El tratamiento antiagregante y anticoagulante complica el manejo de los pacientes con fractura osteoporótica de cadera (FOC).
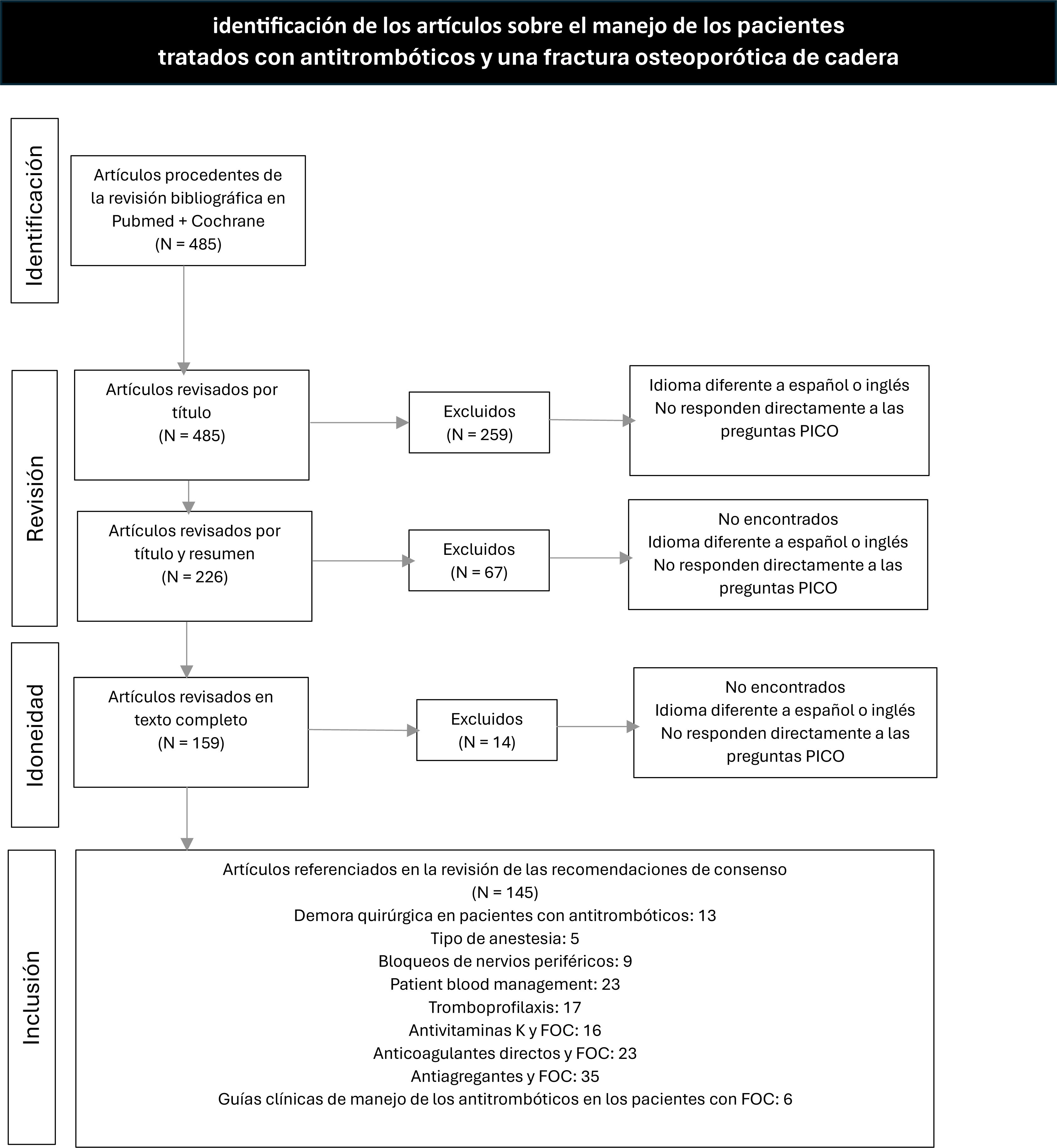
MétodosLa sección de hemostasia de la SEDAR constituyó un grupo de trabajo, con el objetivo de establecer un plan de actuación basado en la evidencia de las mejores prácticas en el manejo de los pacientes que, estando anticoagulados o antiagregados, sufren una FOC. Posteriormente un grupo multidisciplinar revalidó las recomendaciones.
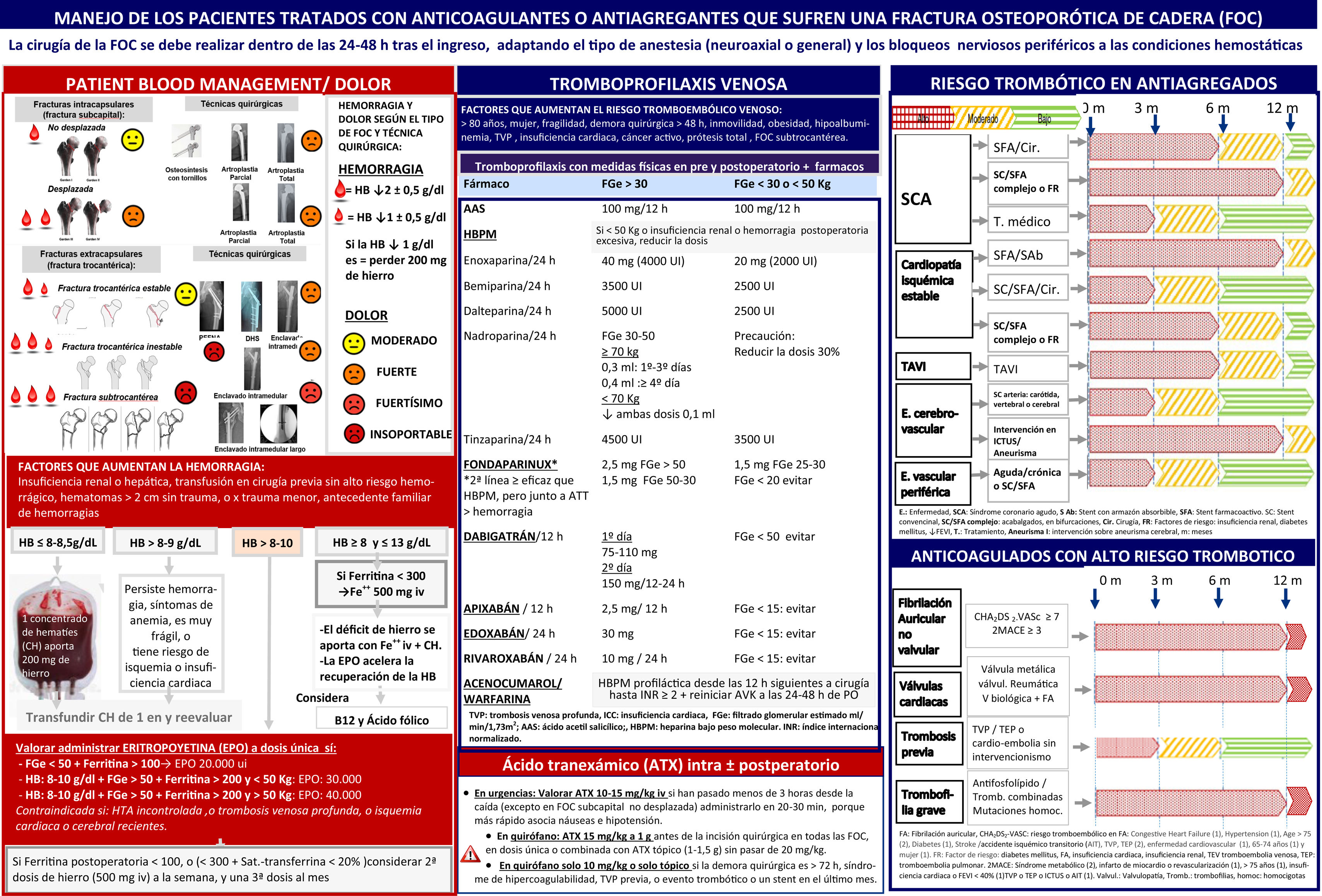
ResultadosLa cirugía precoz disminuye las complicaciones y la mortalidad y mejora el bienestar y la recuperación funcional de los pacientes, mientras que la tasa de mortalidad no difiere por realizar una anestesia intradural o general.
ConclusionesAunque persisten incertidumbres se recomienda realizar la cirugía en las 24-48horas siguientes al ingreso, adaptando los bloqueos nerviosos periféricos y el tipo de anestesia (neuroaxial o general) a las condiciones hemostáticas. Se sugiere optimizar la hemostasia, la hemoglobina y la tromboprofilaxis desde el ingreso.
Antiaggregant and anticoagulant therapy complicate the management of patients with osteoporotic hip fracture.
MethodsThe haemostasis section of SEDAR established a working group to define an action plan for the management of antiaggregated or anticoagulated patients with an osteoporotic hip fracture. The suggested recommendations are based on evidence of best practices, and have been validated by a multidisciplinary group formed by 6 specialties.
ResultsEarly surgery reduces complications and mortality and improves patient comfort and functional recovery, with no difference in mortality between intradural and general anaesthesia.
ConclusionsAlthough uncertainties remain, it is recommended to perform surgery within 24-48hours of admission, adapting peripheral nerve blocks and type of anesthesia (neuraxial or general) an to the haemostatic conditions. A multimodal management of antithrombotics, and the optimisation of haemostasis, haemoglobin and venous thromboprophylaxis since admission are suggested.