Identificar la frecuencia de errores en los documentos de consentimiento informado en cirugía radioguiada en un hospital de tercer nivel y detectar posibles causas o factores asociados a un mayor riesgo de error.
Material y métodoSe analizaron los consentimientos informados de un total de 369 intervenciones de cirugía radioguiada, cumplimentados por los servicios de Medicina Nuclear y Cirugía General, y se analizó el grado de cumplimentación de los mismos y su correlación con facultativos responsables, tipo de enfermedad e intervención, tiempo de espera y cumplimentación del consentimiento de la otra especialidad.
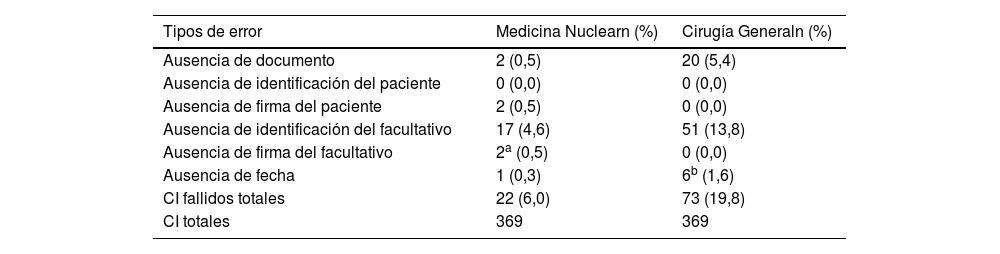
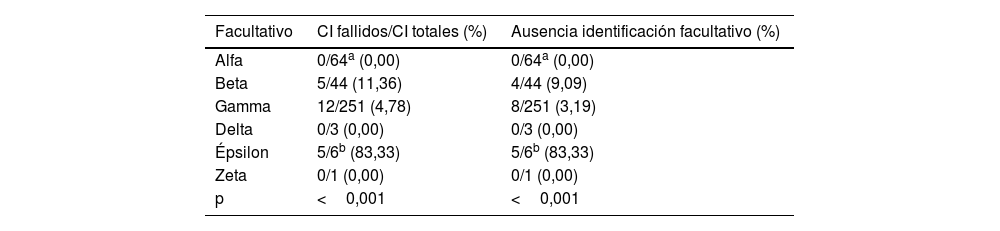
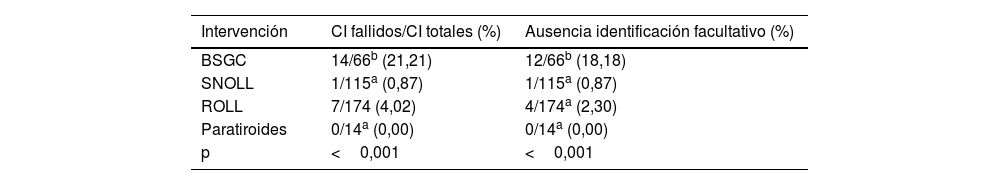
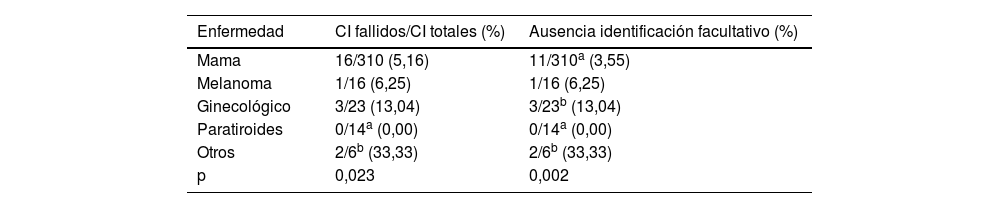
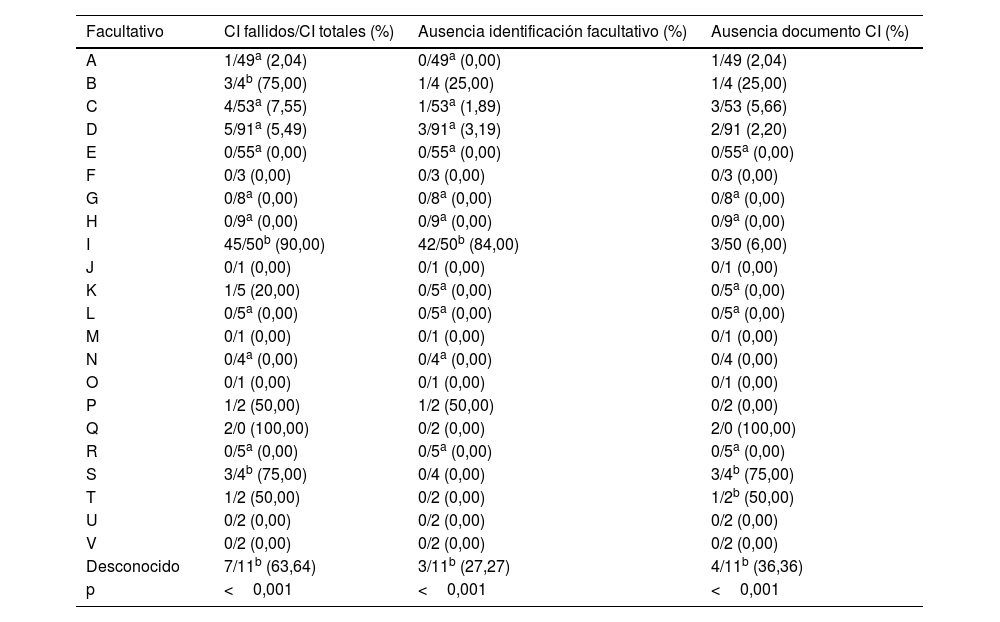
ResultadosSe identificaron errores en 22 consentimientos de Medicina Nuclear y 71 consentimientos de Cirugía General. El error más común fue la ausencia de identificación del facultativo responsable (17 en Medicina Nuclear, 51 en Cirugía General), y el segundo más común la ausencia de documento (2 en Medicina Nuclear, 20 en Cirugía General). Existieron diferencias significativas en los errores cometidos en función del médico responsable, sin encontrarse correlación significativa con el resto de las variables.
ConclusionesLos médicos responsables fueron el principal factor asociado a un mayor riesgo de error en la cumplimentación de consentimientos informados. Serían recomendables nuevos estudios para analizar factores casuales y posibles intervenciones para minimizar errores.
To identify the frequency of errors in the informed consent documents in radioguided surgery in a third level hospital and to detect possible causes or factors associated with a greater risk of error.
Material and methodThe informed consents of a total of 369 radioguided surgery interventions, completed by the Nuclear Medicine and General Surgery services, were analyzed, as well as their degree of completion and its correlation with responsible physicians, type of pathology and intervention, waiting time and completion of the consent of the other specialty.
ResultsErrors were identified in 22 consent forms for Nuclear Medicine and 71 consent forms for General Surgery. The most common error was the absence of identification of the responsible physician (17 in Nuclear Medicine, 51 in General Surgery), and the second most common was the absence of a document (2 in Nuclear Medicine, 20 in General Surgery). There were significant differences in the errors made depending on the doctor in charge, without finding a significant correlation with the other variables.
ConclusionsThe responsible physicians were the main factor associated with a greater risk of error in the completion of informed consent. New studies would be recommended to analyze causal factors and possible interventions to minimize errors.