COVID-19 became a threat to the public health system, compromising the health of the population. Patients with hip fractures, due to their age and comorbidity, were high-risk patients in this pandemic. The purpose of this study was to observe how the pandemic affected the management of hip fractures in elderly patients.
MethodsThis is a descriptive, retrospective study of all patients over the age of 65 diagnosed with a hip fracture that came to the emergency room of Vall d’Hebron University Hospital in the COVID-19 pandemic period, from the 11th of March to the 24th of April 2020. They were followed up during their hospital stay and 30 days after the fracture.
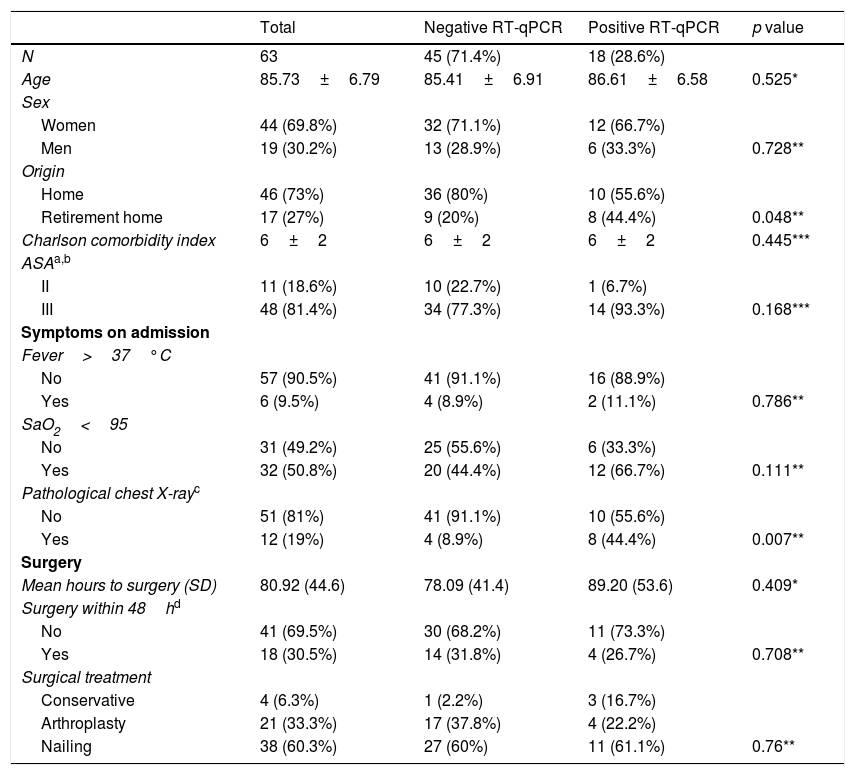
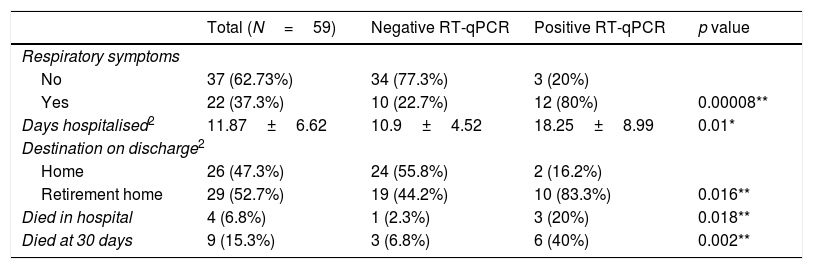
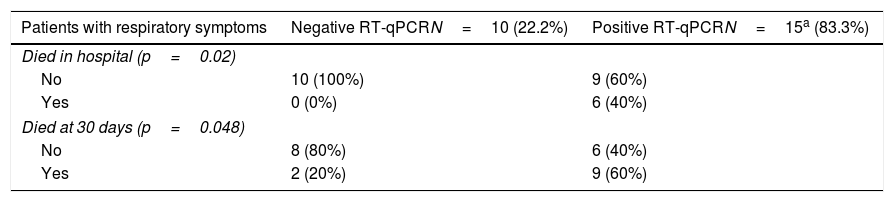
ResultsA total of 63 patients were included, 18 (28.6%) of whom had a positive RT-qPCR for COVID-19. Four could not be operated on due to the severity of the disease they presented with upon admission, dying a few days afterwards. Three of these patients had COVID-19. The 83.3% of the patients with positive RT-qPCR presented respiratory symptoms during their hospitalization. The length of hospital stays of patients with a positive RT-qPCR (18.25±8.99 days) was longer than that of patients that were RT-qPCR negative (10.9±4.52 days) (p=.01). In-hospital mortality in operated patients was 20% in patients with a positive RT-qPCR, compared with 2.3% in the group of patients who tested negative (p=.018). Mortality at 30 days was 40% in the group with positive RT-qPCR vs 6.8% in patients not infected by SARS-CoV-2 (p=.002).
ConclusionSARS-CoV-2 infection in elderly patients with hip fractures increases both the length of hospital stay, as well as in-hospital and 30-day mortality.
La COVID-19 se convirtió en una amenaza para el sistema de salud público, comprometiendo la salud de la población. Los pacientes con fractura de cadera, debido a su edad y comorbilidad, fueron pacientes de alto riesgo en esta pandemia. La finalidad de este estudio fue observar cómo afectó la pandemia al manejo de las fracturas de cadera del paciente anciano.
MétodosSe trata de un estudio descriptivo, retrospectivo de todos los pacientes mayores de 65 años diagnosticados de fractura de cadera que acudieron a urgencias del Hospital Universitario Vall d’Hebron en el periodo de pandemia COVID-19 comprendido entre el 11 de marzo y el 24 de abril de 2020. Fueron seguidos durante su ingreso hospitalario y a los 30 días de la fractura.
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 63 pacientes, 18 (28,6%) de los cuales tenían una RT-qPCR positiva para COVID-19. Cuatro no pudieron ser operados debido a la gravedad que presentaban al ingreso, falleciendo a los pocos días. Tres de estos pacientes tenían la COVID-19. El 83,3% de los pacientes con RT-qPCR positiva presentaron clínica respiratoria durante su hospitalización. La duración de la estancia hospitalaria de los pacientes con RT-qPCR positiva (18,25±8,99 días) fue mayor que los pacientes no COVID (10,9±4,52 días) (p=0,01). La mortalidad intrahospitalaria de los pacientes intervenidos fue del 20% en los pacientes con RT-qPCR positiva en comparación con el 2,3% del grupo de pacientes que testaron negativo (p=0,018). La mortalidad a los 30 días fue del 40% en el grupo con RT-qPCR positiva vs. el 6,8% de los pacientes no infectados por SARS-CoV-2 (p=0,002).
ConclusiónLa infección por SARS-CoV-2 en pacientes ancianos con fractura de cadera aumenta tanto el tiempo de ingreso hospitalario como la mortalidad intrahospitalaria y a los 30 días.