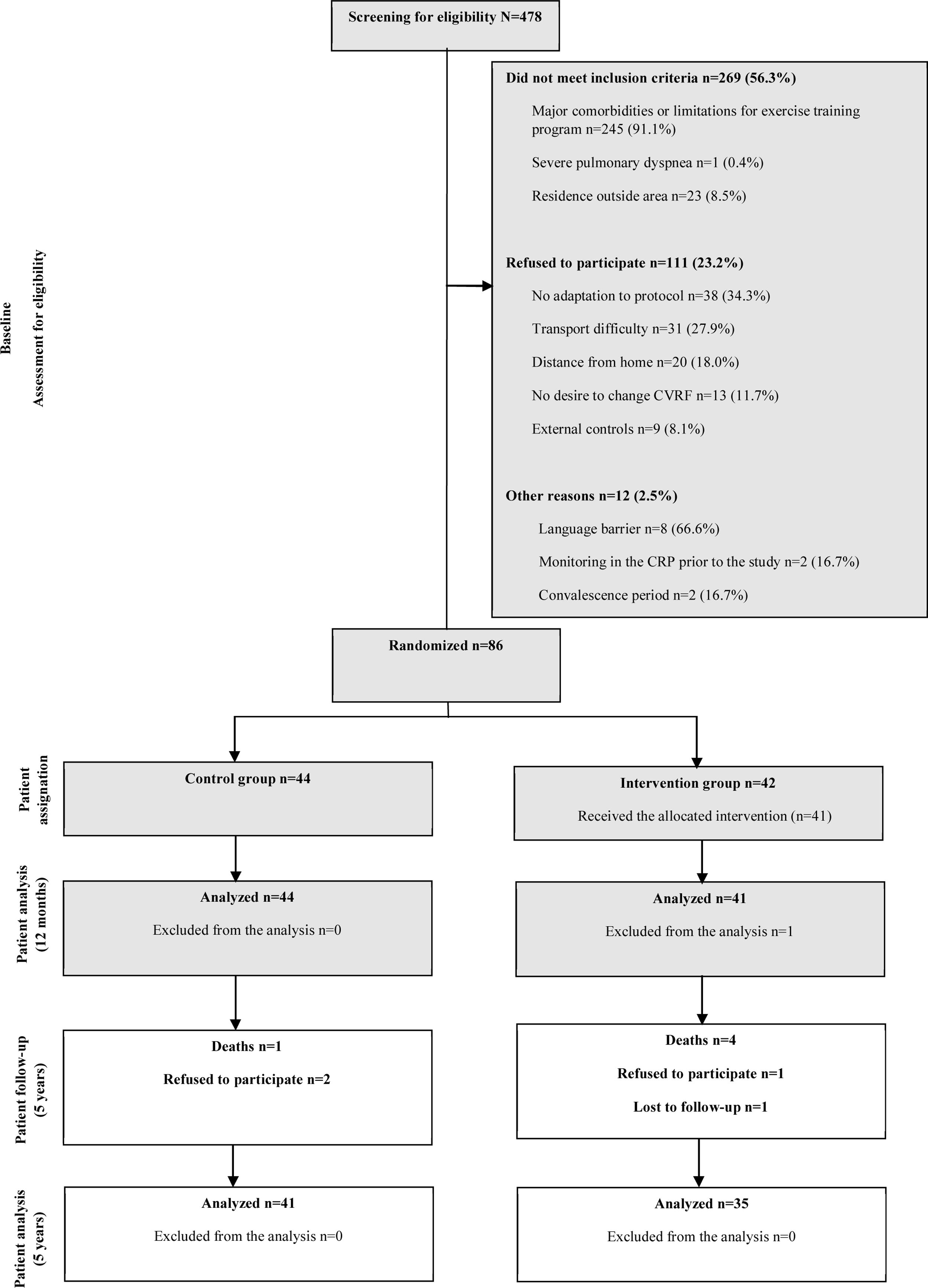
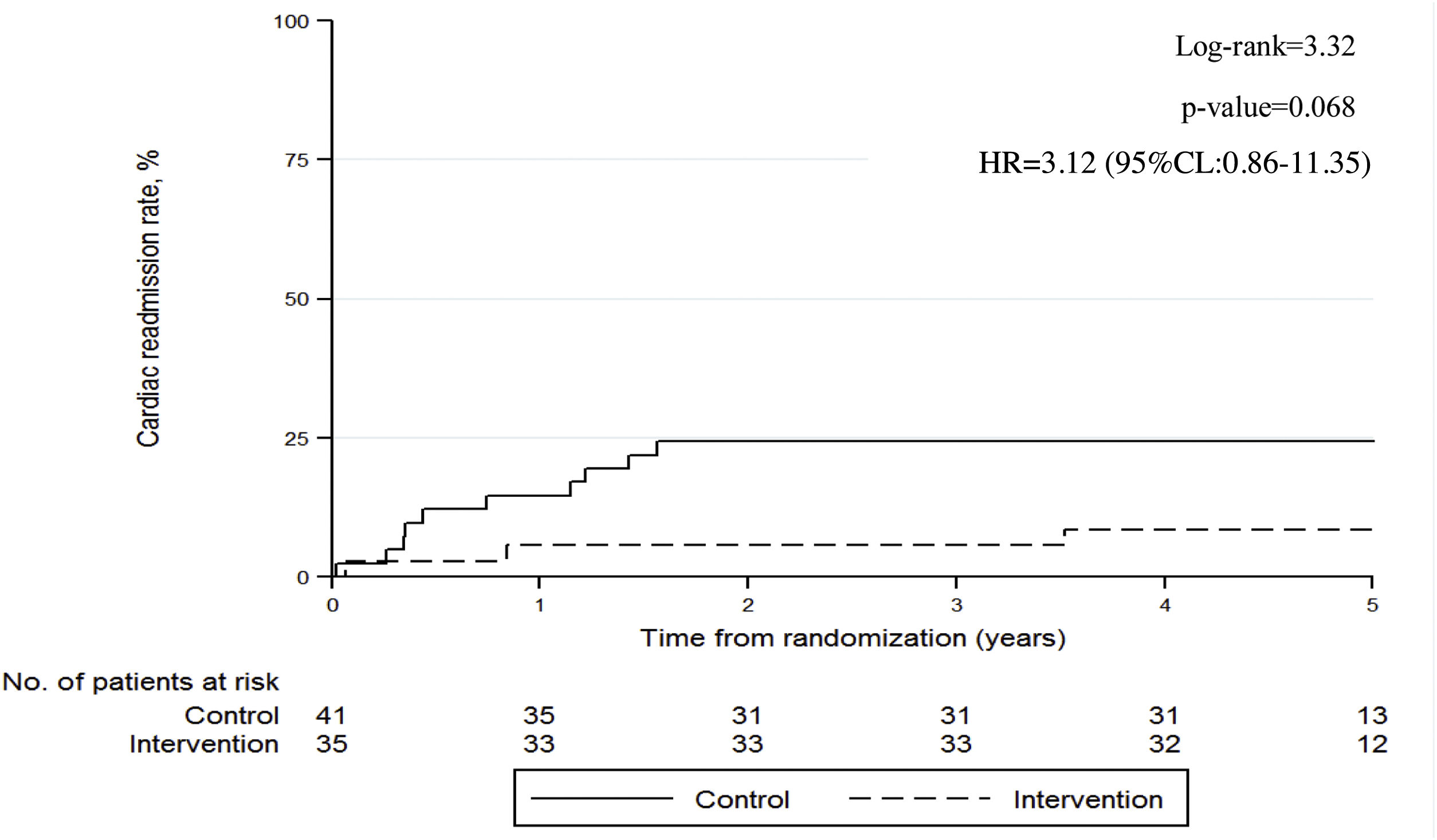
ResultsSeventy-six patients [41 CG, 35 IG, mean age 59.2 (SD 10.4), 82.9% men] were included. Cardiac readmission rates at 5 years were 24% in the CG compared to 9% in the IG (p=0.068), and readmission rates for all causes were 42% in the CG and 23% in the IG (p=0.085). Emergency care for cardiac disease was required more frequently in the CG (17% vs 11%, p=0.486). IG patients performed more regular and intensive exercise (62% vs. 33%, p=0.088). In both groups there were significant deterioration in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, body mass index, waist circumference, HbAc1, triglycerides, LDL and diet, and a significant increase in HDL.
ConclusionsPatients who participated in the supervised exercise training programme were readmitted less often than controls for cardiac disease and for all causes at 5 years, the reduction was clinically meaningful although not statistically significant. Control of cardiovascular risk factors deteriorated in both groups.
Los programas de rehabilitación cardíaca basados en ejercicio físico pueden reducir la mortalidad, pero sus efectos en los reingresos hospitalarios no son concluyentes. El objetivo principal fue evaluar la eficacia de un programa de rehabilitación cardíaca supervisado basado en ejercicio en los reingresos cardíacos en pacientes con cardiopatía isquémica a los 5 años.
MétodosEnsayo clínico aleatorizado, abierto, controlado y de ámbito hospitalario. Los pacientes se asignaron al grupo control (GC), que recibió atención estándar, o al grupo intervención (GI), que participó en un programa de ejercicio supervisado (3 h por semana durante 10 semanas). Los pacientes fueron evaluados a los 5 años.
ResultadosSetenta y seis pacientes (41 GC, 35 GI, edad media 59,2 [DE 10,4], 82,9% hombres) fueron incluidos. Los reingresos cardíacos a los 5 años fueron del 24% en el GC frente al 9% en el GI (p=0,068) y los reingresos por todas las causas fueron del 42% en el GC y el 23% en el GI (p=0,085). El GC asistió más a urgencias por motivo cardíaco (17% vs 11%; p=0,486). El GI realizó más ejercicio regular e intensivo (62% vs 33%; p=0,088). En ambos grupos hubo un deterioro significativo de presión arterial sistólica y diastólica, el índice de masa corporal, el perímetro abdominal, HbAc1, los triglicéridos, LDL y dieta, y un aumento significativo de HDL.
ConclusionesLos pacientes que participaron en el programa de entrenamiento de ejercicio supervisado fueron readmitidos con menos frecuencia que los controles por enfermedad cardíaca y por todas las causas a los 5 años; la reducción fue clínicamente relevante, aunque no estadísticamente significativa. El control de los factores de riesgo cardiovascular se deterioró en ambos grupos.