To assess by [18F]FDG PET/MR the biomarkers of HIV-induced inflammation at baseline and 1 year post-antiretroviral therapy (ART).
MethodsProspective study, 14 patients, newly diagnosed HIV-positive, asymptomatic.
[18F]FDG PET/MRI (PET/MR-3.0T, Signa.GE) whole body and heart was performed, baseline and 1 year post-ART.
Qualitative vascular assessment (hepatic reference). Quantitative assessment (SUVmax) of the whole body. T1 and T2 value estimation in 16 myocardial segments.
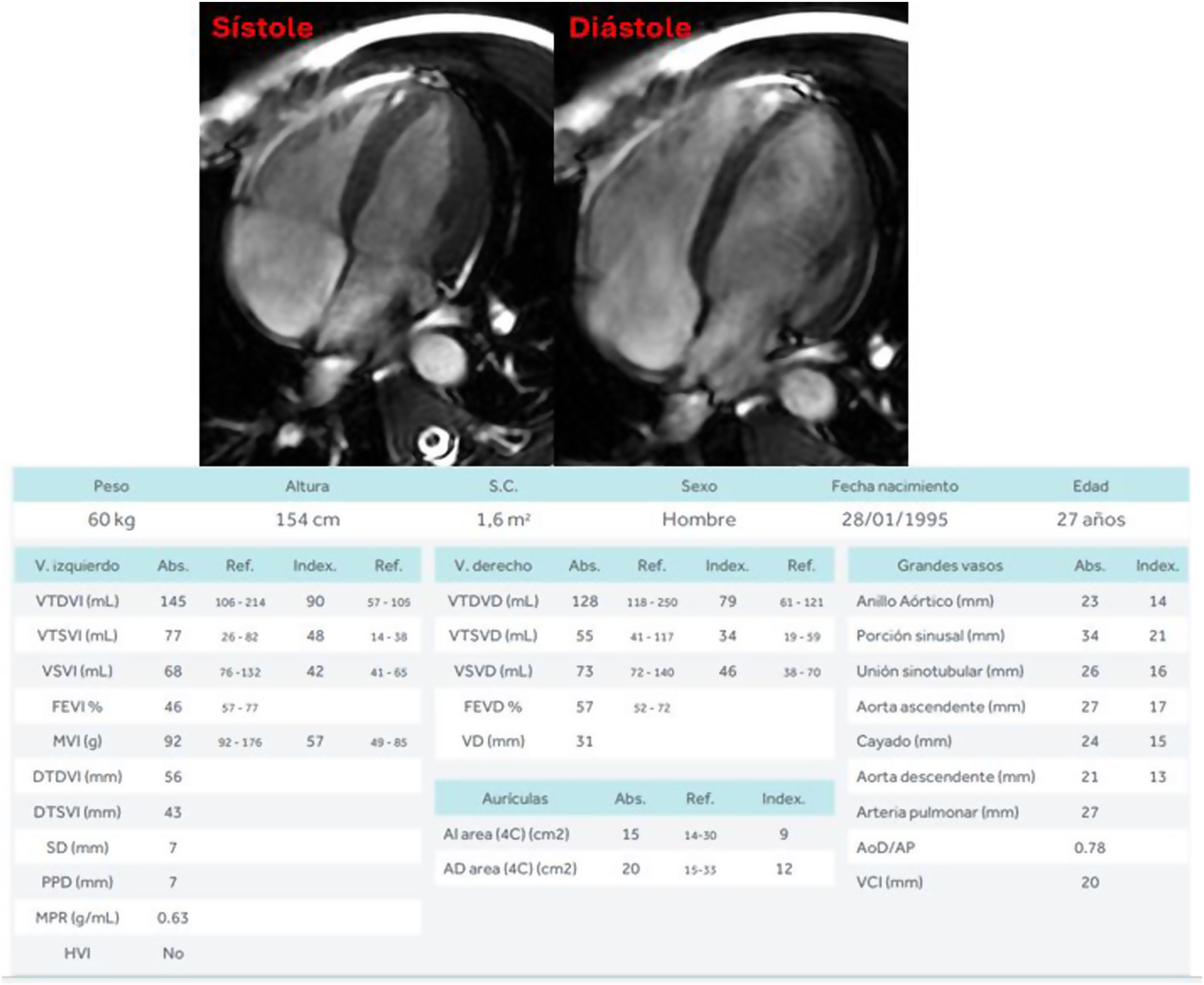
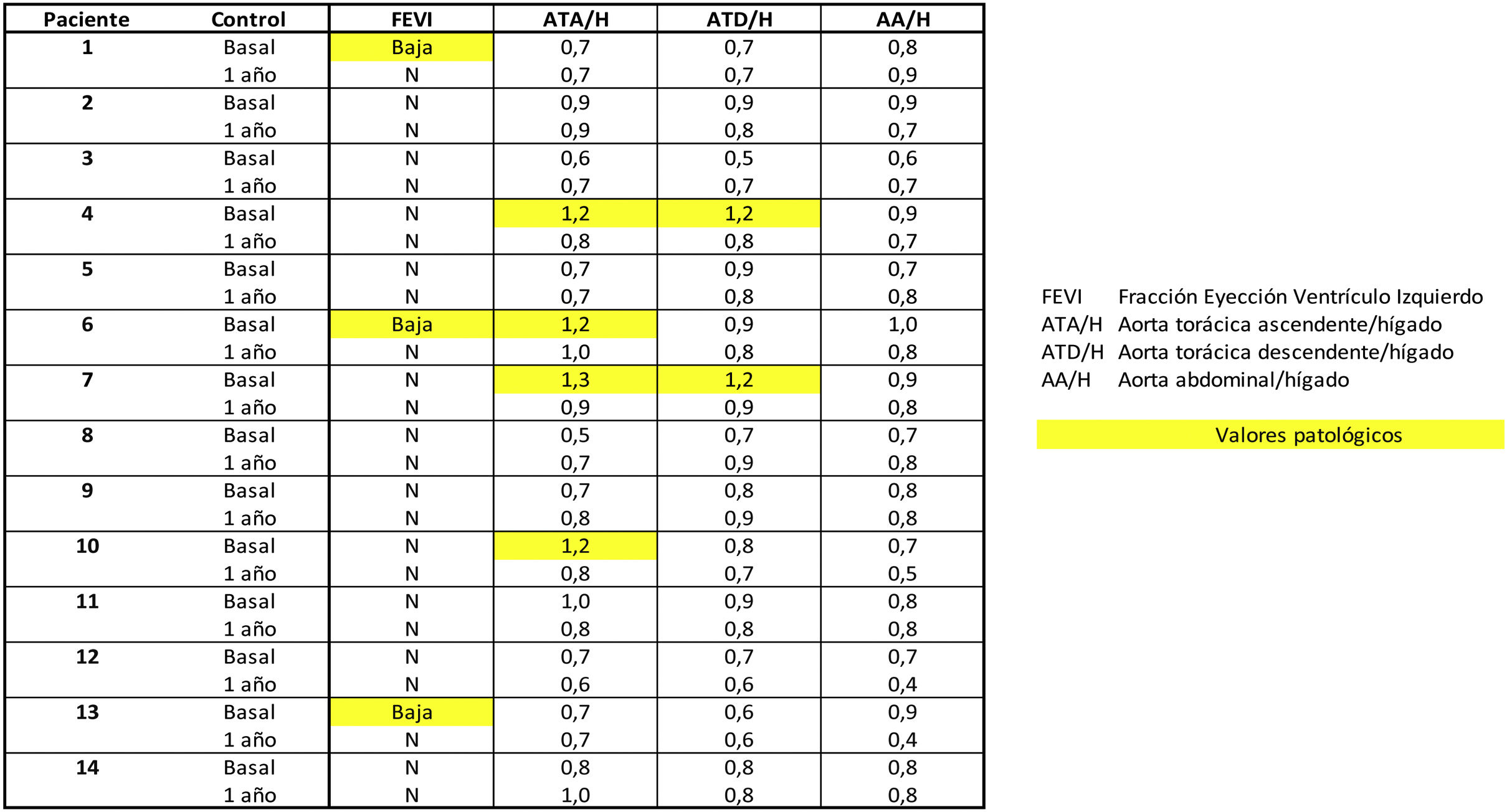
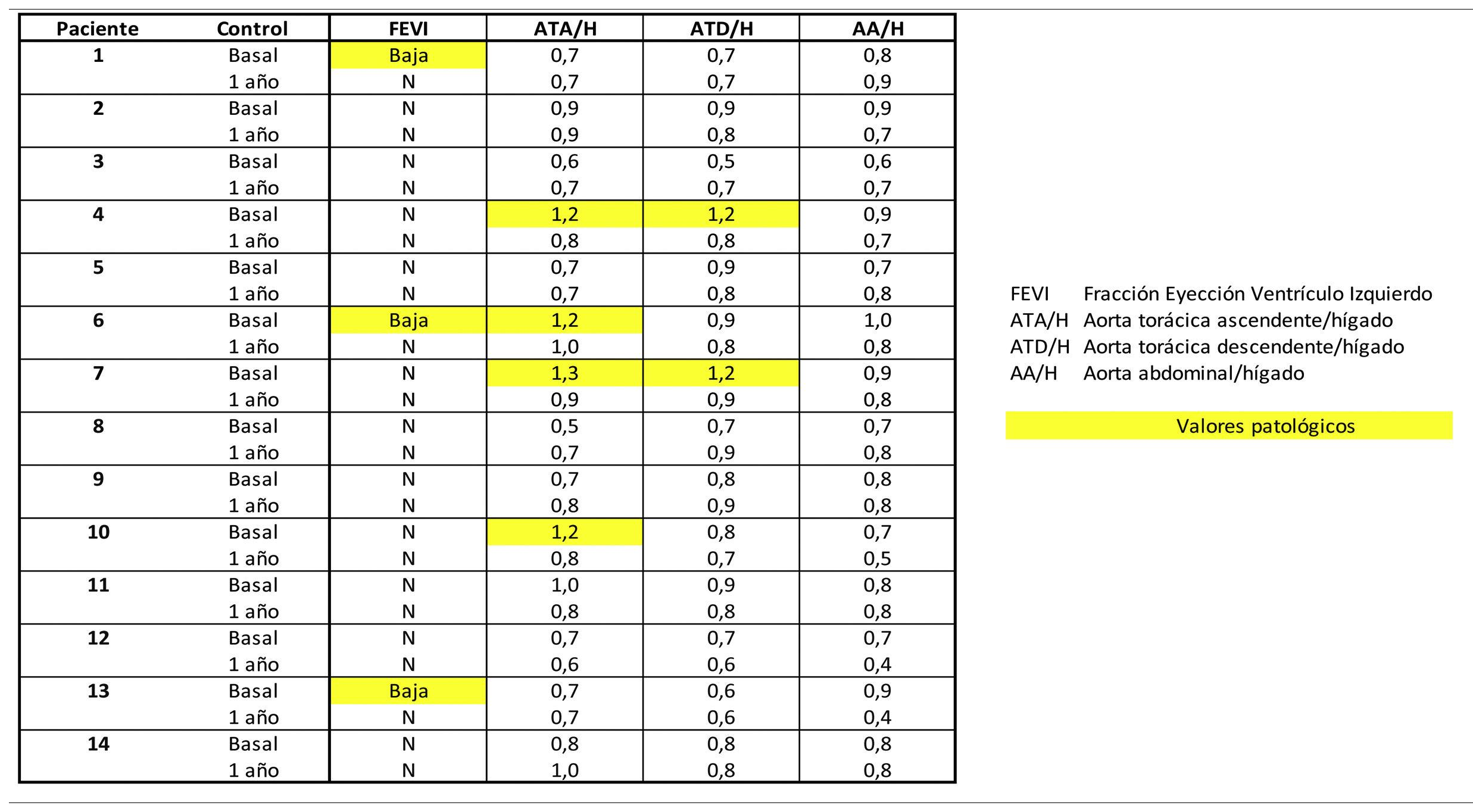
ResultsBaseline CMR showed in 3 (21.4%) a decreased LVEF, normalising post-TAR. Fibrosis was ruled out (T1), with no signs of myocardial oedema (T2) at baseline or post-TAR.
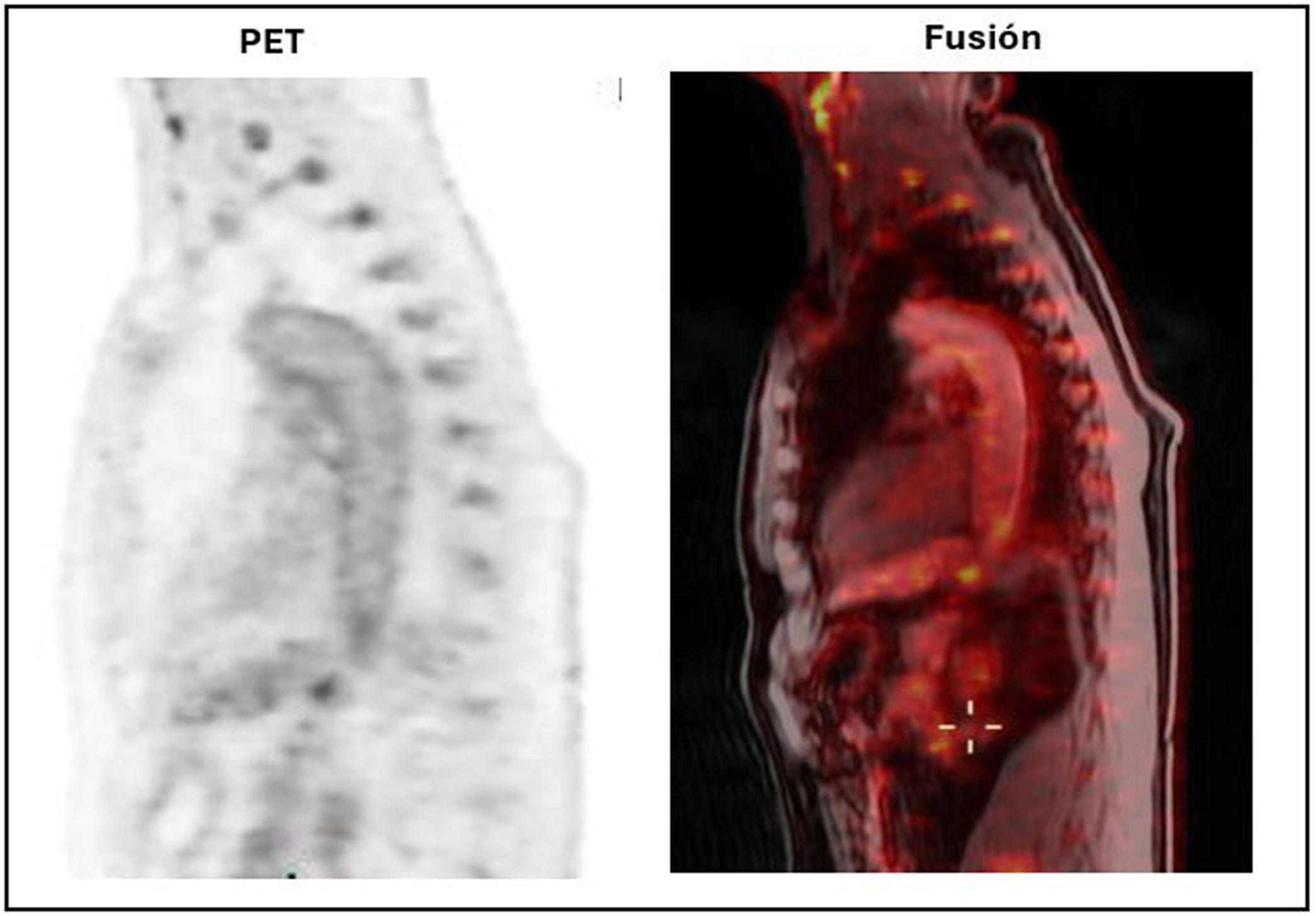
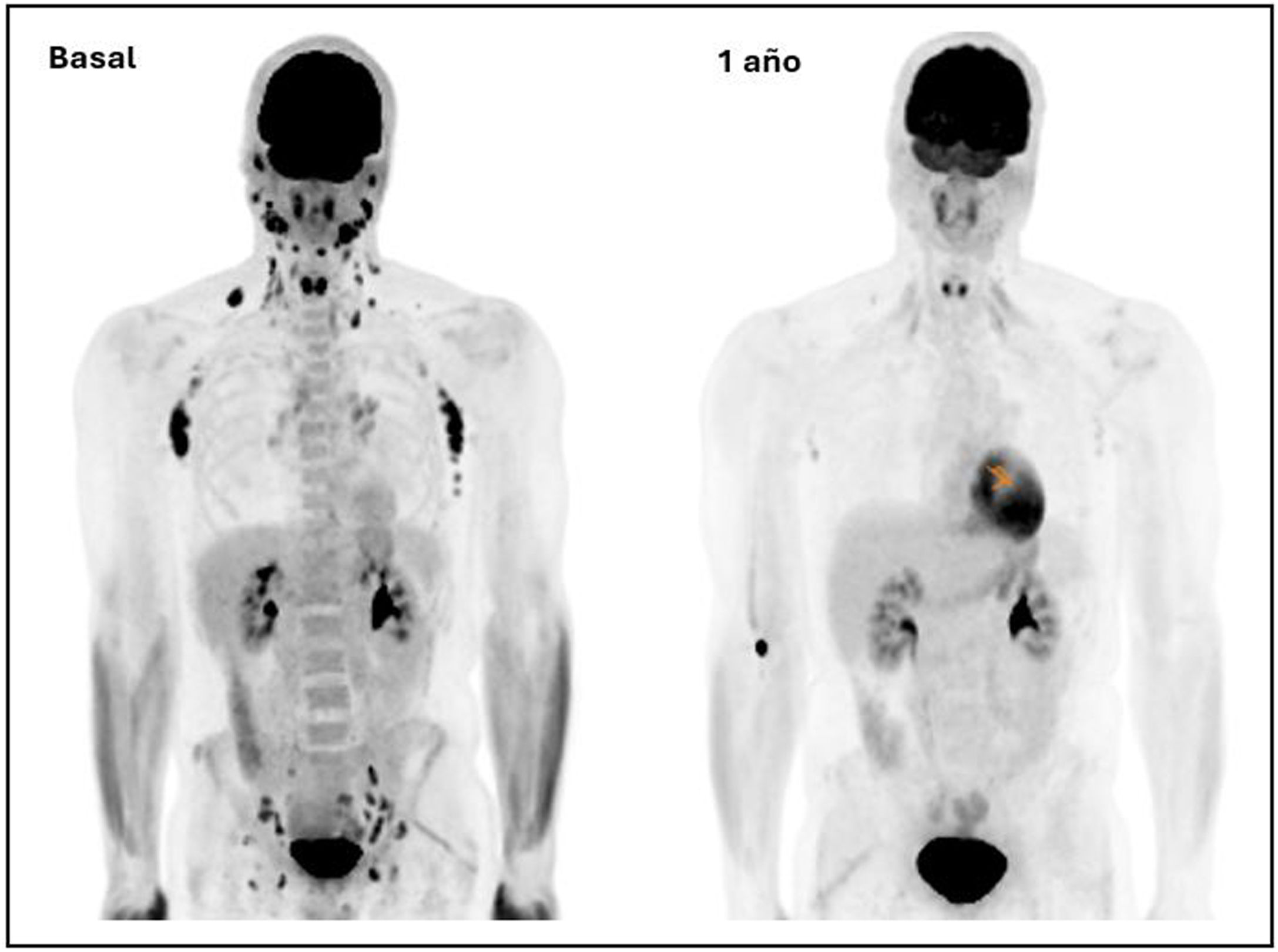
Four (28.6%) showed baseline vascular [18F]FDG uptake, two in ascending thoracic aorta and two in ascending and descending thoracic aorta, normalising post-TAR.
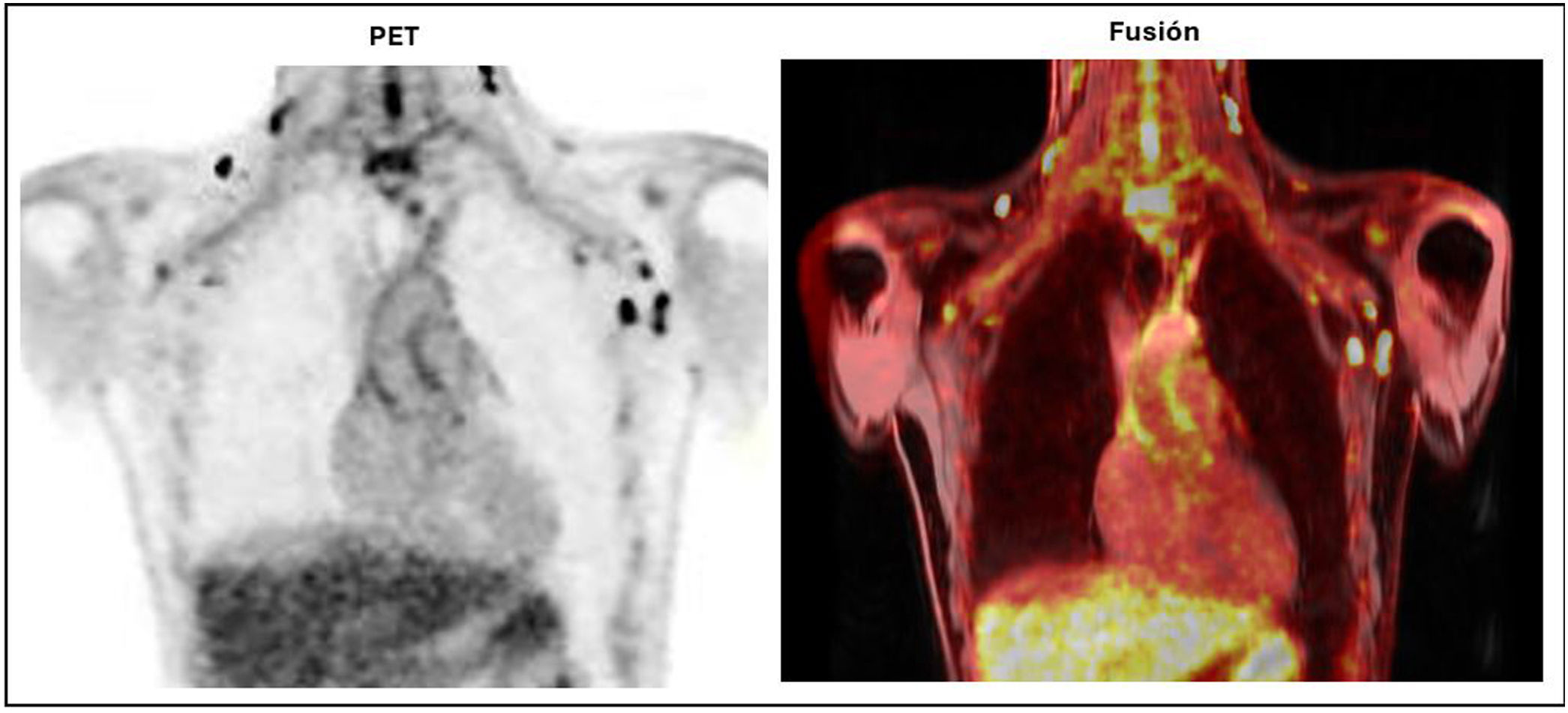
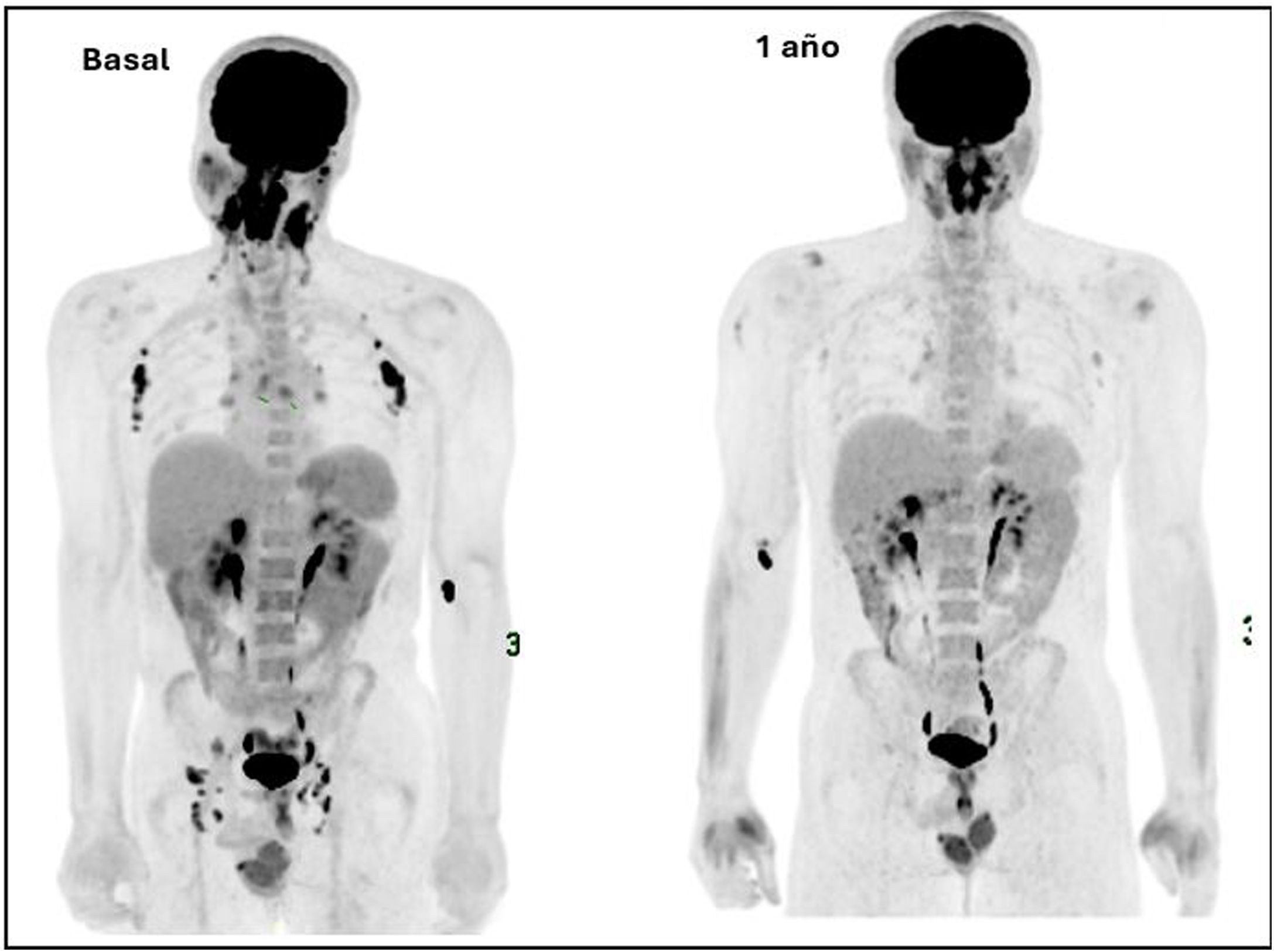
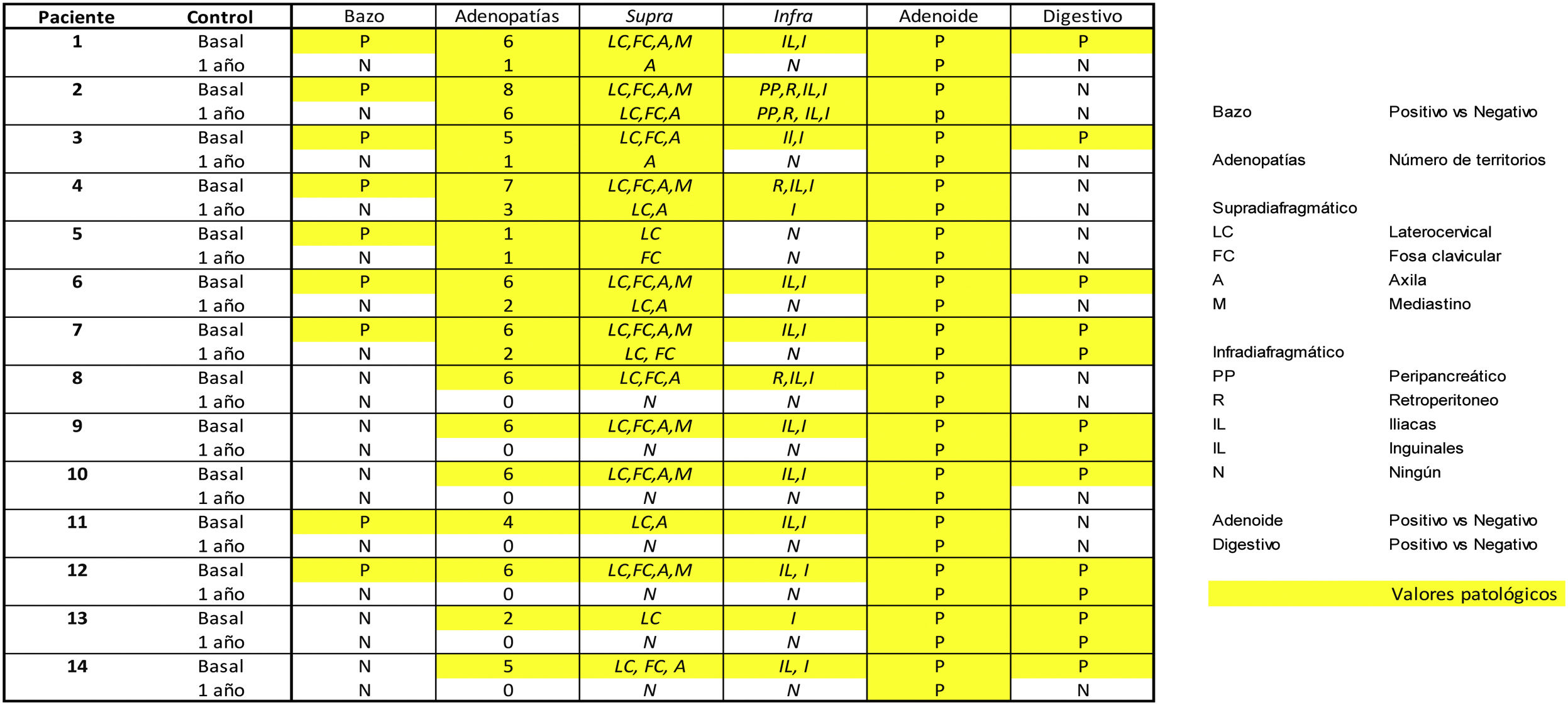
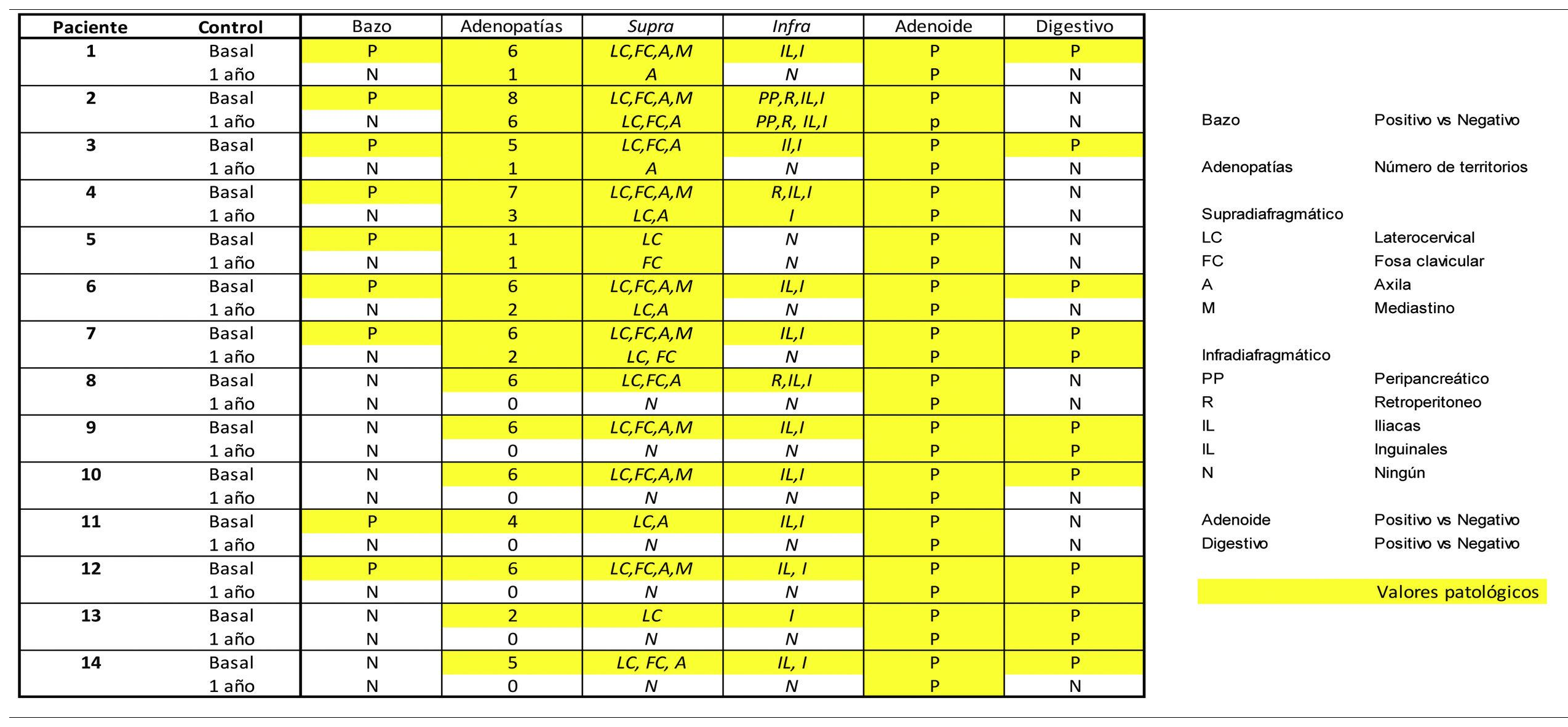
All (100%) showed basal lymph-nodes activity; supra (n:14) and infradiaphragmatic (n:13), laterocervical (n:14) and inguinal (n:13), with variable number of territories (9 patients >6;64.3%). Post-ART, 7 patients (50%) showed resolution and the other 7 reduction in extension (0 patients >5): 7 supra (100%) and 2 infradiaphragmatic (28.6%), 5 in the axilla and 2 in the groin.
All (100%) had persistent basal adenoid uptake post-ART, 9 (64.3%) splenic all resolved post-ART and 7 (50.5%) gastric, persistent 3 post-ART.
ConclusionsCardiovascular biomarkers by [18F]FDG PET/MR have shown baseline 28.6% of patients with large vessel activity and 21.4% with low LVEF, normalising post-ART.
Inflammatory/immune biomarkers showed baseline activity in 100% of lymph-nodes, 100% adenoids, 64.3% splenic and 50.5% gastric. Post-TAR the reduction was 50% lymph-nodes, 0% adenoid, 100% splenic and 57.1% gastric.
Evaluar mediante [18F]FDG PET/RM los biomarcadores de inflamación inducidos por el VIH basal y 1 año post-tratamientos antirretrovirales (TAR).
MétodoEstudio prospectivo, 14 pacientes, recién diagnosticados de VIH, asintomáticos.
Se realizó [18F]FDG PET/RM (PET/MR-3.0T, Signa.GE) de cuerpo completo y cardiaco, basal y 1 año post-TAR.
Valoración cualitativa vascular (referencia hepática). Valoración cuantitativa (SUVmax) de cuerpo completo. Estimación del valor T1 y T2 en 16 segmentos miocárdicos.
ResultadoLa RMC basal mostró en 3 pacientes (21,4%) una FEVI disminuida, normalizándose post-TAR. Se descartó la presencia de fibrosis (T1), sin signos de edema miocárdico (T2) basal ni post-TAR.
En 4 (28,6%) se evidencio hipercaptación de [18F]FDG vascular basal, dos en aorta torácica ascendente y dos en aorta torácica ascendente y descendente, normalizándose post-TAR.
Todos (100%) mostraron actividad adenopática basal; supra (n:14) e infradiafragmática (n:13), laterocervical (n:14) e inguinal (n:13), variable el número de territorios (9 pacientes >6;64,3%). Post-TAR 7 pacientes (50%) mostraron su resolución y los otros 7 reducción en su extensión (0 pacientes >5): 7 supra (100%) y 2 infradiafragmáticos (28,6%), 5 en axila y 2 en ingle.
Todos (100%) presentaron captación adenoidea basal persistente post-TAR, 9 (64,3%) esplénica todas resueltas post-TAR y 7 (50,5%) gástrica, persistente 3 post-TAR.
ConclusionesLos biomarcadores cardiovasculares mediante [18F]FDG PET/RM han mostrado basalmente un 28,6% de pacientes con actividad en grandes vasos y un 21,4% una baja FEVI, normalizándose post-TAR.
Los biomarcadores inflamatorios/inmunes han mostrado actividad basal en un 100% de adenopatías, 100% adenoides, 64,3% esplénica y 50,5% gástrica. Post-TAR la reducción fue del 50% adenopática, 0% adenoidea, 100% esplénica y 57,1% gástrica.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)