La hipoterapia (HPOT) y los simuladores de hipoterapia (SHPOT) se utilizan en niños con parálisis cerebral para lograr su máxima funcionalidad e independencia. El objetivo es conocer si la HPOT y los SHPOT producen los mismos efectos beneficiosos sobre el equilibrio, la función motora gruesa y el control postural en menores de 18 años con parálisis cerebral.
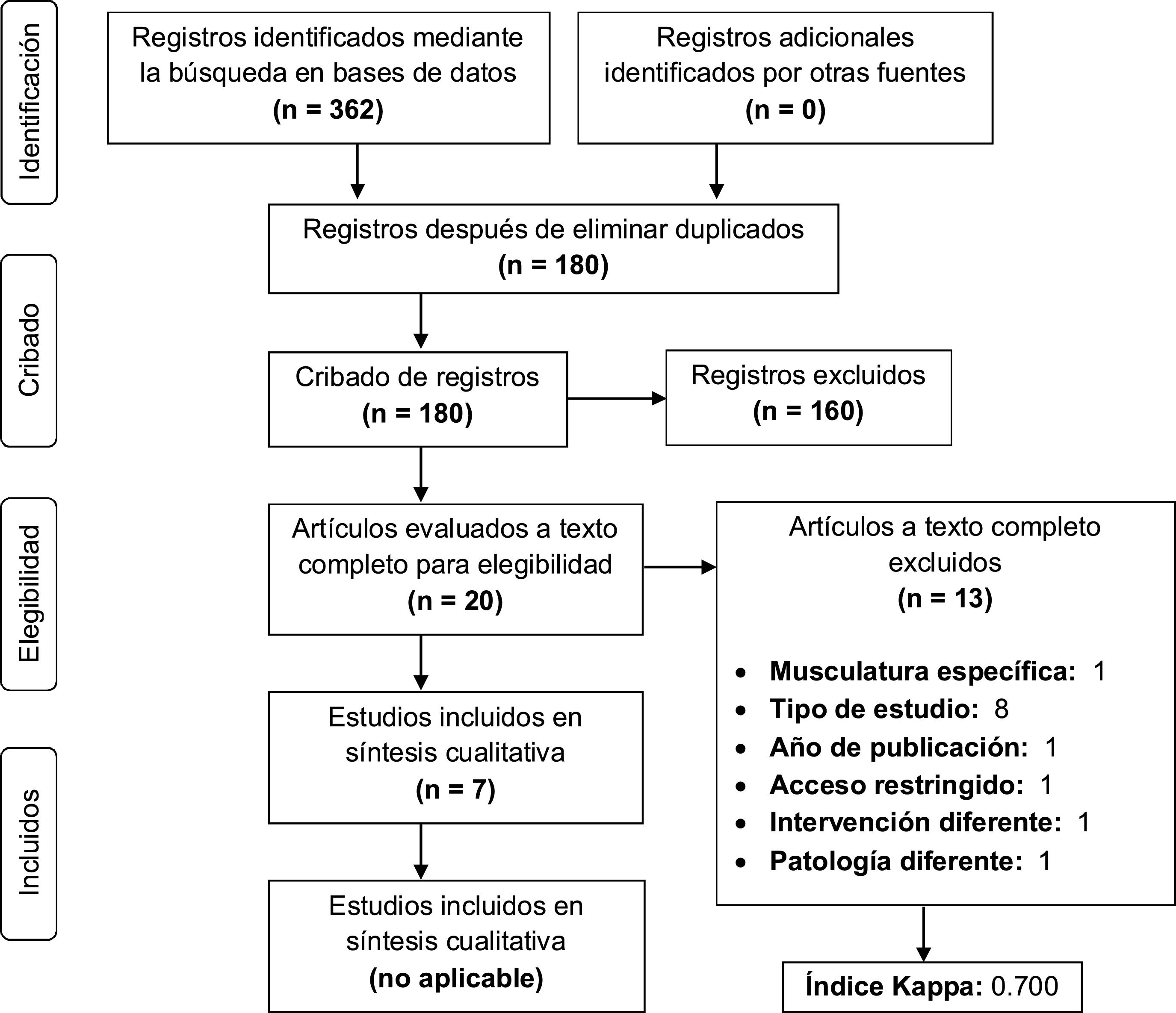
Materiales y métodosSe utilizaron como palabras clave: hippotherapy, equine-assisted therapy y cerebral palsy. Las bases de datos utilizadas fueron: PeDro, Scopus, LILACS, ScienceDirect, Cochrane Library, Web of Science y CINAHL Complete (Ebsco). Fueron incluidos ensayos clínicos aleatorizados que estudiaran el efecto de la HPOT y/o los SHPOT sobre las variables mencionadas.
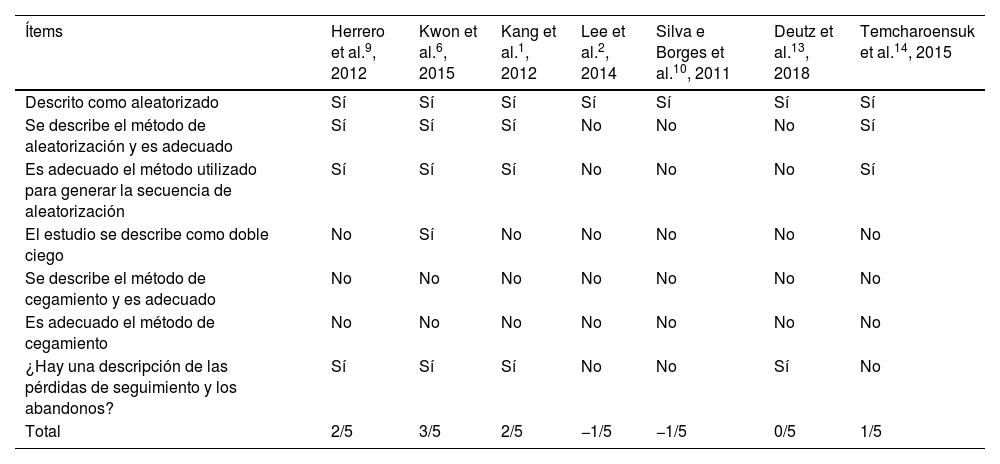
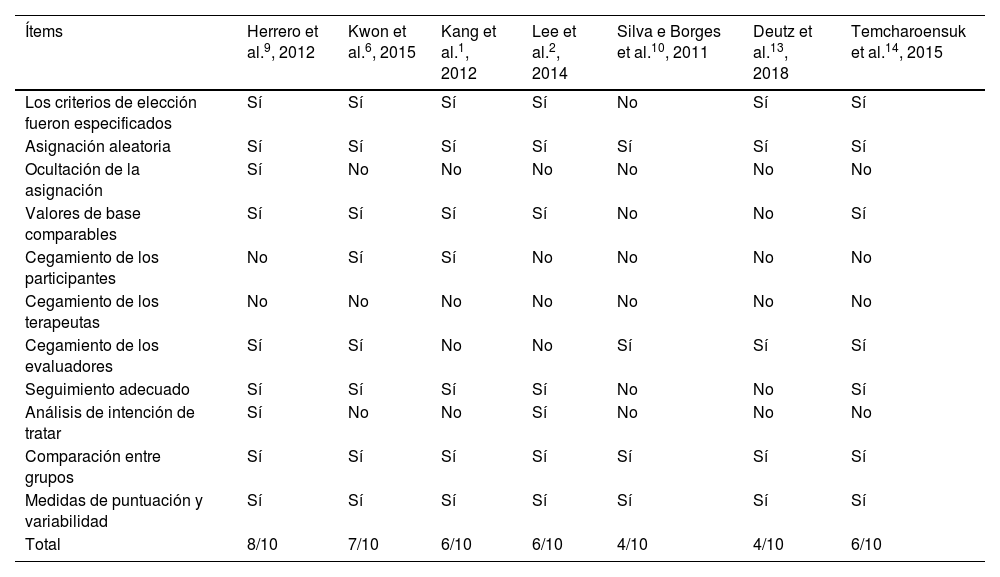
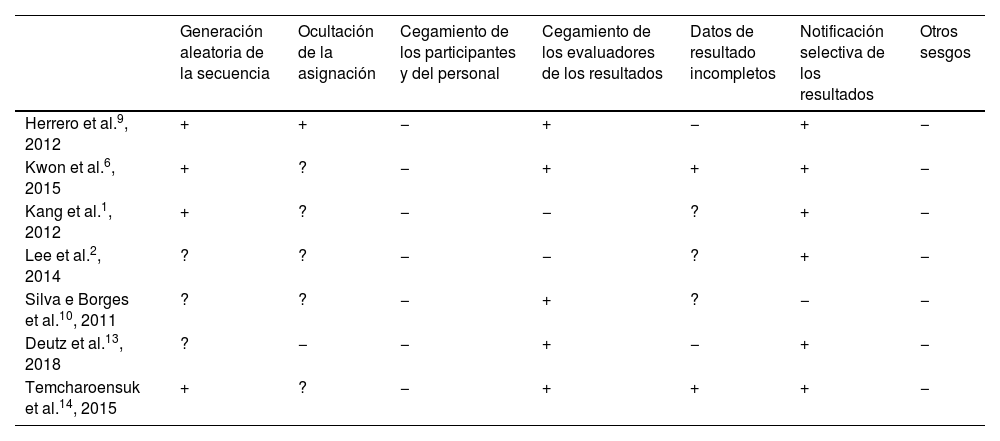
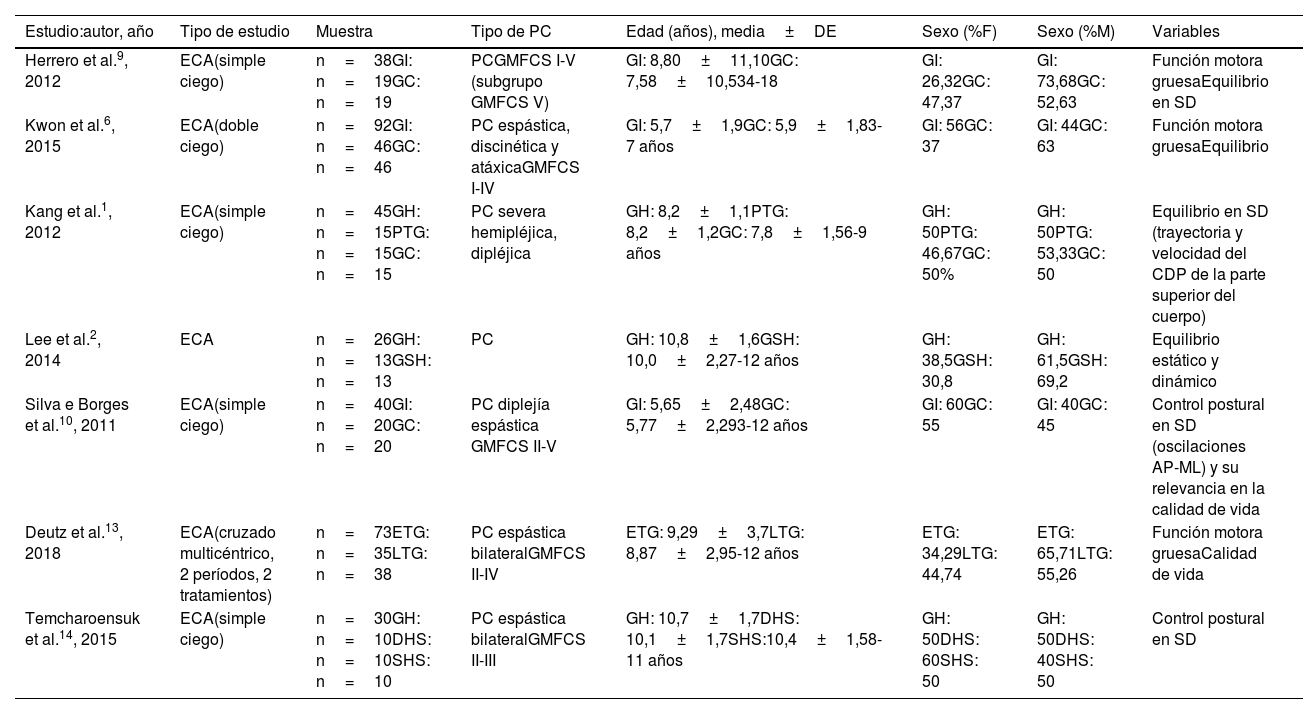
ResultadosCuatro estudios evaluaron el equilibrio, 4 la función motora gruesa y 2 el control postural. La HPOT y los SHPOT produjeron beneficios en todos ellos.
ConclusionesAmbas intervenciones producen mejoras sobre las variables estudiadas, aunque aumentan con la HPOT posiblemente debido a una mayor estimulación sensorial.
Hippotherapy (HPOT) and hippotherapy simulators (SHPOT) are used in children with cerebral palsy to achieve their maximum functionality and independence. The aim is to find out if HPOT and SHPOT produce the same effects on balance, gross motor function, and postural control in children under 18 years old with cerebral palsy.
Materials and methodsThe keywords used were: hippotherapy, equine-assisted therapy and cerebral palsy. The databases used were PeDro, Scopus, LILACS, ScienceDirect, Cochrane Library, Web of Science and CINAHL Complete (Ebsco). Studies were included if they were randomized clinical trials that studied the effect of HPOT and/or SHPOT on the variables mentioned in these patients.
ResultsFour studies assessed balance, 4 studied gross motor function, and 2 investigated postural control. Both HPOT and SHPOT produced benefits in all of them.
ConclusionsAccording to the studied variables both interventions produce similar improvements. Although, they increase with HPOT possibly due to greater sensory stimulation.