The aim is to investigate the use of 18F-FDG (fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose) PET/CT in head and neck cancer (HNC) staging and its effect on the therapeutic strategy and radiotherapy (RT) planning.
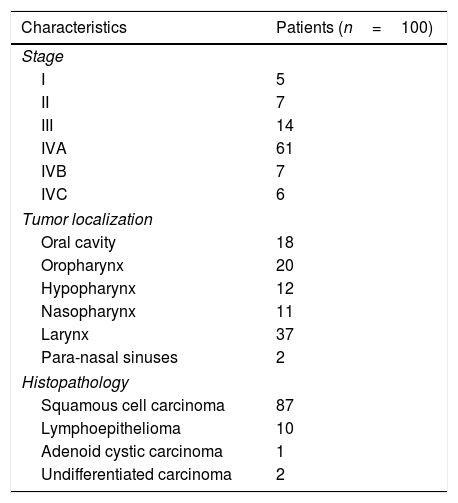
Methods and materialsOne hundred patients with HNC were included. Primary tumor sites: 18% oral cavity, 20% oropharynx, 12% hypopharynx, 11% nasopharynx, 37% larynx, 2% paranasal sinuses. Patients were staged according to the American Joint Committee of Cancer 7th edition. Stage: 5% stage I, 7% stage II, 14% stage III, 61% stage IVA, 7% stage IVB and 6% stage IVC. A contrast-enhanced CT and a 18F-FDG PET/CT acquired under RT position were performed. Both exams were compared to analyze patients’ staging reclassification. Changes in therapeutic strategy were analyzed.
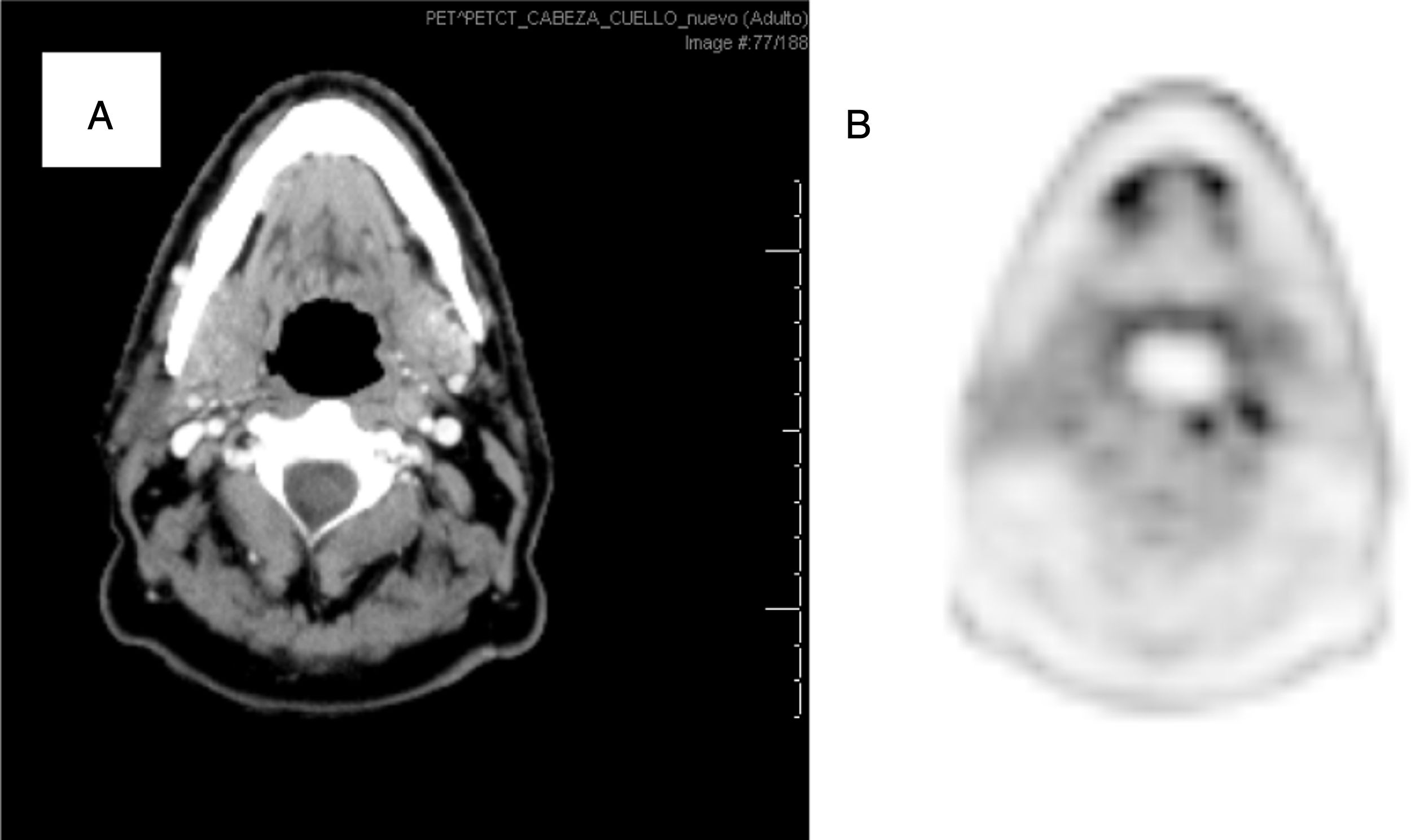
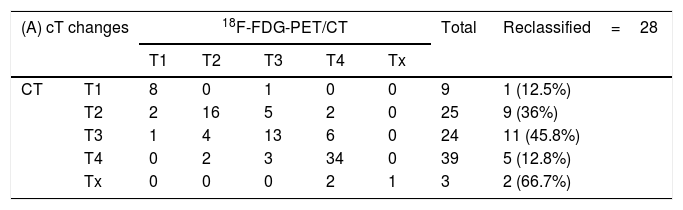
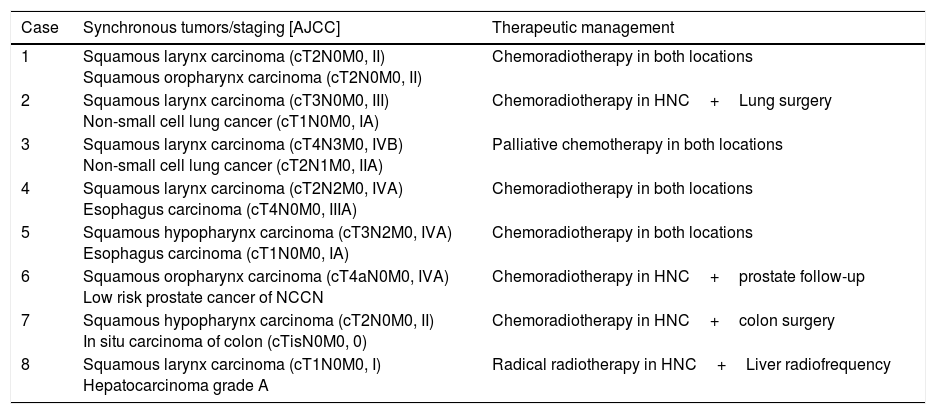
Results18F-FDG PET/CT detected 6 distant metastases and treatment intention changed to palliative. Eight synchronous tumors were detected; one received palliative treatment. 18F-FDG PET/CT reclassified cTNM staging in 27patients. Tumor extension changed in 28 (14% up-staged; 14% down-staged), implying a change in GTV (Gross Tumor Volume) delineation. Nodal detection was reclassified in 47 patients: 8 patients down-staged (N2C to N2A/N2B/N1) and 2 were false positive. Nineteen patients were false negatives and 5 staged as N+(N1/N2A/N2B) turned out into N2C. These staging modifications imply adapting the nodal volume to be irradiated.
Conclusions18F-FDG PET/CT reclassification was higher than 10% in almost all categories studied (cTNM, tumor extension and nodal disease) and detects more metastases and synchronous tumors than conventional studies, which has an impact on the therapeutic patient management and RT planning.
Investigar el uso de la 18F-FDG(flúor-18 fluorodesoxiglucosa) PET/TC en la estadificación del cáncer de cabeza y cuello (CCC) y su repercusión en la decisión terapéutica y planificación de tratamiento radioterápico.
Material y métodosSe incluyen 100 pacientes con CCC y la siguiente localización tumoral: 18% cavidad oral, 20% orofaringe, 12% hipofaringe, 11% nasofaringe, 37% laringe, 2% senos paranasales. La estadificación tumoral según la AJCC (American Joint Committee of Cancer, 7th) es: 5%-I, 7%-II, 14%-III, 61%-IVA, 7%-IVB, 6%-IVC. Se les realiza una TC y una 18F-FDG PET/TC en condiciones de simulación para comparar la reclasificación del estadiaje. Además, se analizan los cambios de actitud terapéutica.
ResultadosLa 18F-FDG PET/CT detecta 6 pacientes metastásicos que requieren tratamiento paliativo y 8 tumores sincrónicos, siendo uno paliativo. Se produce una reclasificación del estadiaje en 27 pacientes. La extensión tumoral varía en 28 (14% sobre-estadificación, 14% infra-estadificación), implicando una variación en el contorneo del GTV (Gross Tumor Volume). La estadificación ganglionar cambia en 47: 8 pacientes son infra-estadificados (N2C cambia a N2A/N2B/N1) y 2 son falsos positivos. Diecinueve pacientes son falsos negativos y 5 con afectación ganglionar unilateral (N1/N2A/N2B) muestran actividad metabólica bilateral. Estos cambios de estadificación implican una adaptación del volumen ganglionar a irradiar.
ConclusionesLa 18F-FDG PET/TC produce una reclasificación superior al 10% en casi todas las categorías estudiadas (cTNM, extensión tumoral, enfermedad ganglionar) y detecta más estadíos metastásicos y tumores sincrónicos que los estudios convencionales, lo que genera un impacto en el manejo del paciente y contorneo de los volúmenes de radioterapia.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)