Los equivalentes metabólicos (MET) son una medida fisiológica que representa el coste metabólico de una actividad de la vida cotidiana. Un MET equivale al consumo metabólico en reposo. Los MET se pueden estimar mediante cuestionarios o calcular a partir de la medida del máximo consumo de oxígeno (VO2máx). El objetivo de este estudio es determinar si existe concordancia entre los MET estimados en la consulta de preanestesia (METSe) con los MET calculados a partir de VO2máx (METVO2).
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo en pacientes candidatos a cirugía de resección pulmonar. La estimación de los METSe se obtuvo en la consulta de preanestesia de acuerdo a las guías europeas y americanas de valoración cardiovascular preoperatoria en cirugía no cardiaca de 2014. El VO2máx se calculó en el laboratorio de ergometría.
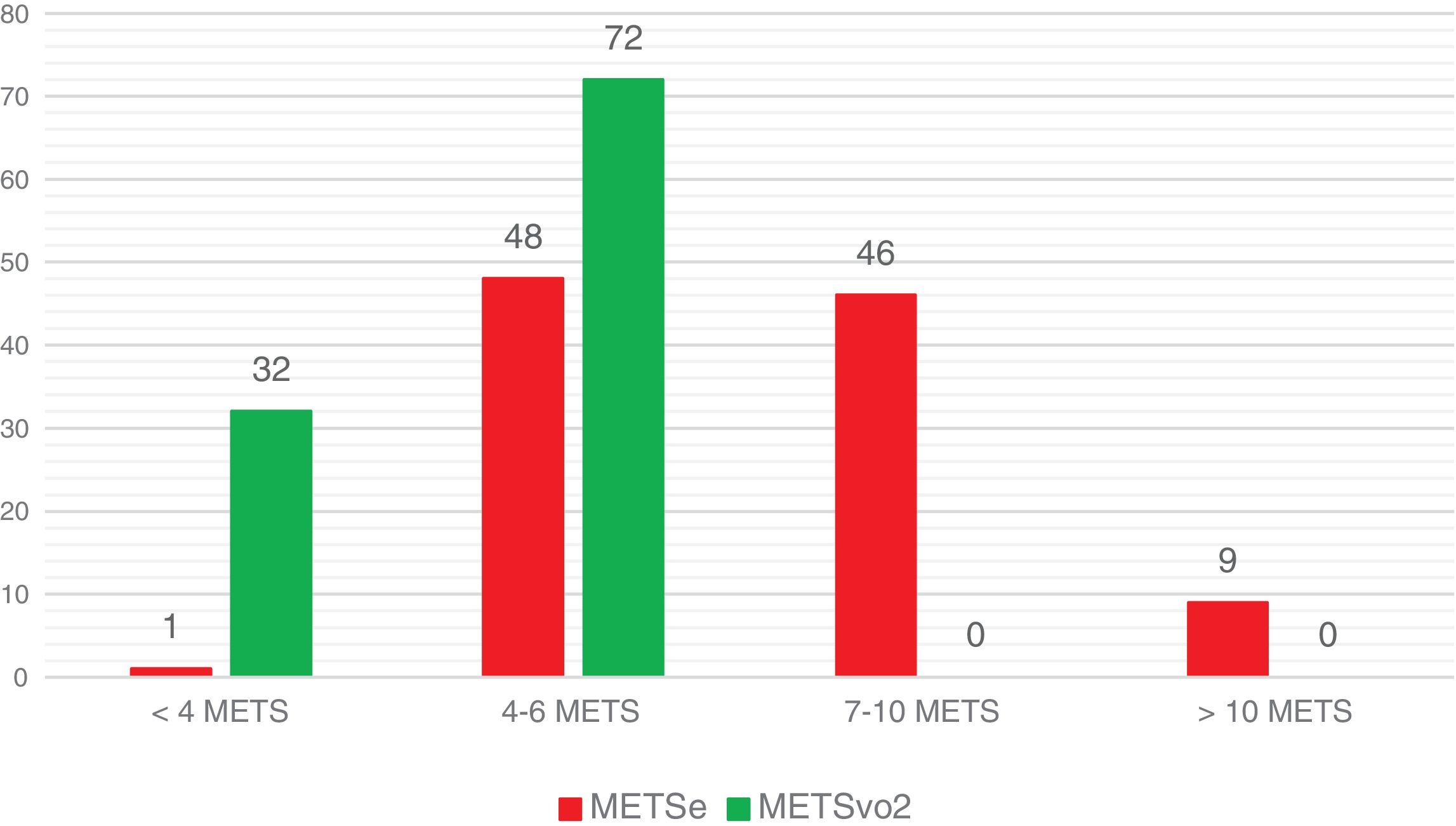
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 104 pacientes en el estudio, de los que 25 (24%) eran mujeres. La edad media fue de 65,1 años (±9,8). Veintiséis pacientes (25%) presentaron una clasificación concordante de METSe con METVO2 (κ=−0,107; p=0,02). En el resto de los pacientes, los METSe sobreestimaron la capacidad funcional medida por ergometría (METSe>METVO2).
ConclusionesLa valoración subjetiva sobreestima la capacidad funcional y no debe reemplazar la realización de pruebas objetivas en pacientes propuestos para cirugía de resección pulmonar.
Metabolic equivalent of task (MET) is a physiological measure that represents the metabolic cost of an activity of daily living. One MET is equivalent to the resting metabolic rate. METs can be estimated by questionnaires or calculated by measuring maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max). The aim of this study is to determine whether METs estimated in the pre- consultation (METse) correlates with METs calculated from VO2max (METsVO2).
Patients and methodsRetrospective observational study in patients scheduled for lung resection surgery. The estimation of METs was obtained in the pre- consultation according to the 2014 European and American guidelines for preoperative cardiovascular assessment in non-cardiac surgery. VO2max was calculated in the ergometry laboratory.
ResultsA total of 104 patients were included in the study, of whom 25 (24%) were female. The mean age was 65.1 years (±9.8). In 26 patients (25%), the METse classification correlated with METsVO2 (κ=−0.107; P=0.02). In the remaining patients, METse overestimated functional capacity measured by ergometry (METse>METsVO2).
ConclusionsSubjective assessment overestimates functional capacity and should not replace objective testing in patients scheduled for lung resection surgery.