Describir nuestra experiencia con un protocolo basado en el uso de sevoflurano para la sedación y analgesia durante la infiltración de toxina botulínica tipo A (BoNT-A), en niños con parálisis cerebral (PC), especialmente en términos de seguridad y eficacia.
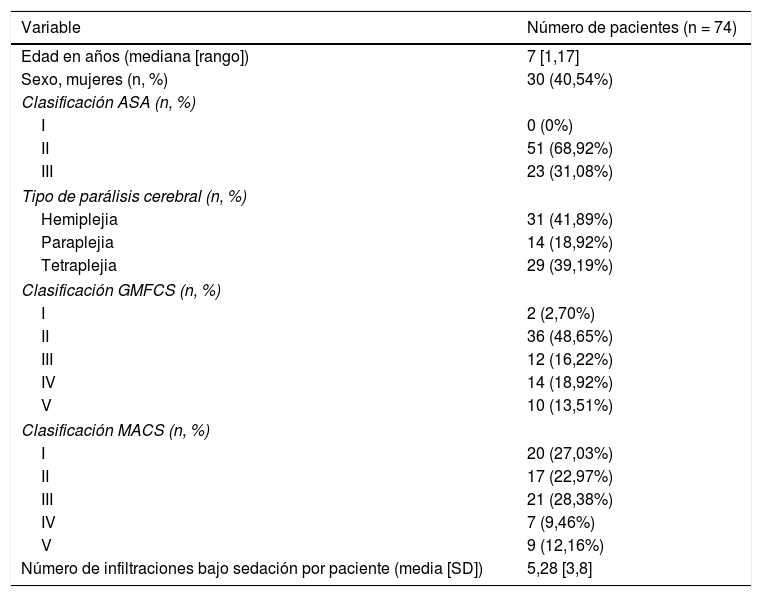
Material y métodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo de pacientes con PC a los que se realizó infiltración con BoNT-A bajo sedación con sevoflurano desde noviembre de 2012 hasta diciembre de 2019. Se revisaron las características demográficas, las características clínicas y funcionales, la efectividad de la sedación, los eventos adversos (EA) y la satisfacción del profesional.
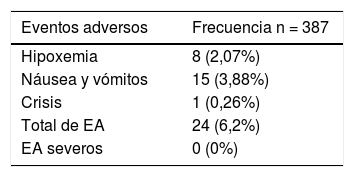
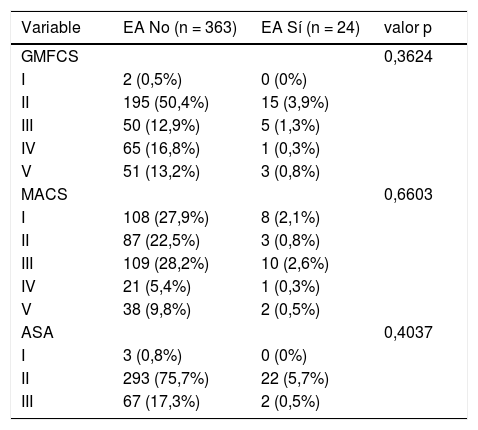
ResultadosSe realizaron 387 sedaciones en 74 pacientes diagnosticados de PC. La sedación efectiva se logró en el 100% de los procedimientos, facilitando la colaboración durante la infiltración y la satisfacción del profesional. Se notificaron EA en el 6,02% de los procedimientos, siendo los más frecuentes las náuseas y los vómitos (3,88%) y la hipoxemia transitoria (2,07%). No se informaron EA graves. No se encontró asociación entre la incidencia de EA y las variables clínicas, funcionales o el riesgo antes de la anestesia.
ConclusionesLa sedación con sevoflurano muestra resultados prometedores en términos de seguridad y efectividad para el manejo de la agitación y el dolor durante la infiltración de BoNT-A en nuestra práctica clínica diaria. Además, puede facilitar la infiltración, permitir la exploración bajo sedación e infiltración multinivel con buena tolerancia.
This study aimed to describe our experience with a protocol based on sevoflurane sedation to control pain and agitation during botulinum toxin-A (BoNT-A) infiltration in children with cerebral palsy (CP), especially in terms of safety and efficacy.
Material and methodsWe conducted a retrospective observational study of patients diagnosed with CP who underwent BoNT-A infiltration with sevoflurane sedation from November 2012 to December 2019. Demographic, clinical and functional characteristics, the effectiveness of sedation, adverse events (AE) and professional satisfaction were reviewed.
ResultsA total of 387 sedations were successfully performed in 74 patients. Effective sedation was achieved in 100% of procedures, facilitating collaboration during infiltration and improving professional satisfaction. AE were reported in 6.02% of the procedures, the most frequent being nausea and vomiting (3.88%) and transient hypoxemia (2.07%). There were no severe AE. No association was found between the incidence of AE and the clinical and functional variables or risk before anaesthesia.
ConclusionSevoflurane sedation shows promising results in terms of safety and effectiveness for the management of agitation and pain during BoNT-A infiltration in our daily clinical practice. In addition, it can facilitate infiltration, allowing examination under sedation and multilevel infiltration with good tolerance.