Lung cancer is the second type of cancer with the second highest incidence rate and the first with the highest mortality rate in the world. Machine learning through the analysis of imaging tests such as positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) has become a fundamental tool for the early and accurate detection of cancer. The objective of this study was to propose an image analysis architecture (PET/CT) ordered in phases through the application of ensemble or combined machine learning methods for the early detection of lung cancer by analyzing PET/CT images.
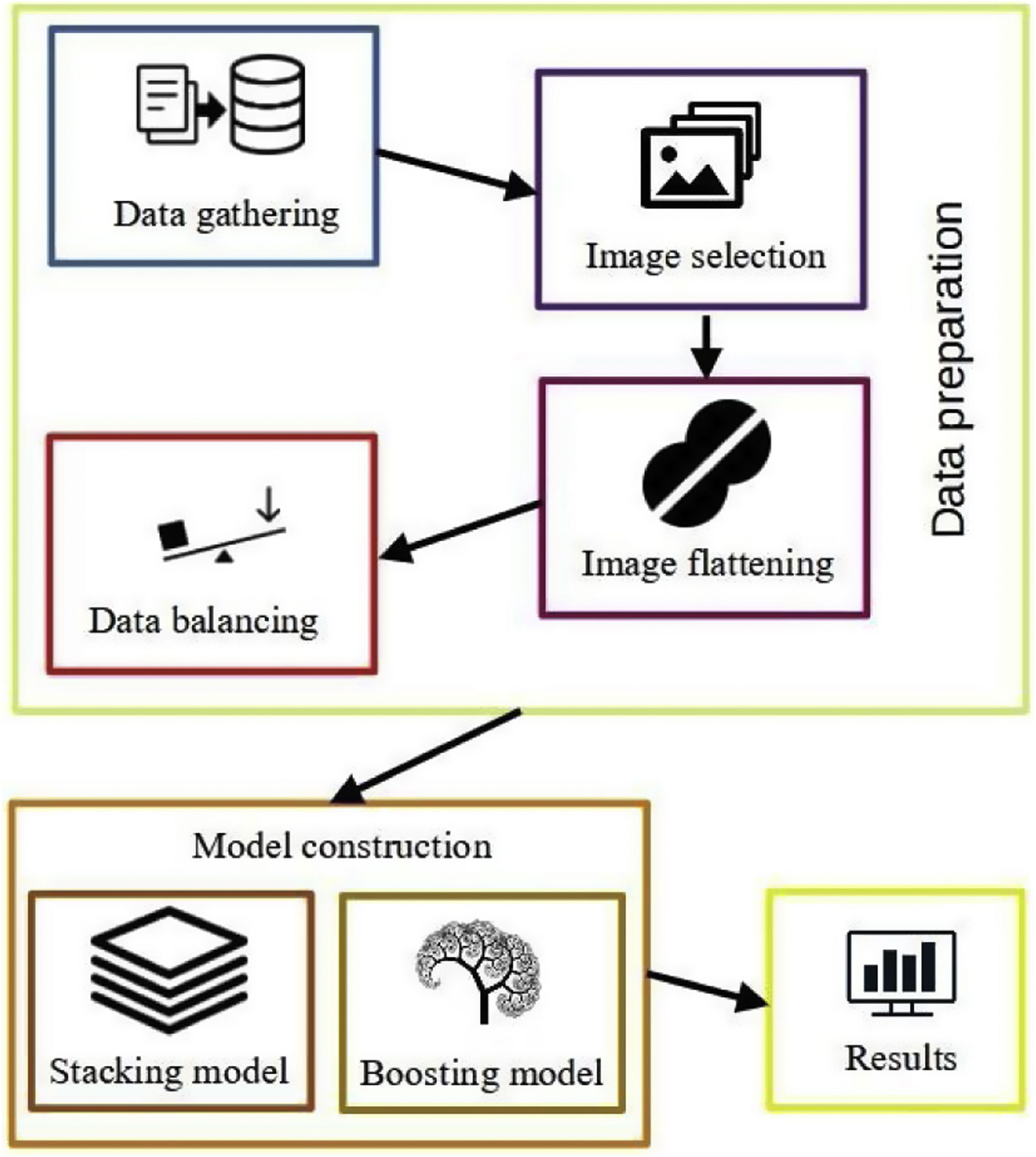
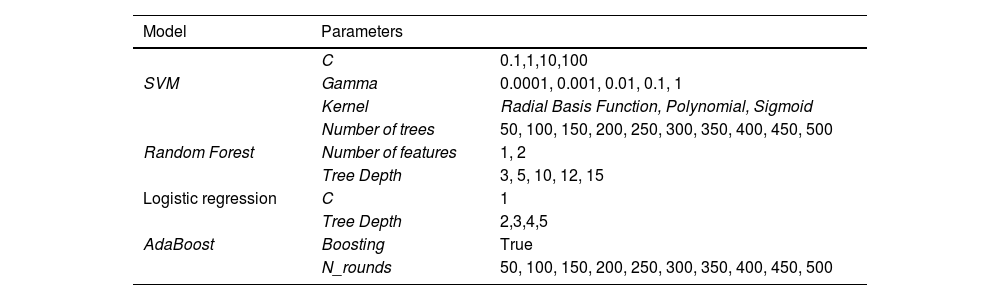
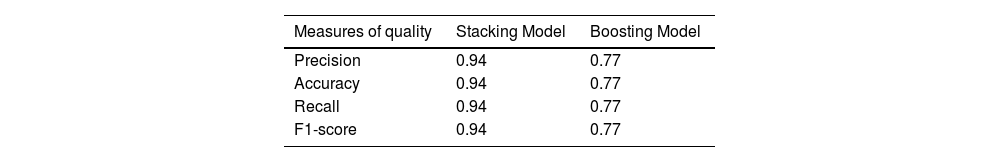
Material and methodsA retrospective observational study was conducted utilizing a public dataset entitled “A large-scale CT and PET/CT dataset for lung cancer diagnosis.” Various imaging modalities, including CT, PET, and fused PET/CT images, were employed. The architecture or framework of this study comprised the following phases: 1. Image loading or collection, 2. Image selection, 3. Image transformation, and 4. Balancing the frequency distribution of image classes. Predictive models for lung cancer detection using PET/CT images included: a) the Stacking model, which used Random Forest and Support Vector Machine (SVM) as base models and complemented them with a logistic regression model, and b) the Boosting model, which employed the Adaptive Boosting (AdaBoost) model for comparison with the Stacking model. Quality metrics used for evaluation included accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score.
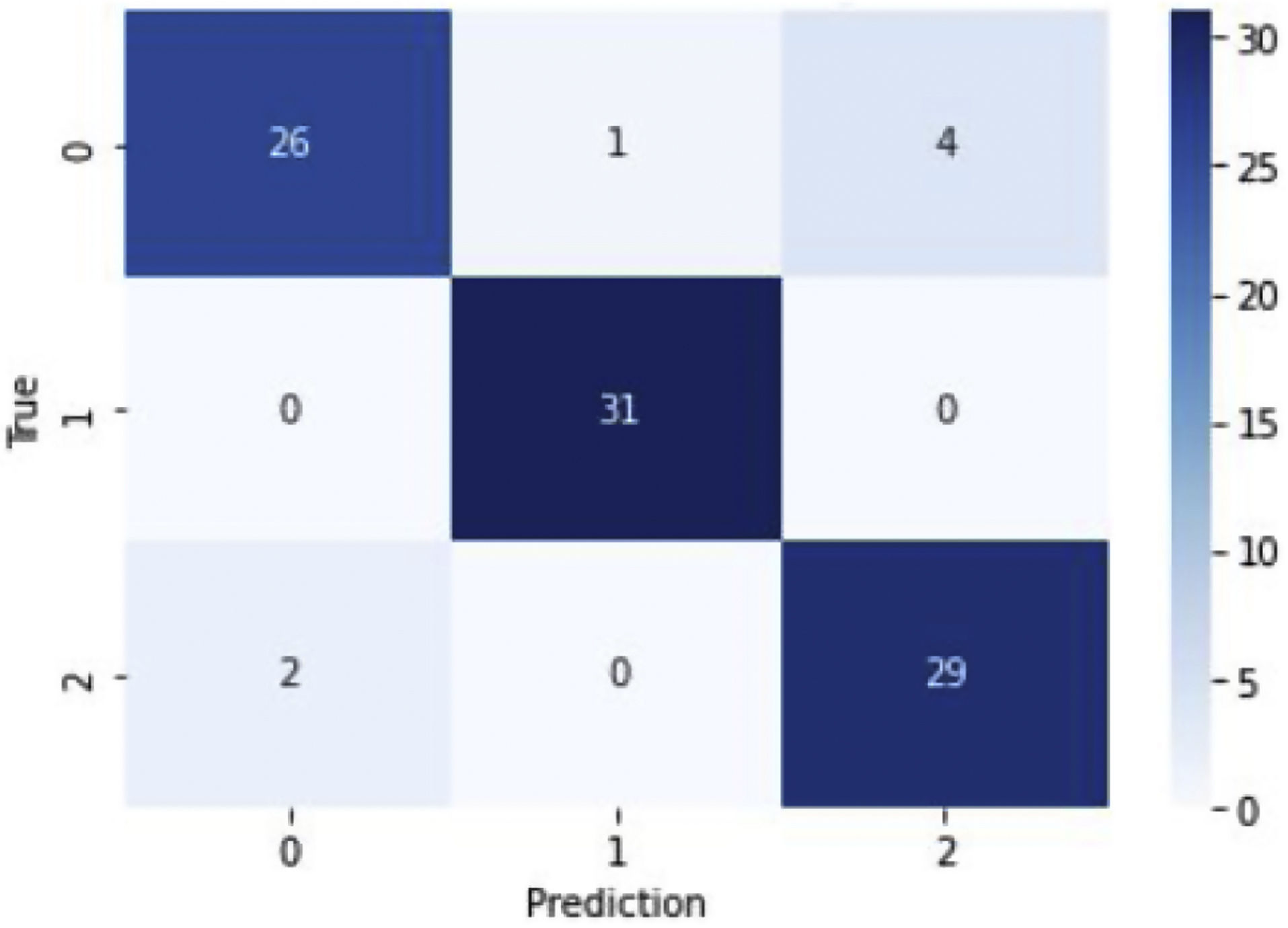
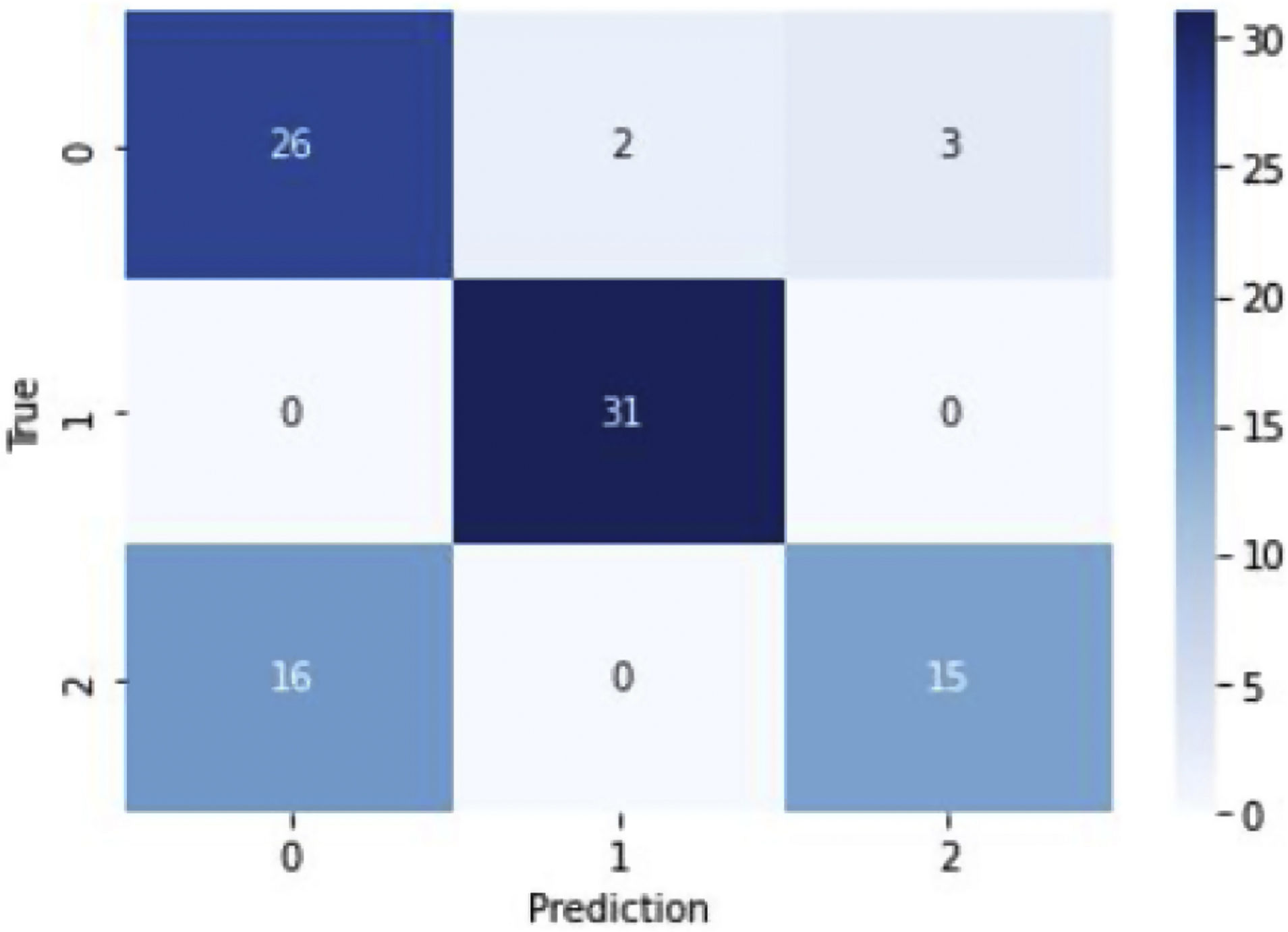
ResultsThis study showed a general performance of 94% with the Stacking method and a general performance of 77% with the Boosting method.
ConclusionsThe Stacking method proved to be a model with high performance and quality for lung cancer detection when analyzing PET/CT images.
El cáncer de pulmón es el segundo tipo de cáncer con mayor tasa de incidencia y el primero de mortalidad en el mundo. El aprendizaje automático o machine learning a través del análisis de pruebas de imagen como la tomografía por emisión de positrones/tomografía computarizada (PET/TC) se ha convertido en una herramienta fundamental para la detección temprana y precisa del cáncer. El objetivo de este estudio fue plantear una arquitectura de análisis de imágenes (PET/TC) ordenada en fases mediante la aplicación de métodos de machine learning combinado o ensemble para la detección temprana del cáncer de pulmón analizando imágenes PET/TC.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo de observación. Se utilizó una base de datos pública «A large-scale CT and PET/CT dataset for lung cancer diagnosis», en la que se usaron modalidades de exploraciones: TC, PET e imágenes fusionas PET/TC. Las fases de la arquitectura o marco de trabajo de este estudio fueron: 1. Carga o recolección de imágenes, 2. Selección de imágenes, 3. Transformación de imágenes y 4. Balanceo de distribución de frecuencia de clases de imágenes. Los modelos predictivos para la detección del cáncer de pulmón analizando imágenes PET/TC fueron: a) el modelo Stacking, el cual utilizó como modelos base al modelo Random Forest y el modelo Máquina de Soporte Vectorial (SVM, siglas en inglés) para luego complementarlo con una Regresión Logística como modelo final y, b) el modelo Boosting, el cual utilizó el modelo de Adaptive Boosting (AdaBoost, siglas en inglés) para ser comparado con el modelo Stacking. Las medidas de calidad utilizadas fueron: precisión, exactitud, exhaustividad, valor-F1.
ResultadosEn este estudio se pudo apreciar un rendimiento general del 94% con el método de Stacking y un rendimiento general del 77% con el método de Boosting.
ConclusionesEl método Stacking demostró ser un modelo con un gran rendimiento y calidad para la detección del cáncer de pulmón al analizar imágenes PET/TC.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)