Comparar la utilidad de la RM y la PET/TC en la estadificación ganglionar (N) de pacientes con cáncer de recto localmente avanzado (CRLA).
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de pacientes con CRLA que completaron su estadificación inicial con PET/TC entre enero de 2020 y marzo de 2023. Se valoraron los ganglios locorregionales, determinando N por ambas técnicas según TNM. Se analizó la concordancia entre la RM y la PET/TC. Se calculó la exactitud diagnóstica (ED) de ambas técnicas en aquellos pacientes sometidos a cirugía directa. Se evaluó la afectación ganglionar pélvica no locorregional por ambas modalidades.
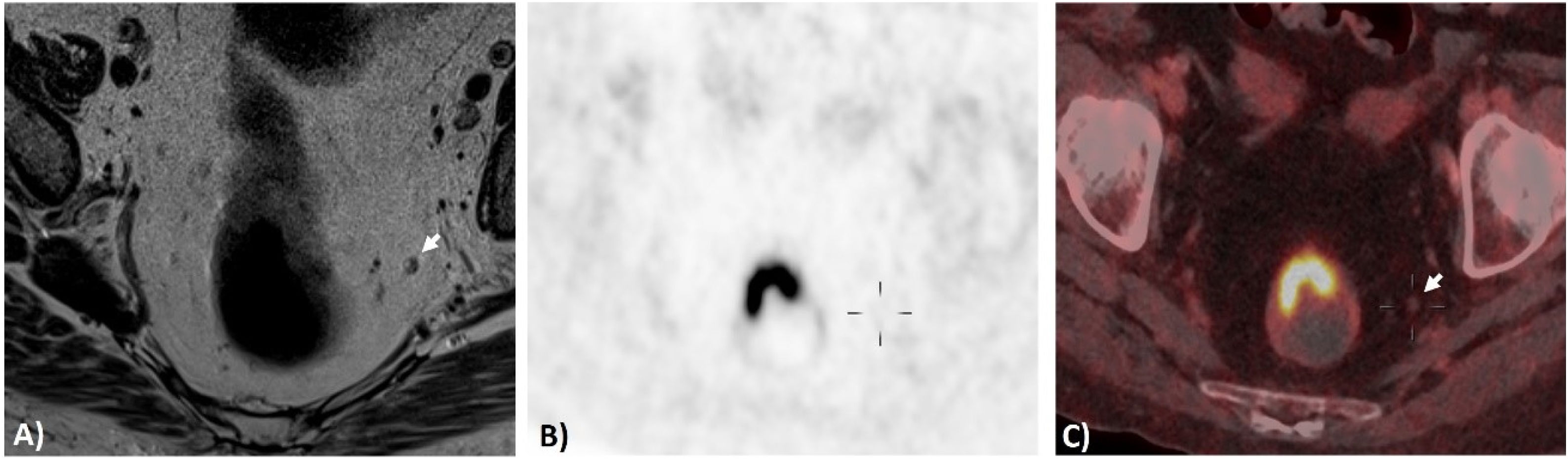
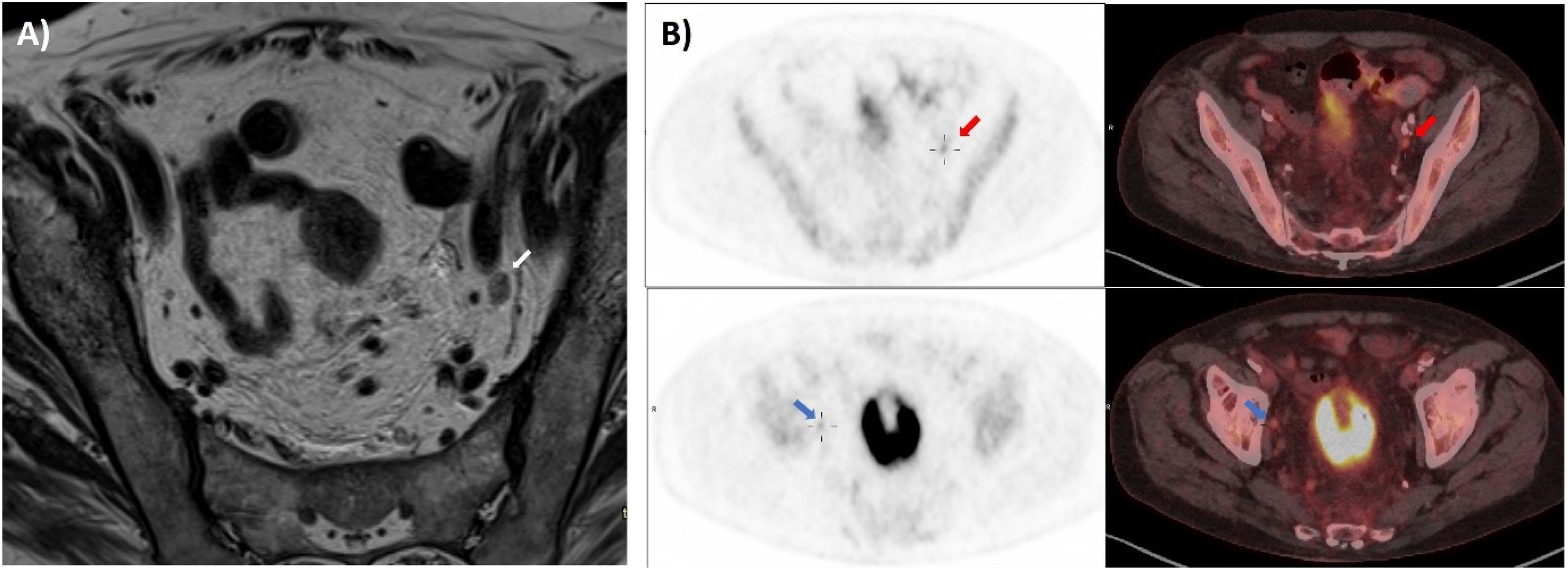
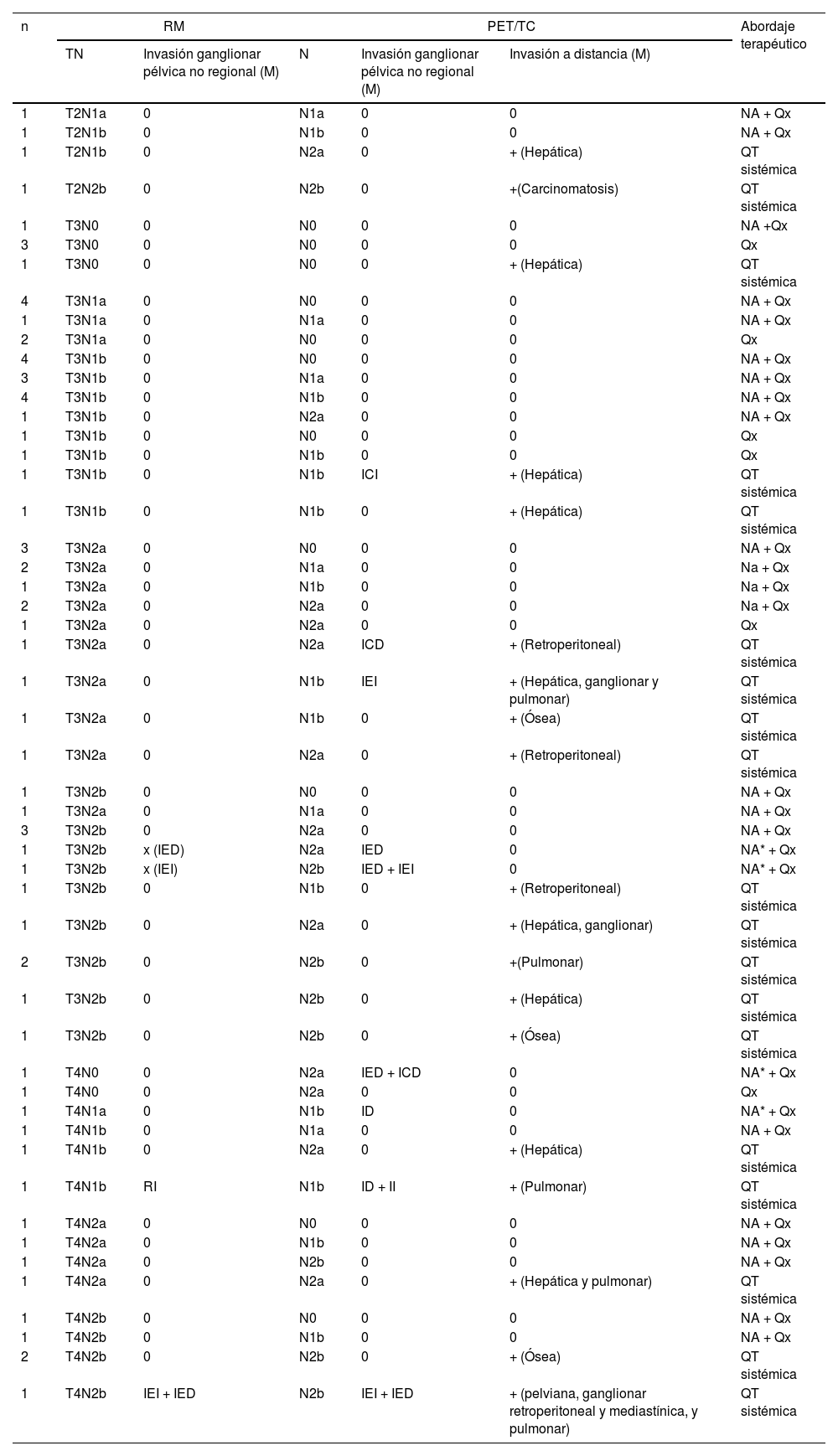
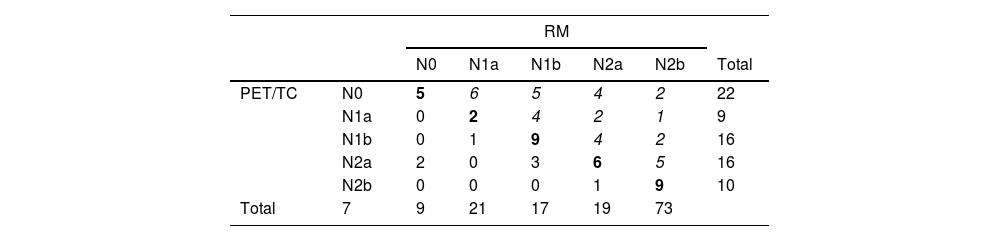
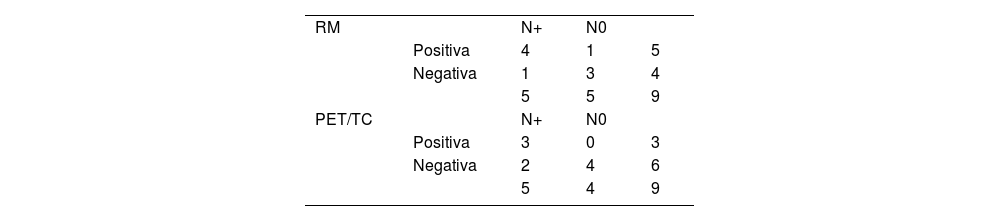
ResultadosDe 73 pacientes, 48 presentaron finalmente un estadio localmente avanzado; de estos, 39 fueron tratados con neoadyuvancia (quimio-radioterapia) y cirugía, y 9 con cirugía directa. En 25 pacientes, al completar el estudio de extensión mediante PET/TC se encontró enfermedad a distancia, por lo que recibieron tratamiento sistémico. Se obtuvo concordancia débil entre RM y PET/TC para determinar N (k=0,286; p<0,005), con 31/73 (42%) concordantes y 42/73 (58%) discordantes. De los discordantes, en 35/42 (83%) la RM supraestadificó en relación con la PET/TC, siendo 17 de estos N+ (RM) y N0 (PET/TC). Valores de ED: 78% para ambas técnicas. S, E, VPP y VPN: del 80%, 75%, 80% y 75% para la RM, y del 60%, 100%, 100% y 67% para la PET/TC. En 8 pacientes la PET/TC identificó adenopatías metastásicas pélvicas no visibles/dudosas por RM.
ConclusionesEn la estadificación ganglionar inicial del cáncer de recto la RM supraestadifica en relación con la PET/TC. Ambas modalidades son complementarias: la PET/TC ofrece mayor especificidad y la RM, mayor sensibilidad.
To compare the usefulness of MRI and PET/CT in nodal staging (N) of patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC).
Material and methodsRetrospective study of patients with LARC, who completed their initial staging with PET/CT, between January 2020 and March 2023. Regional nodes were assessed, and N was determined using both techniques according to TNM criteria. Concordance between MRI and PET/CT was analyzed. The accuracy of both techniques was calculated for those patients who underwent direct surgery. Non-regional pelvic lymph nodes were evaluated by both modalities.
ResultsAmong the 73 patients, 48 were ultimately diagnosed with a locally advanced stage. Of these, 39 underwent neoadjuvant treatment (chemoradiotherapy) followed by surgery, and 9 direct surgery. In 25, the PET/CT extension study revealed distant disease, leading to systemic treatment. Weak concordance was observed between MRI and PET/CT in determining N (k=0.286; P<.005). Out of 73 patients, 31 (42%) exhibited concordance, and 42 (58%) showed discordance. In 83% of the discordant cases, MRI overstaged compared to PET/CT, with 17 cases indicating nodal involvement (N+) by MRI and N0 by PET/CT. Diagnostic accuracy was 78% for both techniques. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were 80%, 75%, 80%, and 75% for MRI, and 60%, 100%, 100%, and 67%, for PET/CT. PET/CT identified pelvic metastatic adenopathies in 8 patients that were not visible/doubtful by MRI.
ConclusionsIn the initial nodal staging of rectal cancer MRI overstages relative to PET/CT. Both modalities are complementary, PET/CT offers higher specificity and MRI higher sensitivity.