Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
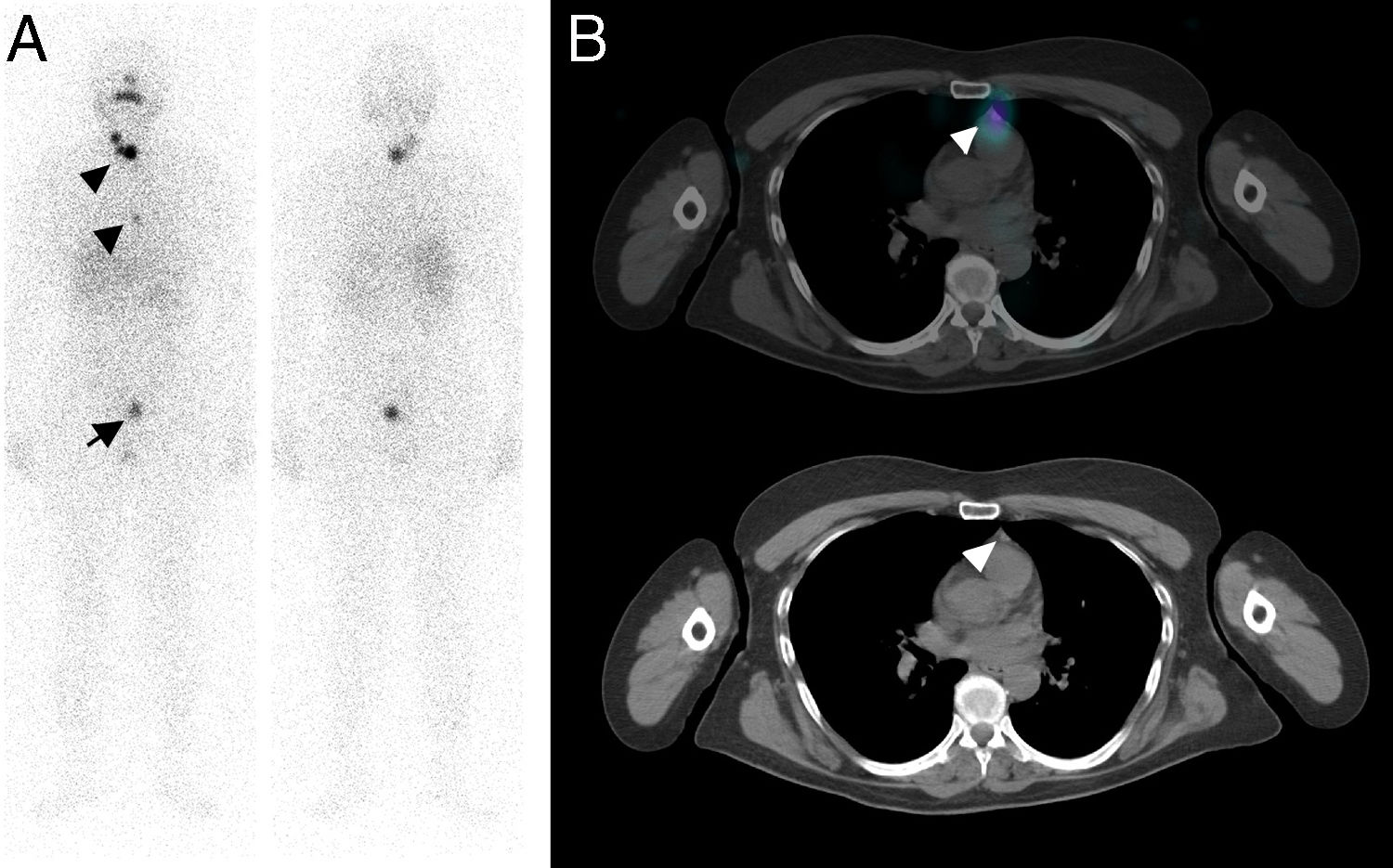
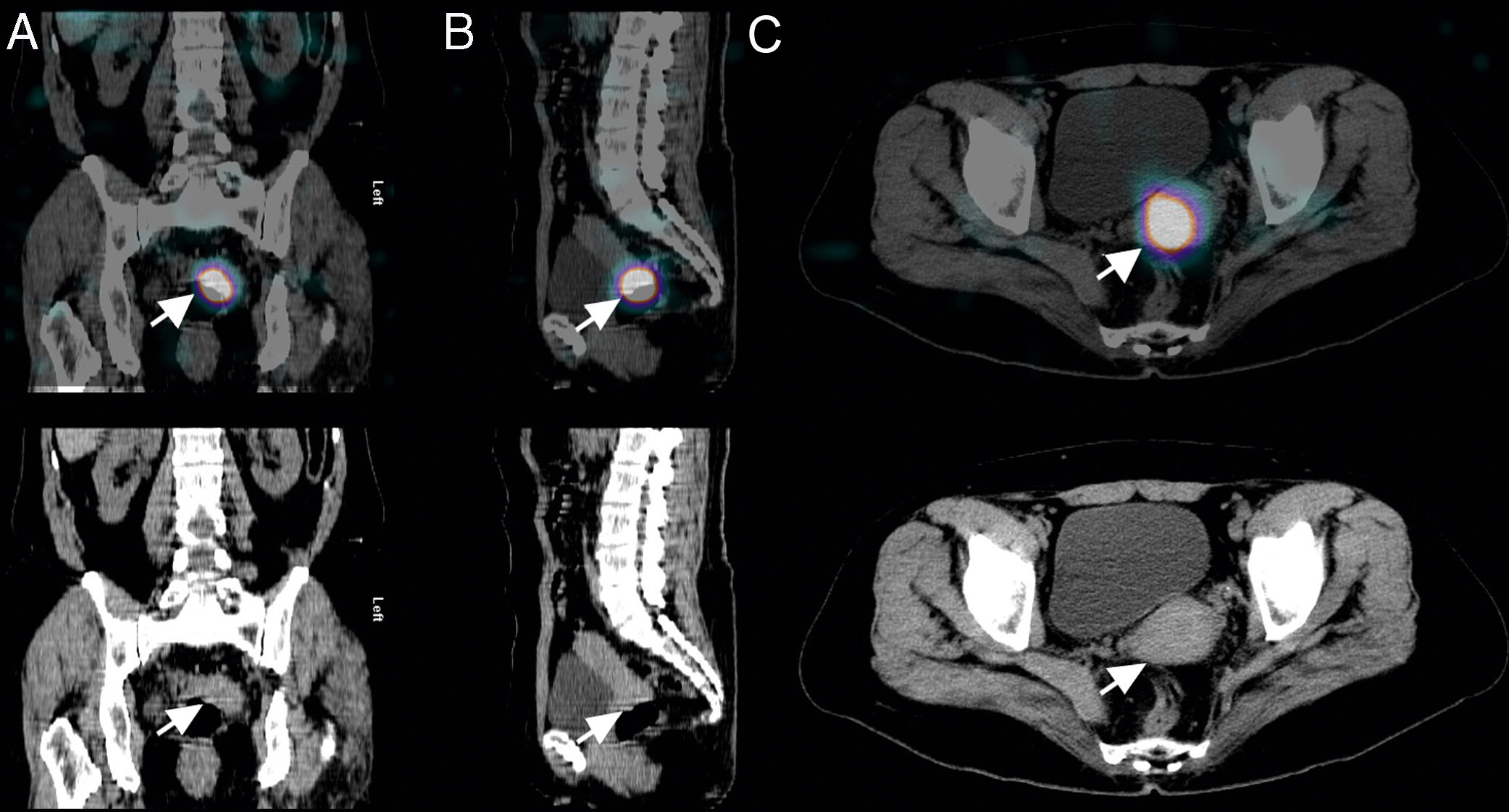
array:24 [ "pii" => "S2253808918300624" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.07.009" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-03-01" "aid" => "998" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "copyrightAnyo" => "2018" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:114-5" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 3 "formatos" => array:2 [ "HTML" => 1 "PDF" => 2 ] ] "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2253654X1830101X" "issn" => "2253654X" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2018.06.002" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-03-01" "aid" => "998" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:114-5" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 119 "formatos" => array:2 [ "HTML" => 86 "PDF" => 33 ] ] "es" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Imágenes de interés</span>" "titulo" => "Falso positivo en rastreo con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">131</span>I por quiste de Naboth" "tienePdf" => "es" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "es" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "114" "paginaFinal" => "115" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "en" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "False-positive <span class="elsevierStyleSup">131</span>I uptake secondary to nabothian cyst" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Figura 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 1121 "Ancho" => 2083 "Tamanyo" => 239934 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "es" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Imágenes de fusión SPECT/TC de región pélvica, en proyecciones coronal (A), sagital (B) y axial (C), en las que se observó un depósito de alta intensidad de captación en relación con lesión hipodensa subcentimétrica en el margen derecho del cérvix uterino (flecha). Tras una exhaustiva exploración ginecológica, se filió como quiste de Naboth, que puede ser causa de falsos positivos en rastreos postablación.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "F.J. García-Gómez, T. Cambil-Molina, J. Jiménez Gallardo, T. Martín-Hernández, J. Castro-Montaño" "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "F.J." "apellidos" => "García-Gómez" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "T." "apellidos" => "Cambil-Molina" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "J." "apellidos" => "Jiménez Gallardo" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "T." "apellidos" => "Martín-Hernández" ] 4 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "J." "apellidos" => "Castro-Montaño" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "en" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253808918300624" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.07.009" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808918300624?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X1830101X?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/2253654X/0000003800000002/v1_201903020653/S2253654X1830101X/v1_201903020653/es/main.assets" ] ] "itemSiguiente" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2253808918300533" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.07.001" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-03-01" "aid" => "994" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:116-7" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 14 "formatos" => array:2 [ "HTML" => 12 "PDF" => 2 ] ] "en" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Interesting images</span>" "titulo" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-MAG3 SPECT/CT in a case of urolithiasis" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "116" "paginaFinal" => "117" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Spect/Tc con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-MAG3 en un caso de urolitiasis" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1635 "Ancho" => 1500 "Tamanyo" => 133183 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">(A) First 16<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>min acquisition. Ascending scintigraphic curves bilaterally which are typical of obstruction. Blue curve right kidney, red curve left kidney. (B) Second 16<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>min acquisition, administration of furosemide at minute 0 (F0) is performed. It is observed how the curves descend bilaterally after diuretic stimulation. Blue curve right kidney, red curve left kidney.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "M.A. Ochoa-Figueroa, A. Davidsson, V. Sánchez-Rodríguez" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "M.A." "apellidos" => "Ochoa-Figueroa" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "A." "apellidos" => "Davidsson" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "V." "apellidos" => "Sánchez-Rodríguez" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253654X1830074X" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2018.05.002" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X1830074X?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808918300533?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/22538089/0000003800000002/v1_201903020621/S2253808918300533/v1_201903020621/en/main.assets" ] "itemAnterior" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S225380891930014X" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.12.003" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-03-01" "aid" => "1046" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "cor" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:112-3" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 1 "HTML" => 1 ] "en" => array:10 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Letter to the Editor</span>" "titulo" => "Quantitative assessment is essential for interpreting lymphoscintigraphy: Response to Ramin Sadeghi's letter to the editor" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "112" "paginaFinal" => "113" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "La evaluación cuantitativa es esencial para la interpretación de la linfogammagrafía: respuesta a la carta al editor de Ramin Sadeghi" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "I. Forner-Cordero, P. Oliván-Sasot, C. Ruiz-Llorca, J. Muñoz-Langa" "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "I." "apellidos" => "Forner-Cordero" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "P." "apellidos" => "Oliván-Sasot" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "C." "apellidos" => "Ruiz-Llorca" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "J." "apellidos" => "Muñoz-Langa" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253654X18303305" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2018.12.003" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X18303305?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S225380891930014X?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/22538089/0000003800000002/v1_201903020621/S225380891930014X/v1_201903020621/en/main.assets" ] "en" => array:16 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Interesting images</span>" "titulo" => "False-positive <span class="elsevierStyleSup">131</span>I uptake secondary to nabothian cyst" "tieneTextoCompleto" => true "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "114" "paginaFinal" => "115" ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "autoresLista" => "F.J. García-Gómez, T. Cambil-Molina, J. Jiménez Gallardo, T. Martín-Hernández, J. Castro-Montaño" "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => array:4 [ "nombre" => "F.J." "apellidos" => "García-Gómez" "email" => array:1 [ 0 => "javier191185@gmail.com" ] "referencia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">*</span>" "identificador" => "cor0005" ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "T." "apellidos" => "Cambil-Molina" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "J." "apellidos" => "Jiménez Gallardo" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">b</span>" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] ] 3 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "T." "apellidos" => "Martín-Hernández" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">c</span>" "identificador" => "aff0015" ] ] ] 4 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "J." "apellidos" => "Castro-Montaño" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] ] ] ] "afiliaciones" => array:3 [ 0 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Servicio de Medicina Nuclear, Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Sevilla, Spain" "etiqueta" => "a" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Sección de Ginecología Oncológica, Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Sevilla, Spain" "etiqueta" => "b" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] 2 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Servicio de Endocrinología y Nutrición, Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Sevilla, Spain" "etiqueta" => "c" "identificador" => "aff0015" ] ] "correspondencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "cor0005" "etiqueta" => "⁎" "correspondencia" => "Corresponding author." ] ] ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Falso positivo en rastreo con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">131</span>I por quiste de Naboth" ] ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Figure 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 1121 "Ancho" => 2083 "Tamanyo" => 239934 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Fused pelvic SPECT/CT images, revealed that the high radioiodine uptake was related to a subcentimetric hypodense lesion on the right margin of the uterine cervix (arrow). After an exhaustive gynaecological examination, the lesion was filiated as a nabothian cyst, which can be cause of false positives findings in post-ablation iodine-131 scans.</p>" ] ] ] "textoCompleto" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSections"><p id="par0005" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">We report a 53-year-old female with previous history of total thyroidectomy due to papillary thyroid carcinoma followed by 100<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mCi of iodine-131 with no side effects reported. A post-ablative whole-body scan was performed 7 days after the administration of iodine-131. Images revealed persistence of thyroid tissue remnants as expected (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0005">Fig. 1</a>, arrow-head). Additionally, other areas with high uptake appeared in anterior mediastinum region related to uncertain millimetric adenopathy (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0005">Fig. 1</a>, arrow-head) as well as in upper pelvic area, next to urinary bladder (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0005">Fig. 1</a>, arrow). SPECT/CT images demonstrated that this finding corresponded to a subcentimetric hypodense lesion located on the right margin of the uterine cervix (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0010">Fig. 2</a>, arrow). The tiroglobulin levels were Tg-On: 0.1<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>ng/ml and Tg-Off: 0.2<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>ng/ml. In order to foreclose gynaecological pathology, the patient was referred to the gynaecology department, where a colposcopy was performed. It showed the existence of a nabothian cyst in this location. It remains to be studied whether this intense uptake could underestimate the real extent of the disease.</p><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0005"></elsevierMultimedia><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0010"></elsevierMultimedia><p id="par0010" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">A considerable number of cases of unexpected radioiodine uptake have been reported. Among the possible causes of iodine uptake in the pelvic region, gynaecological aetiology is extremely rare and may be secondary to struma ovarii, ovarian tumours or cysts, adenocarcinoma of the cervix, uterine fibroids or uterine metastasis from thyroid cancer.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0020"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">1</span></a></p><p id="par0015" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Nabothian cysts are mucus-filled cysts inside cervical crypts which induce to stroma or epithelial squamous metaplasia. Nabothian cysts are a common gynaecological benign disorder in women of childbearing age and usually asymptomatic. A few cases of iodine-131 uptake related to nabothian cysts have been published<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0025"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">2,3</span></a> and suggest that it should be considered as a possible cause of false positive in post-ablative iodine-131 scans.</p></span>" "pdfFichero" => "main.pdf" "tienePdf" => true "fechaRecibido" => "2018-04-24" "fechaAceptado" => "2018-06-06" "NotaPie" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "☆" "nota" => "<p class="elsevierStyleNotepara" id="npar0005">Please cite this article as: García-Gómez FJ, Cambil-Molina T, Gallardo JJ, Martín-Hernández T, Castro-Montaño J. Falso positivo en rastreo con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">131</span>I por quiste de Naboth. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:114–115.</p>" ] ] "multimedia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figure 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 935 "Ancho" => 1500 "Tamanyo" => 208673 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Post-ablative whole-body iodine-131 scan, anterior and posterior projections. An intense uptake of radiotracer was evidenced due to the persistence of thyroid tissue remmants after surgery (arrow-head). In addition, another high intensity uptake was observed in mediastinum (arrow-head), correlated to a millimetric anterior mediastinal adenopathy by SPECT/CT images. However, a third focal uptake in the pelvic region without a clear relation with his thyroid pathology was observed (arrow), so complementary exploratory tests were carried out.</p>" ] ] 1 => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Figure 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 1121 "Ancho" => 2083 "Tamanyo" => 239934 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Fused pelvic SPECT/CT images, revealed that the high radioiodine uptake was related to a subcentimetric hypodense lesion on the right margin of the uterine cervix (arrow). After an exhaustive gynaecological examination, the lesion was filiated as a nabothian cyst, which can be cause of false positives findings in post-ablation iodine-131 scans.</p>" ] ] ] "bibliografia" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "References" "seccion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "bibs0015" "bibliografiaReferencia" => array:3 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0020" "etiqueta" => "1" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "False-positive uptake on radioiodine whole-body scintigraphy: physiologic and pathologic variants unrelated to thyroid cancer" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "J.R. Oh" 1 => "B.C. Ahn" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging" "fecha" => "2012" "volumen" => "2" "paginaInicial" => "362" "paginaFinal" => "385" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23133823" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0025" "etiqueta" => "2" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Nabothian cyst a predominant cause of false-positive iodine uptake in uterus: comparison of SPECT/CT and pelvic MRI" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "T. Isoda" 1 => "S. BaBa" 2 => "Y. Maruoka" 3 => "Y. Kitamura" 4 => "A. Nishie" 5 => "M. Sasaki" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1097/RLU.0000000000000504" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Clin Nucl Med" "fecha" => "2014" "volumen" => "39" "paginaInicial" => "680" "paginaFinal" => "684" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24978344" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0030" "etiqueta" => "3" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Nabothian cyst associated with high false-positive incidence of iodine-131 uptake in whole-body scans after treatment for differentiated thyroid cancer" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "S. Liu" 1 => "M. Zhang" 2 => "Y. Pan" 3 => "Q. Qu" 4 => "H. Wu" 5 => "J. Lv" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1097/MNM.0b013e328365911a" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Nucl Med Commun" "fecha" => "2013" "volumen" => "34" "paginaInicial" => "1204" "paginaFinal" => "1207" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24077637" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "url" => "/22538089/0000003800000002/v1_201903020621/S2253808918300624/v1_201903020621/en/main.assets" "Apartado" => array:4 [ "identificador" => "7927" "tipo" => "SECCION" "en" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Interesting images" "idiomaDefecto" => true ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" ] "PDF" => "https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/22538089/0000003800000002/v1_201903020621/S2253808918300624/v1_201903020621/en/main.pdf?idApp=UINPBA00004N&text.app=https://www.elsevier.es/" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808918300624?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ]
Consulte los artículos y contenidos publicados en éste medio, además de los e-sumarios de las revistas científicas en el mismo momento de publicación
Esté informado en todo momento gracias a las alertas y novedades
Acceda a promociones exclusivas en suscripciones, lanzamientos y cursos acreditados
The Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (Spanish Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging), was founded in 1982, and is the official journal of the Spanish Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, which has more than 700 members. The Journal, which publishes 6 regular issues per year, has the promotion of research and continuing education in all fields of Nuclear Medicine as its main aim. For this, its principal sections are Originals, Clinical Notes, Images of Interest, and Special Collaboration articles. The works may be submitted in Spanish or English and are subjected to a peer review process. In 2009, it became the leading Spanish journal in the field of Medical Imaging on having an Impact Factor , awarded by the Journal Citation Reports.
Science Citation Index Expander, Medline, IME, Bibliomed, EMBASE/Excerpta Medica, Healthstar, Cancerlit, Toxine, Inside Conferences, Scopus
See moreThe Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2022
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more
Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)

¿Es usted profesional sanitario apto para prescribir o dispensar medicamentos?
Are you a health professional able to prescribe or dispense drugs?
Você é um profissional de saúde habilitado a prescrever ou dispensar medicamentos