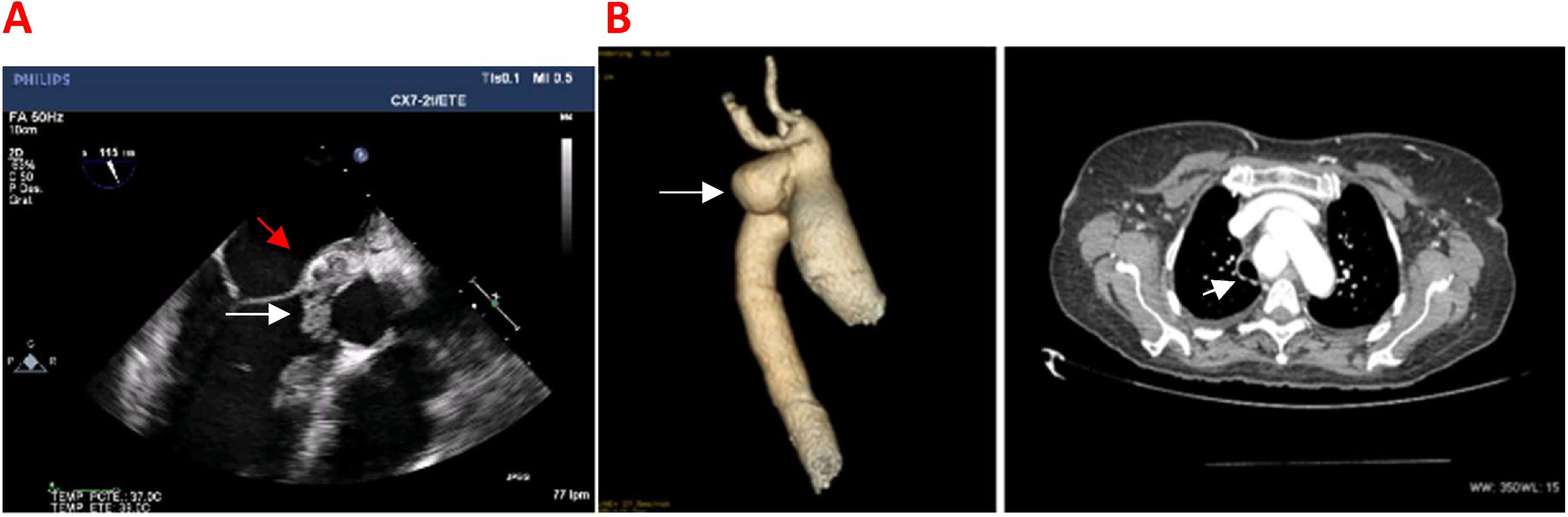
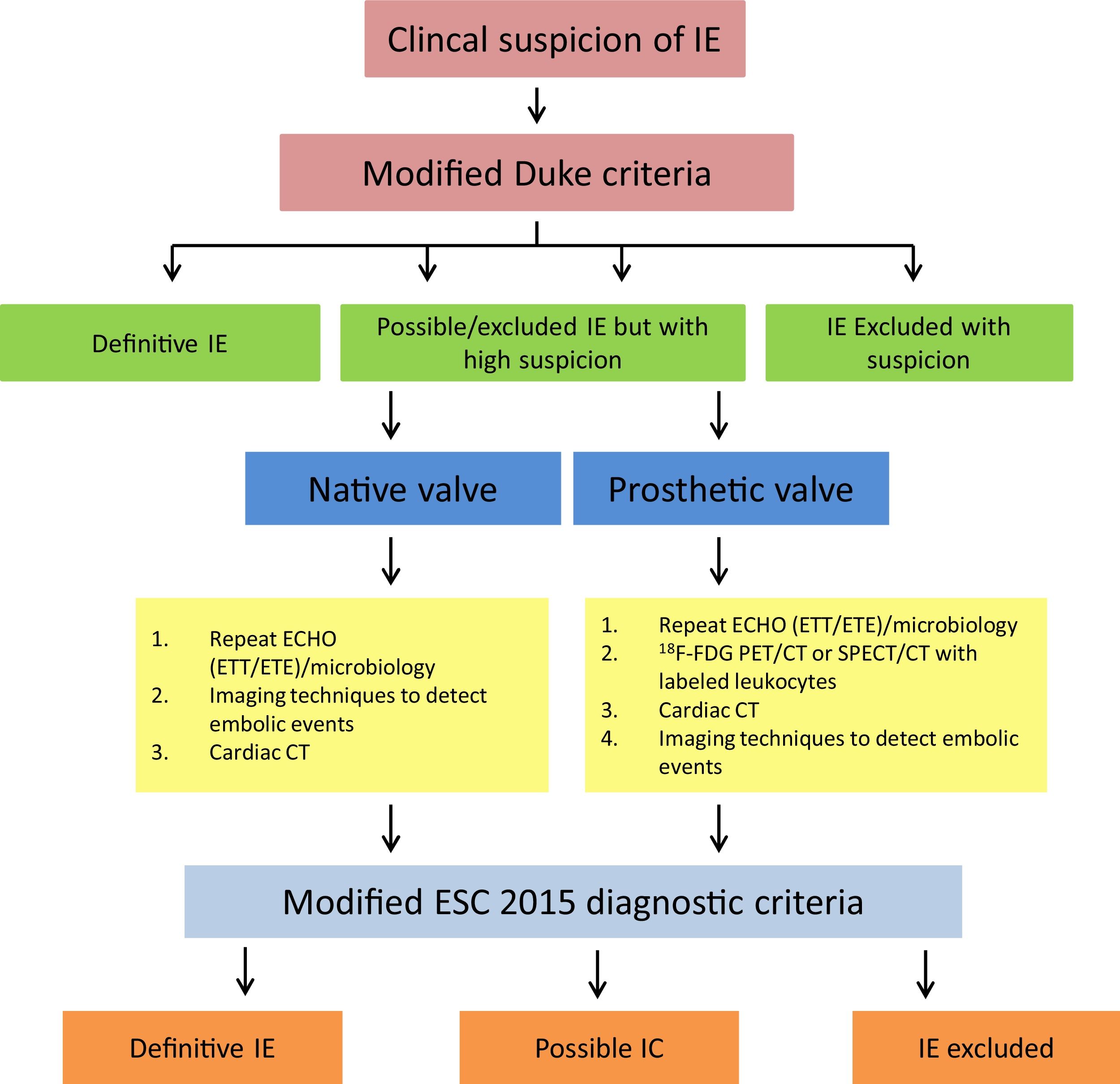
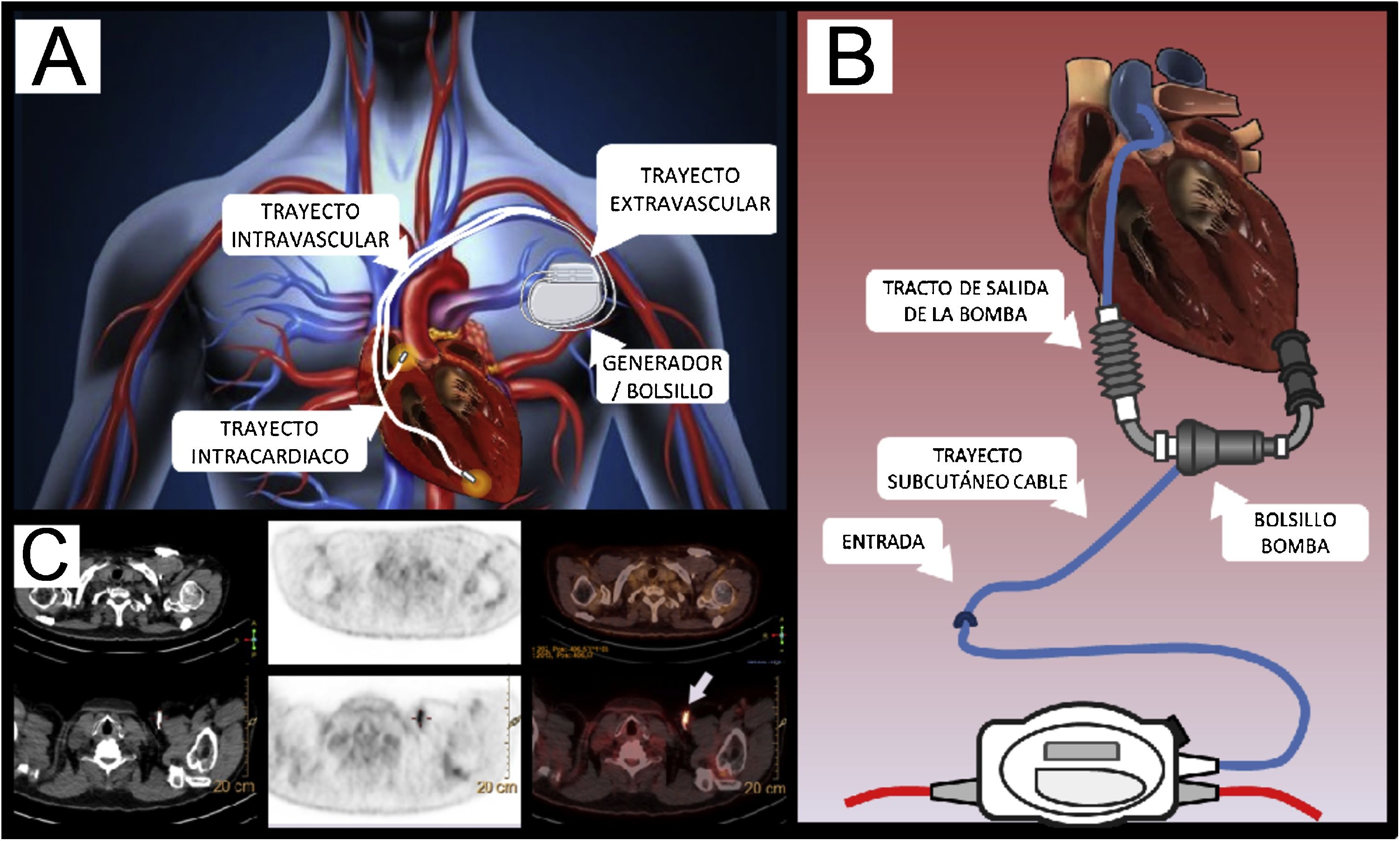
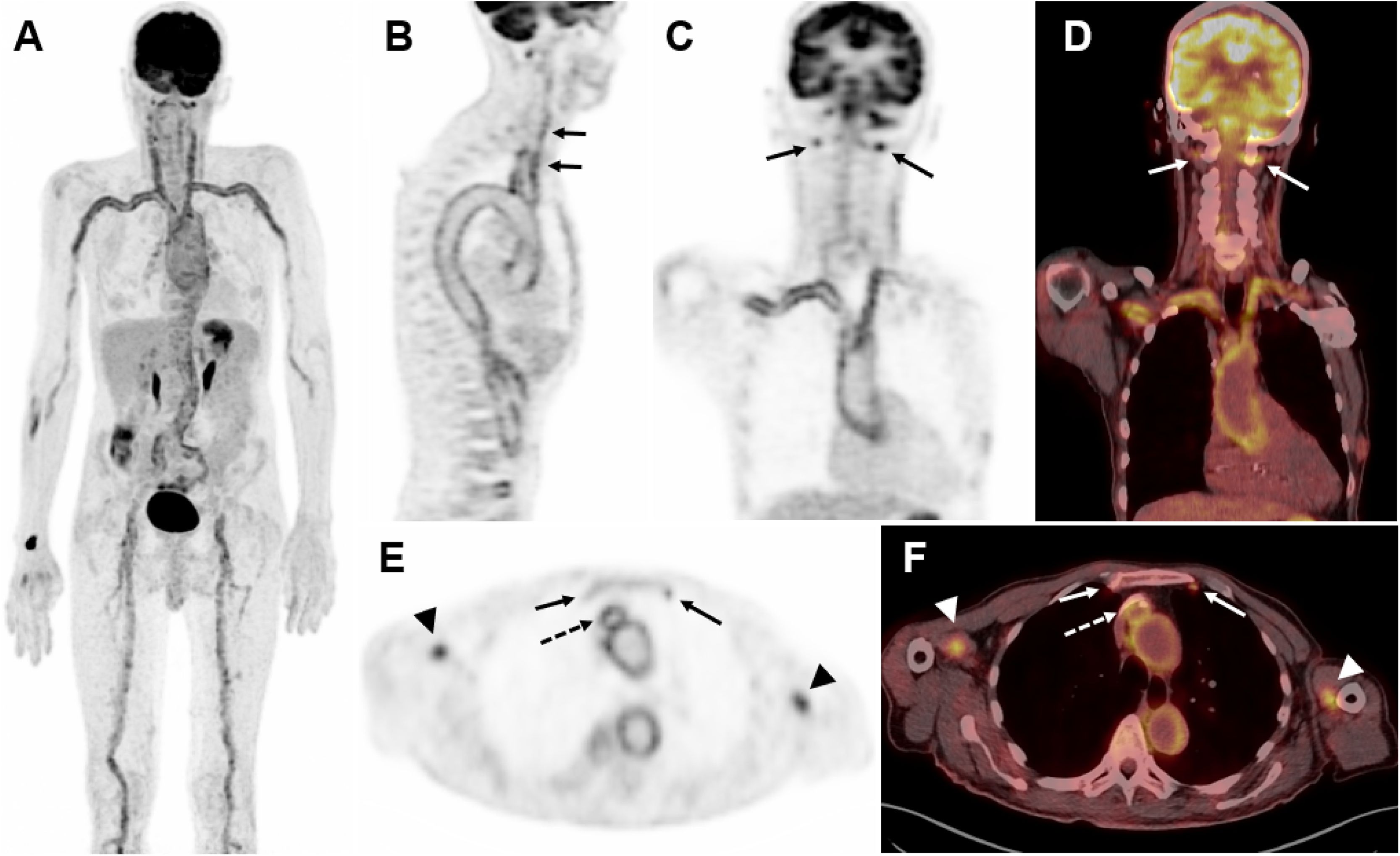
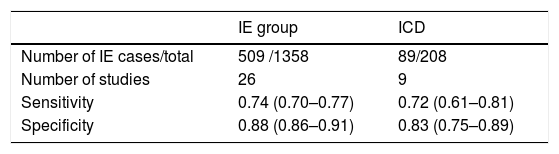
The diagnosis of cardiovascular infection and inflammation by [18F]FDG PET/CT in Nuclear Cardiology is of growing interest, because with respect to echocardiography this technique has improved the certainty in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis in patients with prosthetic valves, the increasing number of patients with implantable cardiac devices because of the progressive ageing of the population, as well as in patients with suspected large vessel vasculitis. All are serious clinical situations which require correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment as soon as possible, because they can cause severe complications, high mortality and also increased health care costs.
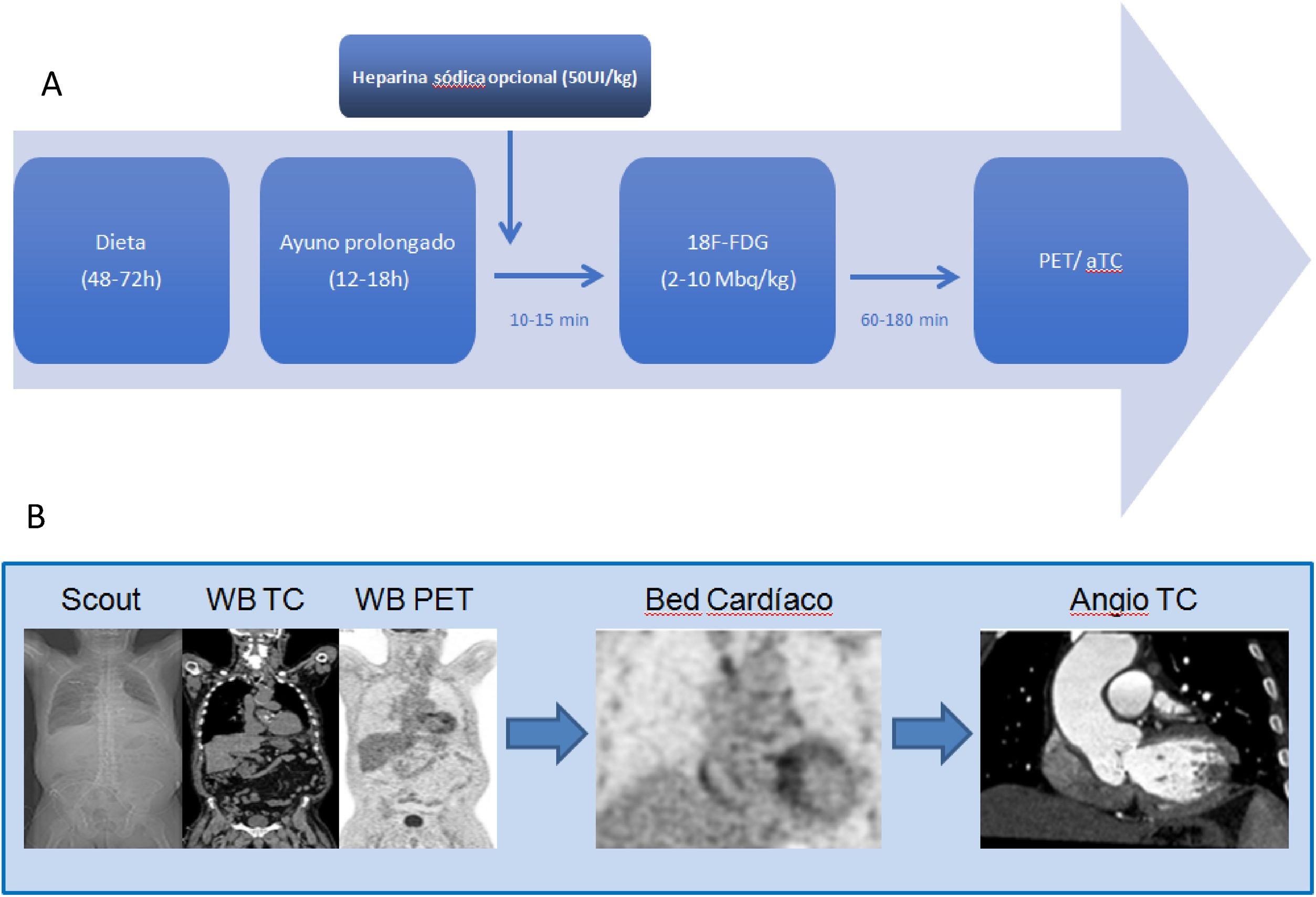
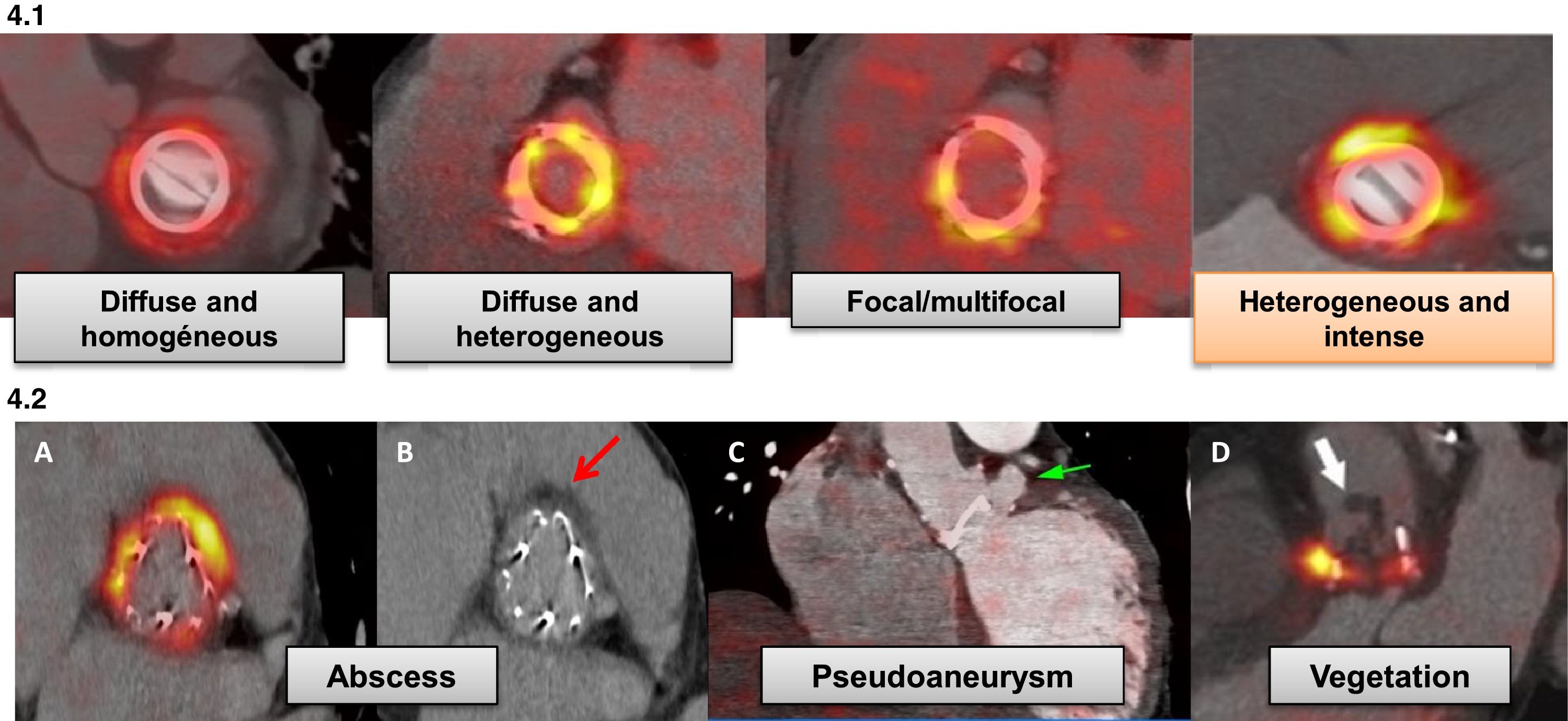
We review the use of [18F]FDG PET/CT in cardiovascular infection and inflammation, including the clinical point of view and the contribution of other image modalities. We focus on the appropriate methodology for this exploration, patient preparation, image acquisition and correct interpretation and the quantification possibilities, defining the specific characteristics of the diagnosis in patients with prosthetic valves, implantable cardiac devices and large vessel vasculitis in the initial diagnosis as well as during follow-up to assess treatment response. We analyze the possible causes of false positive and false negative results and emphasize the special value of a multidisciplinary team for optimal management of these patients.
En Cardiología Nuclear, el diagnóstico de infección e inflamación cardiovascular mediante PET/TC con [18F]FDG es de interés creciente, ya que esta técnica ha mejorado la certeza diagnóstica en pacientes con endocarditis infecciosa en prótesis valvulares respecto a la ecocardiografía, en pacientes con dispositivos intracardíacos, cuya frecuencia de implantación va en aumento debido al progresivo envejecimiento de la población, así como en aquellos con sospecha de vasculitis de grandes vasos. Son situaciones clínicas graves, en las que es necesario establecer lo antes posible el diagnóstico correcto y el tratamiento adecuado, pues pueden producir complicaciones severas, alta mortalidad, además de elevados costes hospitalarios.
Se realiza una revisión del uso de la exploración PET/TC con [18F]FDG en la infección e inflamación cardiovascular, incluyendo el punto de vista clínico y la aportación de otras técnicas de imagen, centrándose en las condiciones para la adecuada realización de esta exploración, preparación del paciente, obtención de imágenes, su interpretación correcta y posibilidades de cuantificación, detallando las características específicas del diagnóstico en los pacientes con prótesis valvulares, dispositivos intracardíacos y vasculitis de grandes vasos, tanto inicialmente como durante el seguimiento, para valorar la respuesta al tratamiento. Se analizan las posibles causas de resultados falsos positivos y falsos negativos y se destaca la especial importancia en estos casos de la colaboración multidisciplinar para obtener la máxima rentabilidad diagnóstica.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)