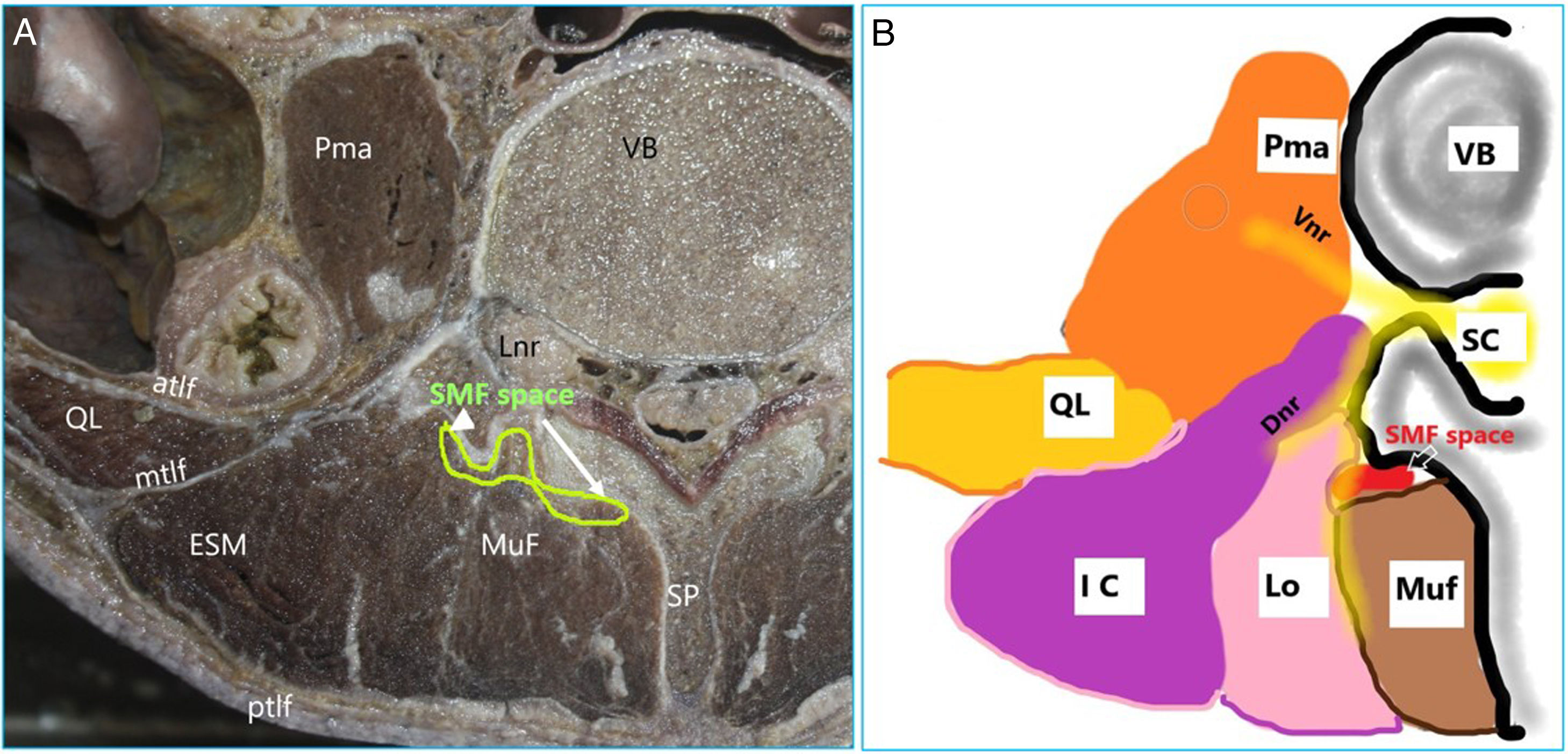
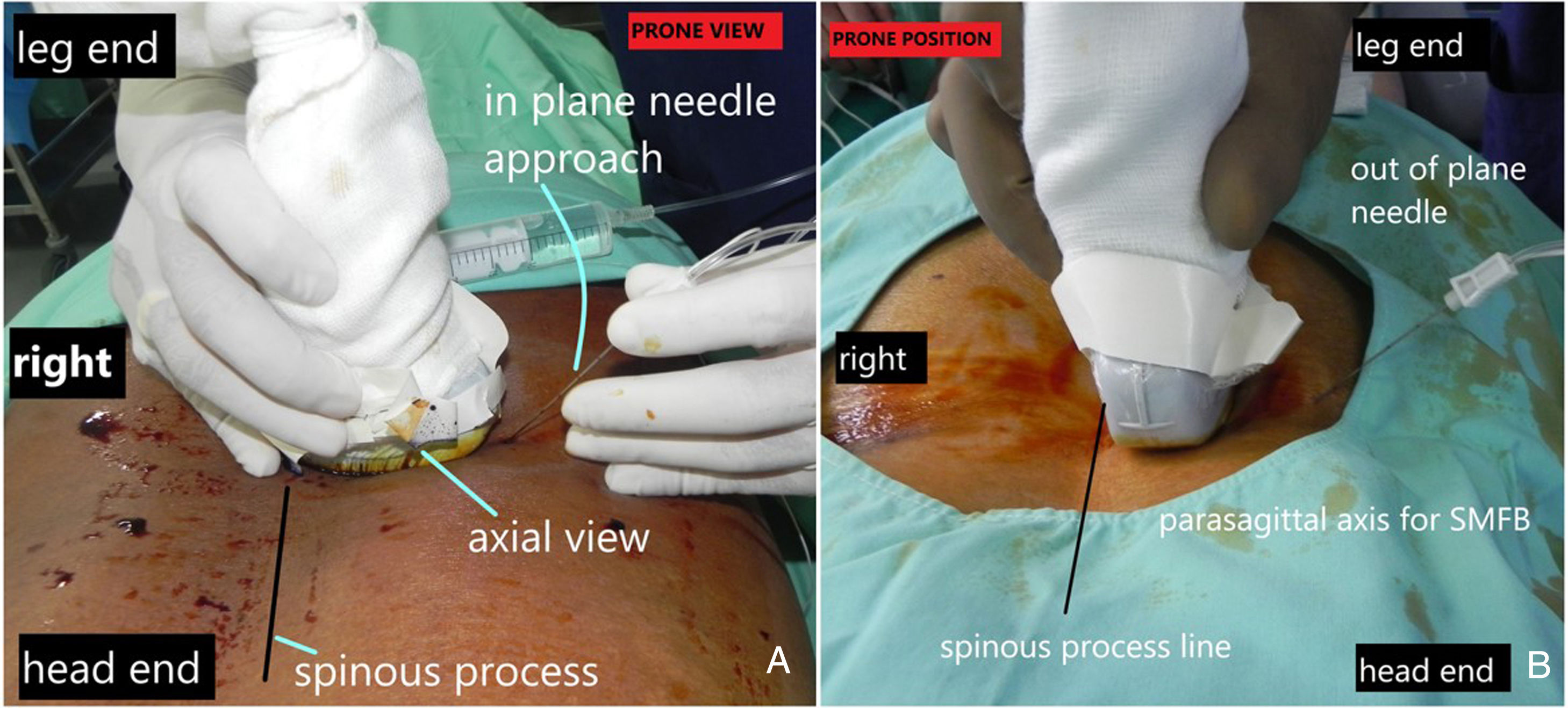
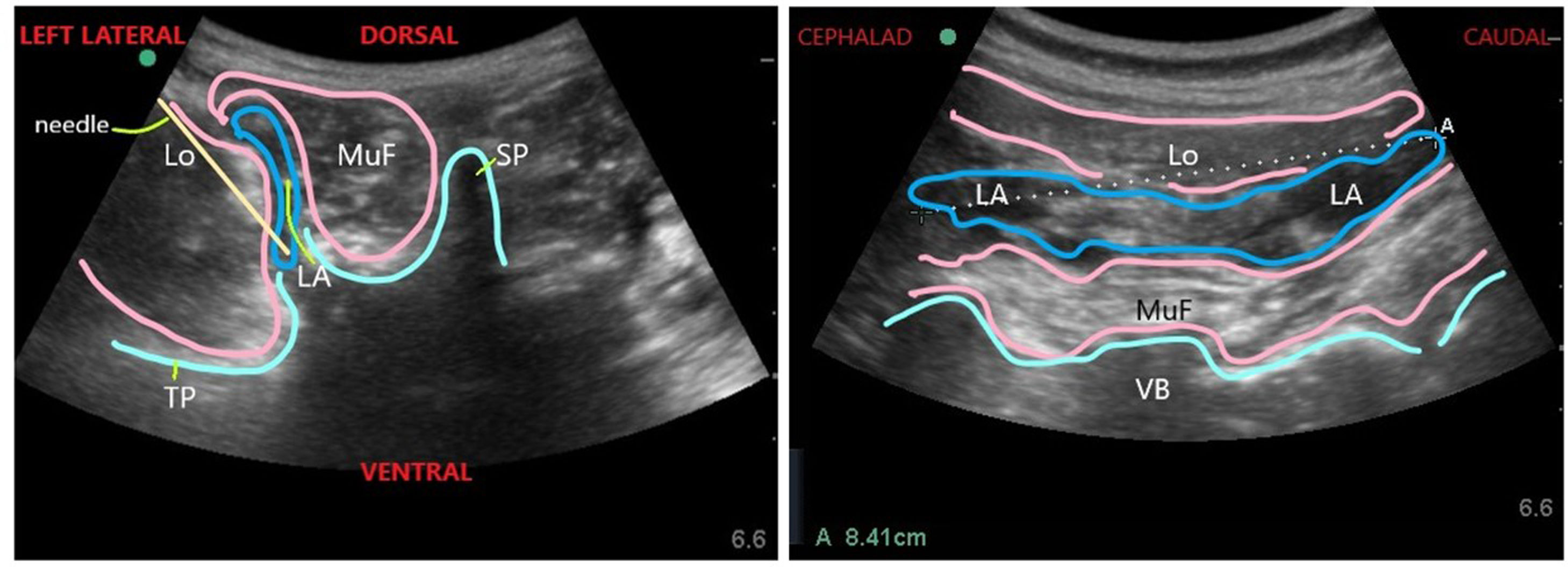
Describimos esta serie de 15casos programados para descompresión de columna lumbar a un único nivel con instrumental, en la que practicamos bloqueo ecoguiado bajo el músculo multífido (SMFB). Se inyectó el anestésico local en profundidad hacia el músculo multífido logrando el bloqueo seguro de las ramas dorsales de los nervios espinales a múltiples niveles en esta serie. Con ultrasonidos (US) puede identificarse el músculo multífido en los planos axial y parasagital. La punta de la aguja se visualiza fácilmente bajo el músculo multífido y en posición medial hacia el proceso transverso. Se documentó la buena calidad de la analgesia utilizando las puntuaciones para el dolor. No se produjeron episodios adversos. Este bloqueo debe compararse con la analgesia multimodal rutinaria o el bloqueo en el plano interfascial del músculo toracolumbar recientemente descrito, en términos de seguridad y eficacia analgésica.
We describe a series of 15 patients scheduled for single level lumbar spine decompression with instrumentation receiving ultrasound (US) guided submultifidus block (SMFB). In this series, injections of local anesthetic deep to the multifidus muscle provided reliable block of dorsal rami of spinal nerves at multiple levels. With US, the multifidus muscle can be identified both in axial and parasagittal planes. Needle tip is easily visualized beneath the multifidus and medial to the transverse process. Good quality analgesia was documented by pain scores. There were no adverse events. Further studies are needed to compare this nerve block with routine multimodal analgesia or with the recently described thoracolumbar interfascial plane block to compare safety and analgesic efficacy.