Assess the effectiveness of priming the extracorporeal circulation system with albumin–mannitol combined with ultrafiltration during extracorporeal circulation to reduce post-operative bleeding and transfusion requirements in heart surgery, as well as its impact on the fluid balance, coagulation and hematocrit parameters, re-operation for bleeding, ICU, and hospital length of stay.
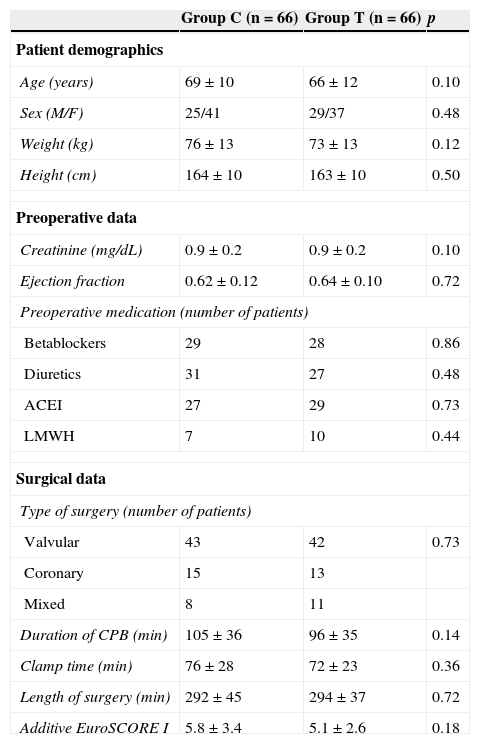
Material and methodsA total of 134 patients scheduled for heart surgery were randomised to receive Ringer's lactate 1500mL in the priming reservoir (group C), or mannitol 20% 250mL, albumin 20% 150mL and Ringer's lactate 1100mL combined with ultrafiltration (group T). Bleeding volume, transfusions, fluid balance, coagulation, and haematology parameters were determined until 48h in the post-operative period.
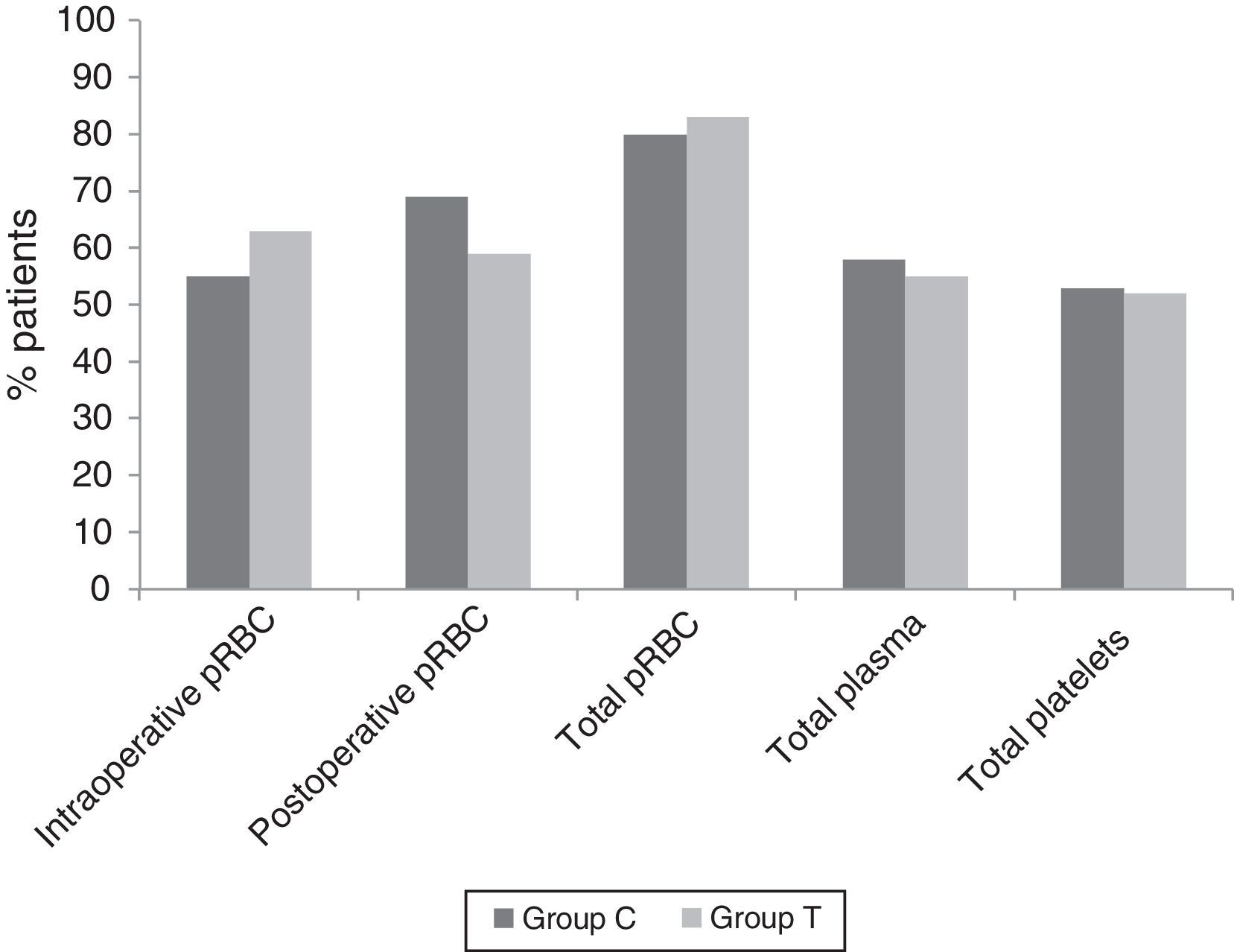
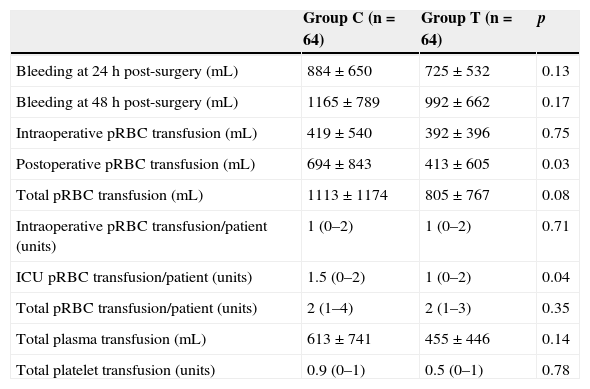
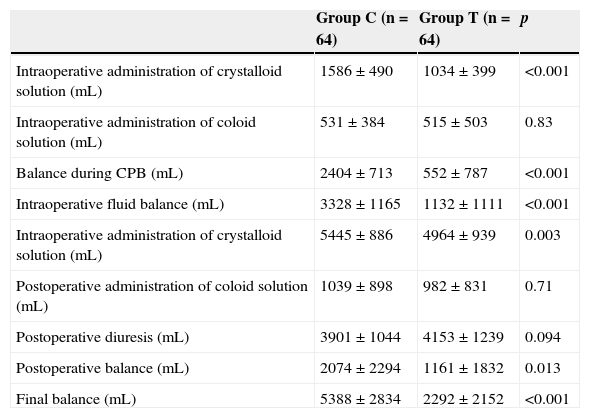
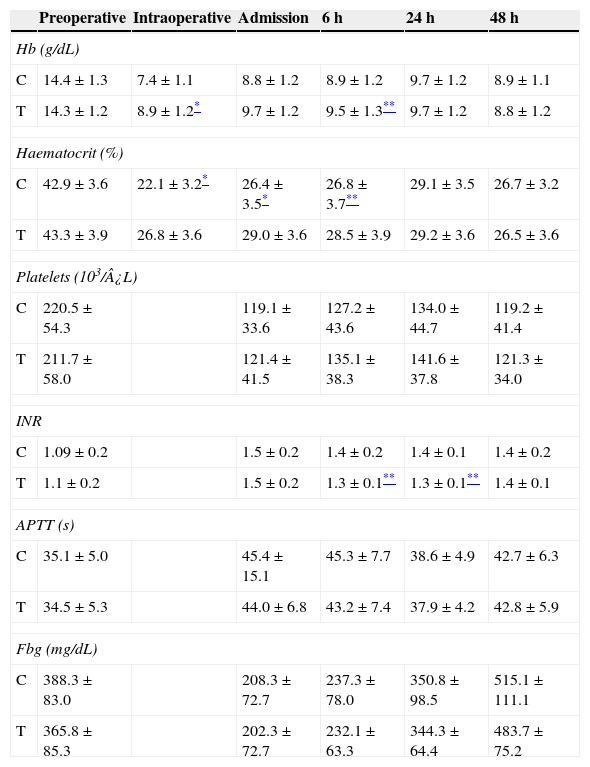
ResultsThere was a reduction of postoperative bleeding in group T, 1165±789mL vs 992±662mL (p=0.17), and red blood cell concentrate transfusions, 694±843mL vs 413±605mL (p=0.03). Intra-operative and post-operative fluid balance was significantly less positive in group T, with an overall balance of 2292±2152mL vs 5388±2834mL (p<0.001). There were higher values of haemoglobin and hematocrit, intraoperative (p<0.001), on admission to ICU (p=0.001), and at 6h (p=0.05) in group T, and lower INR at 6h (p=0.01) and 24h (p=0.02). Re-operation rate and length of stay in ICU were higher in group C, but not statistically significant.
ConclusionsThe priming of extracorporeal reservoir with mannitol, albumin, and Ringer's lactate, combined with ultrafiltration, significantly improves intra- and post-operative fluid balance, resulting in a reduction in blood transfusions, with no significant decrease in post-operative bleeding, re-operation bleeding rate, and length of stay in the ICU.
Valorar la eficacia del cebado del sistema de circulación extracorpórea con albúmina-manitol asociado a ultrafiltración para reducir el sangrado posoperatorio y las necesidades transfusionales en cirugía cardiaca, así como su repercusión sobre los balances hídricos, los parámetros de coagulación y hematimetría, la reintervención por sangrado y la estancia en UCI y hospitalaria.
Material y métodosCiento treinta y cuatro pacientes programados en cirugía cardiaca fueron aleatorizados para recibir en el cebado Ringer lactato 1.500mL (grupo C), o 250mL de manitol 20%, 150mL de albúmina 20% y 1.100mL de Ringer lactato asociado a ultrafiltración (grupo T). Se determinaron el volumen de sangrado, las transfusiones, los balances hídricos, los parámetros de coagulación y la hematimetría hasta las 48h del posoperatorio.
ResultadosEncontramos una reducción en el grupo T del sangrado posoperatorio, 1.165±789mL frente a 992±662mL (p=0,17), y de la transfusión de hematíes, 694±843mL frente a 413±605mL (p=0,03). El balance hídrico intraoperatorio y posoperatorio fue significativamente menos positivo en el grupo T, con un balance global de 2.292±2.152mL frente a 5.388±2.834mL (p<0,001). Hubo valores superiores de hemoglobina y hematocrito intraoperatorio (p<0,001), al ingreso en UCI (p=0,001) y a las 6h (p=0,05) en el grupo T, e inferiores de INR a las 6h (p=0,01) y 24h (p=0,02). Las tasas de reintervención y estancia en UCI fueron superiores en el grupo C, pero no significativas.
ConclusionesEl cebado del sistema de circulación extracorpórea con manitol, albúmina y Ringer lactato, asociado a ultrafiltración, mejora significativamente los balances hídricos intraoperatorio y posoperatorio y reduce el volumen de transfusión de sangre, con una repercusión no significativa sobre el sangrado posoperatorio, reintervenciones por sangrado y estancia en UCI.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora