To assess an educational counselling intervention, based on personalised nurse counselling (NC) in neurological patients [with a diagnosis of epilepsy, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis, cerebrovascular disease, spinal cord injury, and aneurysms].
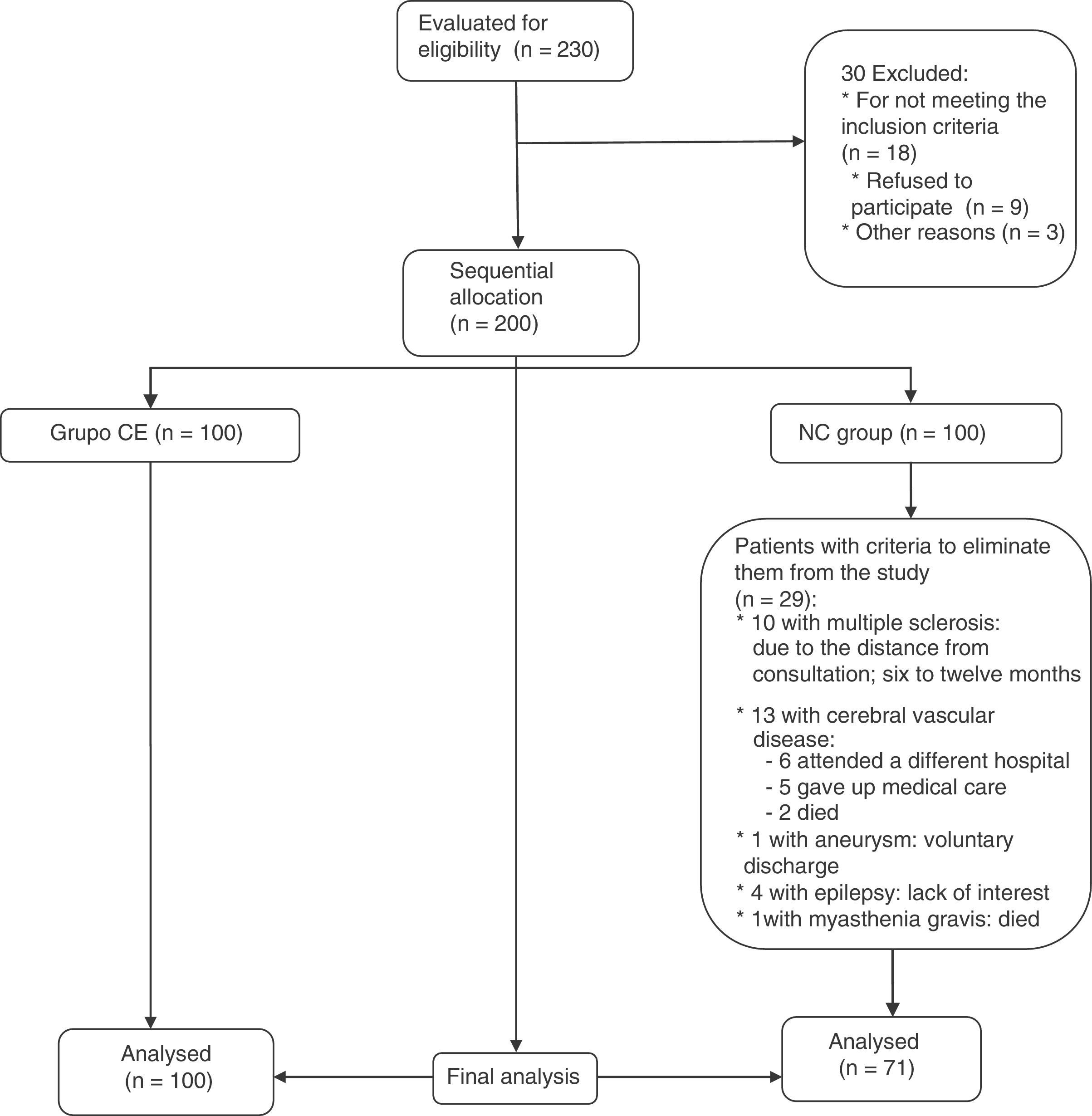
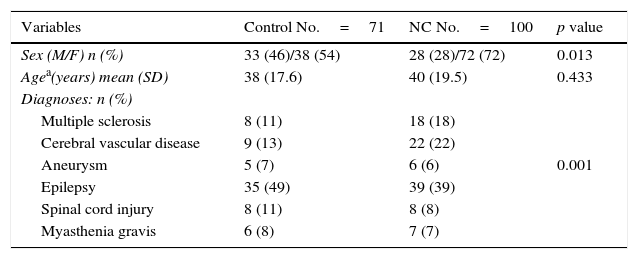
MethodA total of 171 patients were included and sequentially randomised into two arms and followed-up for one year: NC (n=100), and controls (n=71) who were given conventional inpatient care. The independence level was evaluated (Barthel Index), as well as the treatment adherence (Morisky Green Scale), both included in the Marjory Gordon Functional Health Pattern Assessment guidelines. ANCOVA and logistic regression were used (OR; 95% CI), and the size of effect (sef) was calculated.
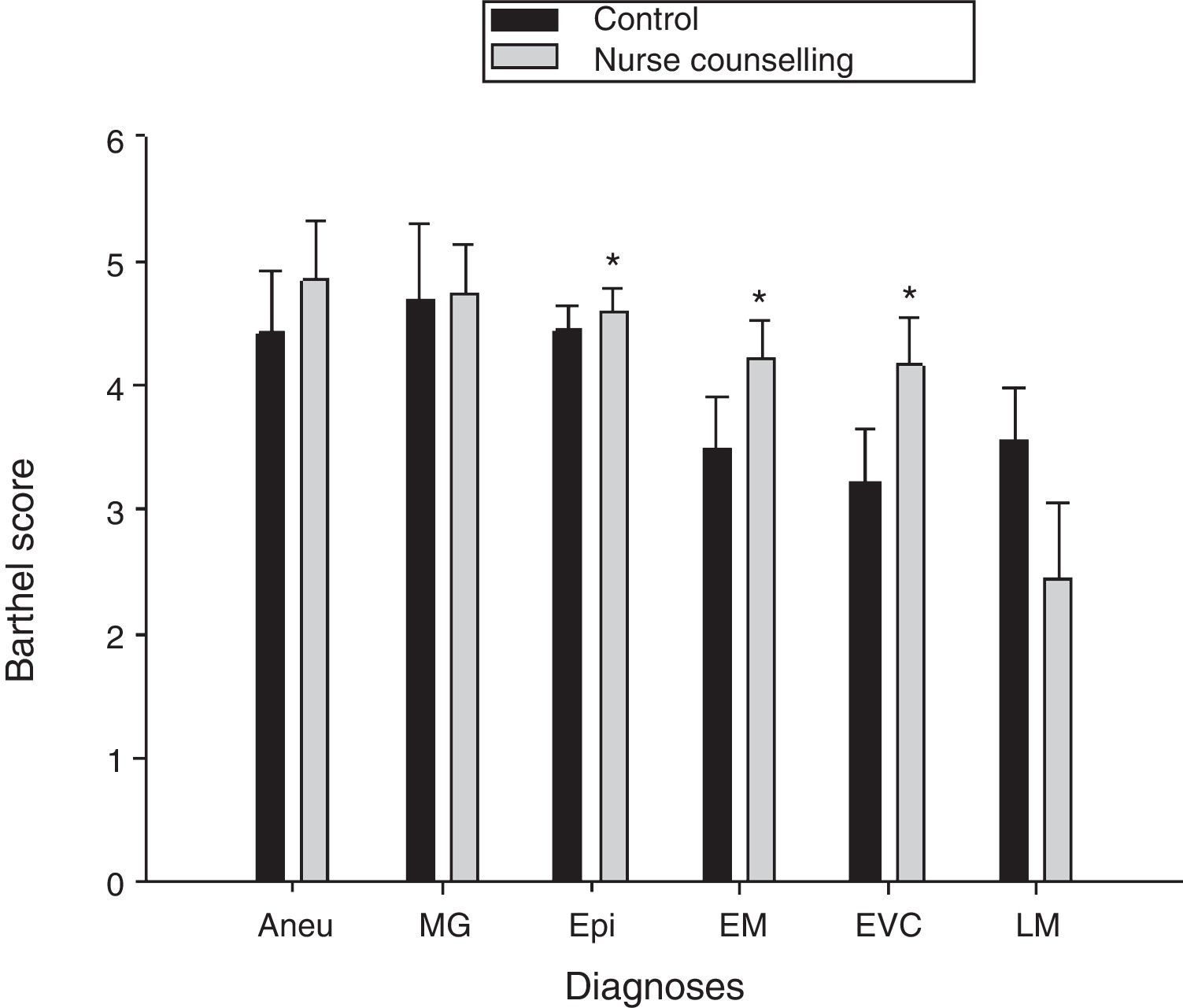
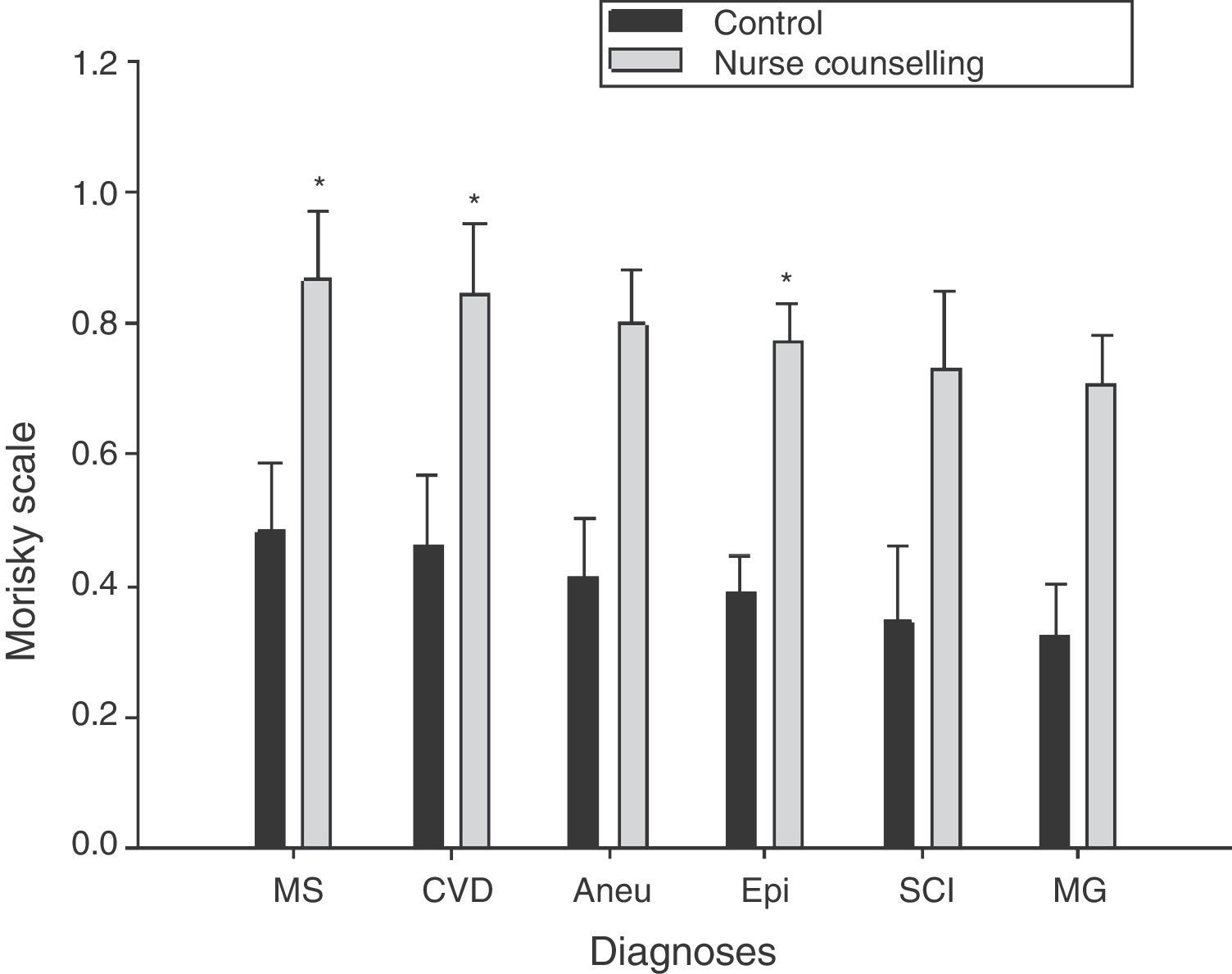
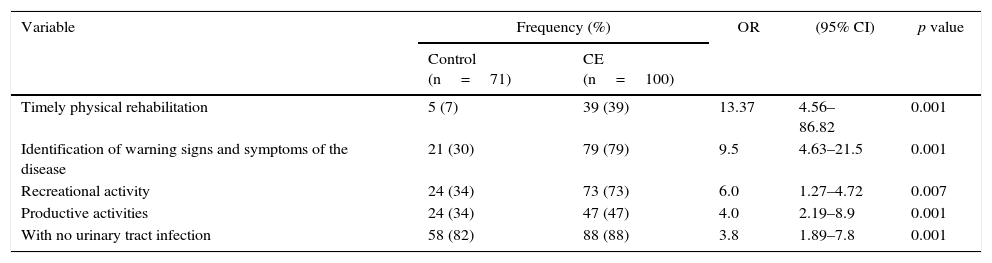
ResultsThe NC group had a higher score of treatment adherence (sef, 74%) and independence (sef, 23%); engaged in recreational activities (OR=6.0; 95% CI; 1.27–4.72), productive activities (OR=4.0; 95% CI; 2.19–8.9), recognition of warning signs and symptoms (OR=9.5; 95% CI; 4.63–21.5), received timely rehabilitation (OR=13.37; 95% CI; 4.56–86.82), and had less urination problems (OR=3.8; 95% CI; 1.89–7.8).
ConclusionsNC shows outstanding benefits for the patients’ health, of treatment adherence, and independence, and enables the patient to return to work and to carry out other daily activities.
DiscussionWe agree with other authors in that it is essential to provide personalised health education to patients with neurological disease and their families.
Evaluar una intervención de enfermería basada en consejería personalizada de enfermería (CE) dirigido a pacientes neurológicos con diagnósticos de epilepsia, miastenia gravis, esclerosis múltiple, enfermedad vascular cerebral, lesión medular y aneurisma.
MétodoLos pacientes fueron asignados en forma secuencial a 2 grupos: CE (n=100) o al grupo control, que recibió atención hospitalaria usual (n=71). Los 2 grupos se evaluaron durante un año. Se identificó el efecto del CE en el grado de independencia (medido con el índice de Barthel), la adherencia al tratamiento (medido con la escala de Morisky Green) integradas en la guía de valoración con los 11 patrones funcionales de Marjory Gordon. Se realizó ANCOVA y regresión logística (OR; IC 95%) y se calculó el tamaño del efecto (ef).
ResultadosEl grupo CE mostró mayor adherencia al tratamiento (ef: 74%), independencia (ef: 23%), realizó actividades recreativas (OR=6,0;IC 95%: 1,27, 4,72), actividades productivas (OR=4,0;IC 95%:2,19, 8,9), identificó signos y síntomas de alarma (OR=9,5;IC 95%: 4,63, 21,5), realizó rehabilitación oportuna (OR=13,37;IC 95%: 4,56, 86,82) y tuvo menos problemas de micción (OR=3,8; IC 95%: 1,89, 7,8).
ConclusionesEl CE mostró notables beneficios, destaca la adherencia al tratamiento y el aumento de la independencia, lo que favorece su reincorporación al trabajo y otras actividades cotidianas.
DiscusiónCoincidimos con otros autores en que es indispensable dar educación para la salud a pacientes con enfermedad neurológica y a sus familiares de manera personalizada.
Artículo
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora