The aim of the study was evaluate the diagnostic performance of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC and [18F]FDG PET/CT in patients with histologically proven neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), as well as the correlation of the visualized findings with the tumor grade.
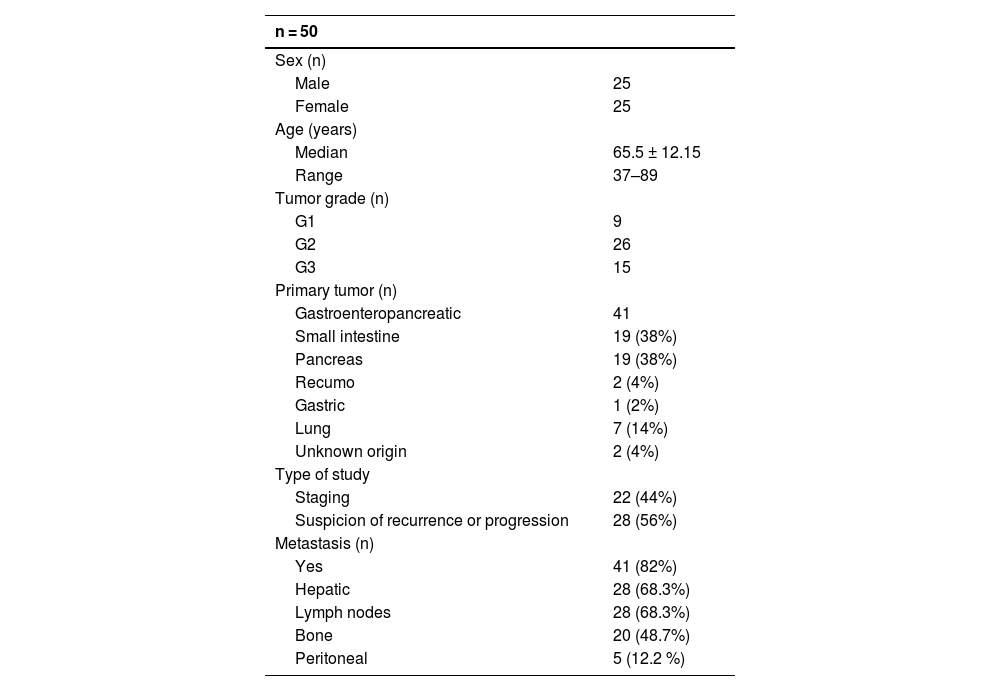
Material and methodsWe included 50 patients with NETs who underwent both [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC and [18F]FDG PET/TC. The pooled sensitivity of both scans was compared, as well as [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC and [18F]FDG for each tumor grade (grade 1/G1, grade 2/G2 and grade 3/G3). Also, the sensitivity of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC and [18F]FDG as a function of the continuous variable Ki-67 was investigated. Finally, the number of lesions detected by both PET radiopharmaceuticals for each tumor grade was compared.
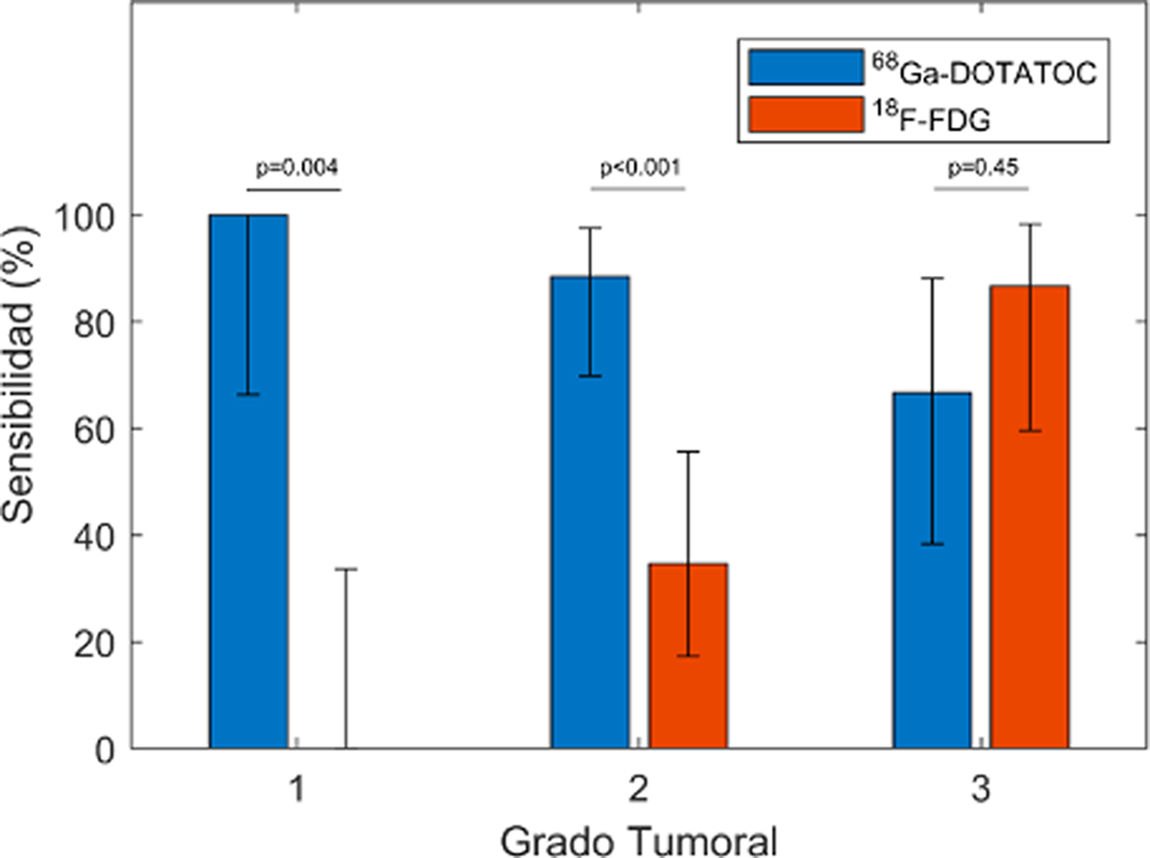
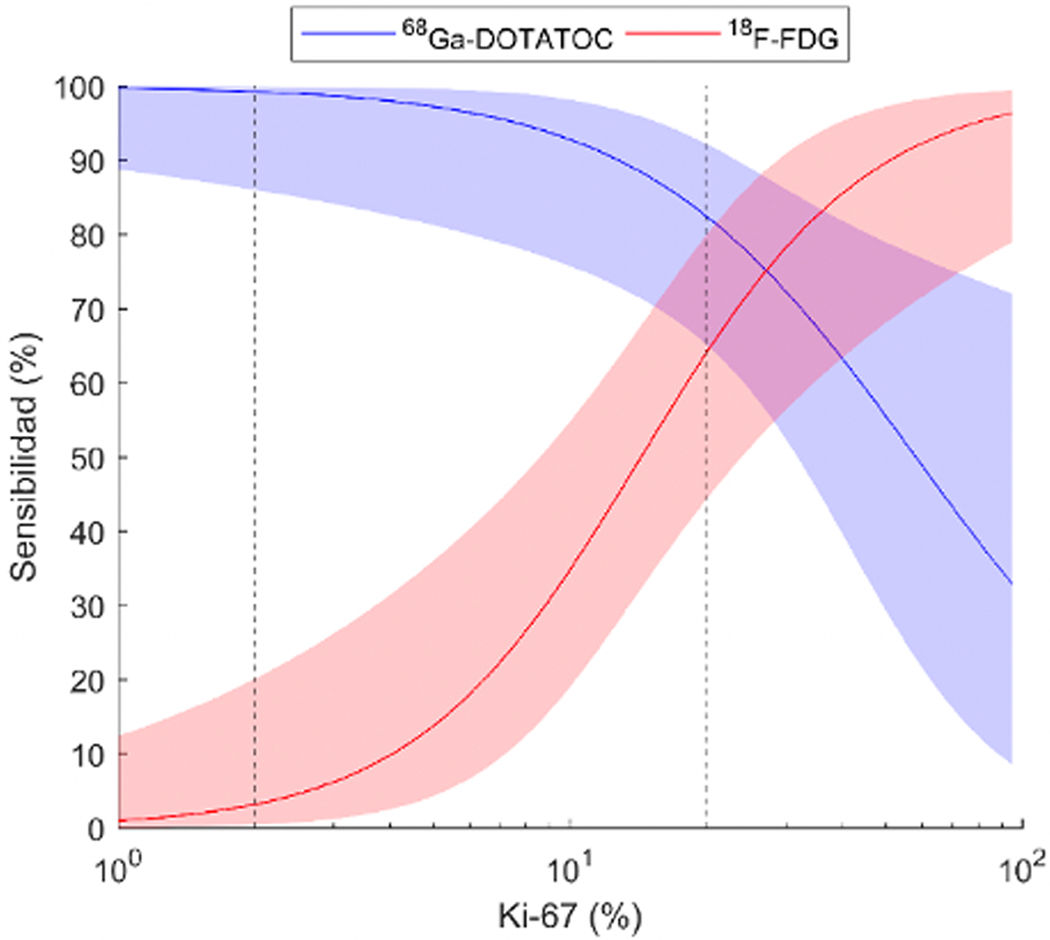
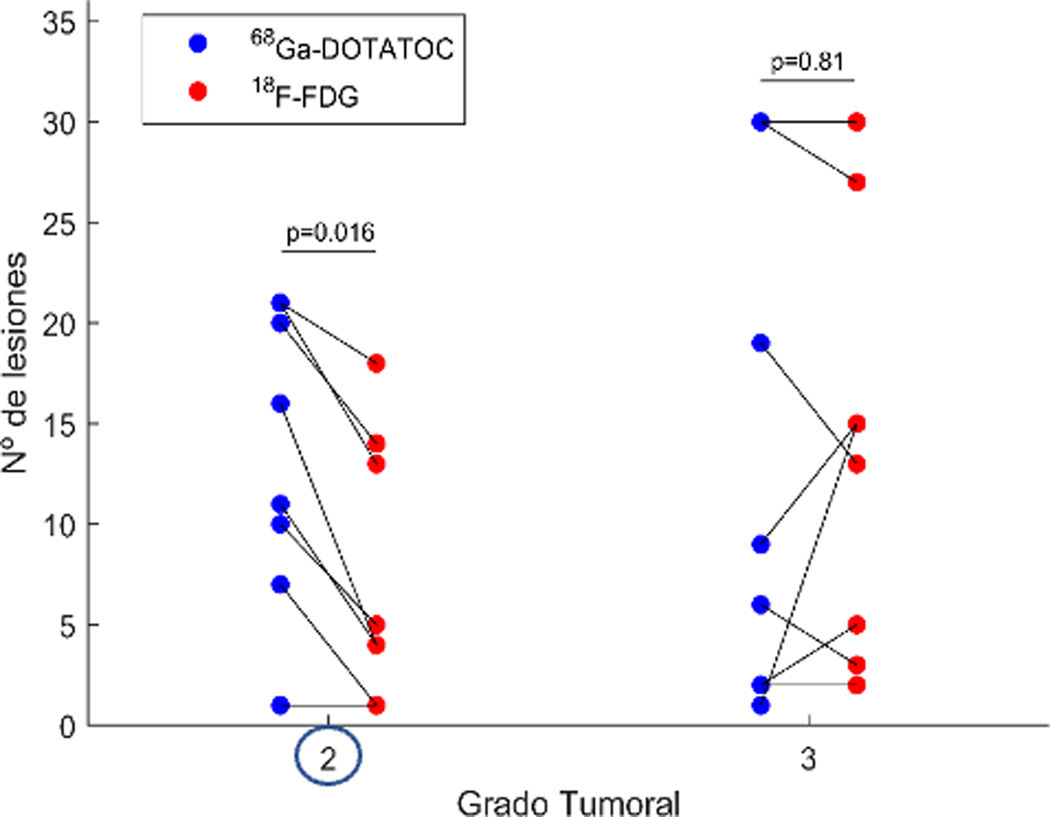
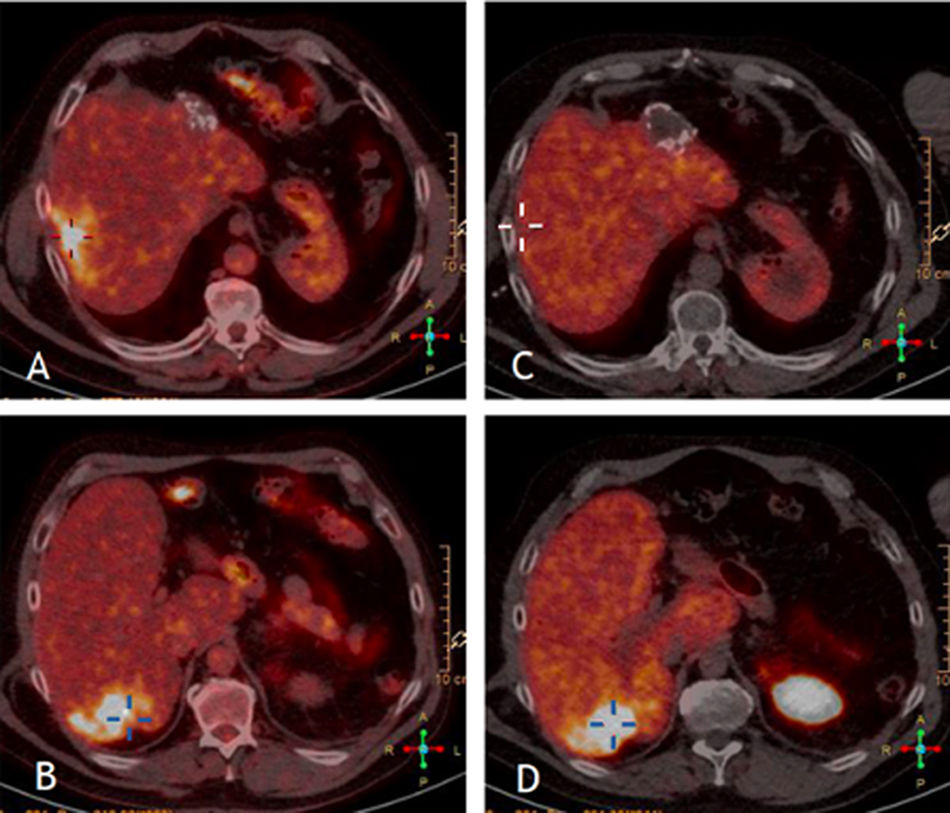
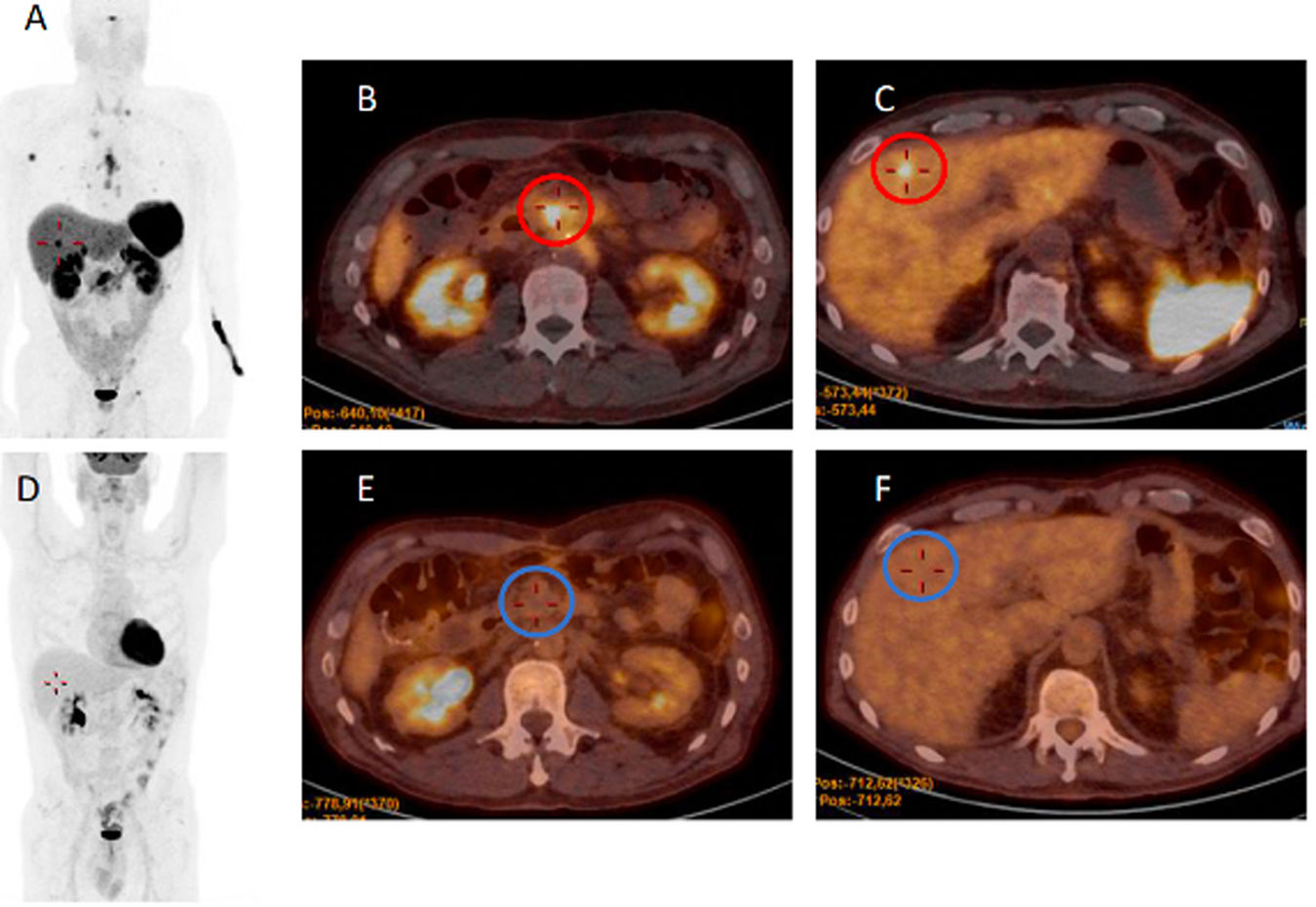
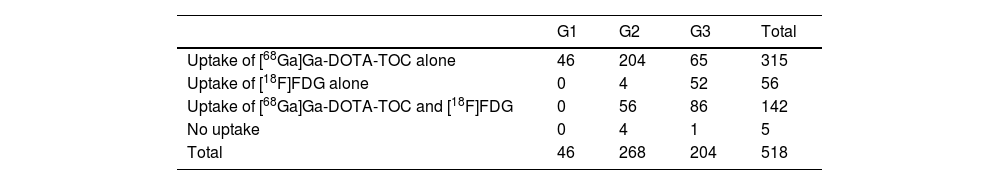
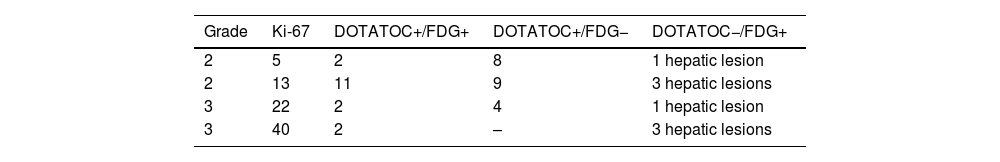
ResultsThe pooled sensitivity of both PET/CT (96%) was higher than [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC (84%) and [18F]FDG (44%) separately, with statistically significant differences. The sensitivity of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC was higher than [18F]FDG in both G1 (p = 0.004) and G2 (p < 0.001). In G3 the performance of both scans detected disease in 100% of this subgroup. The sensitivity of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC and [18F]FDG PET/CT correlated significantly with the Ki-67 proliferative index. In G2 patients the number of lesions detected with [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC was higher than [18F]FDG.
ConclusionsThe performance of both PET/CT, particularly in G2 and G3, demonstrates the molecular heterogeneity of metastatic NETs and contributes to the selection of a more appropriate treatment, particularly in those high-grade patients who may benefit from radionuclide therapy (PRRT).
El objetivo del estudio fue evaluar el rendimiento diagnóstico de las PET/TC con [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC y [18F]FDG en pacientes con tumores neuroendocrinos (TNEs) confirmados histológicamente, así como la correlación de los hallazgos visualizados con el grado tumoral.
Material y métodosSe incluyeron 50 pacientes con TNEs a los que se le realizó una PET/TC con [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC y otra con [18F]FDG. Se comparó la sensibilidad conjunta de ambas exploraciones, así como la del [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC y la de la [18F]FDG para cada grado tumoral (grado 1/G1, grado 2/G2 y grado 3/G3). Asimismo, se investigó la sensibilidad del [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC y de la [18F]FDG en función de la variable continua Ki-67. Finalmente, se compararon el número de lesiones detectadas por cada radiofármaco PET para cada grado tumoral.
ResultadosLa sensibilidad conjunta de ambas PET/TC (96%) fue mayor que la del [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC (84%) y la [18F]FDG (44%) por separado, objetivándose diferencias significativas. La sensibilidad del [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC fue superior a la [18F]FDG tanto en G1 (p = 0.004) como G2 (p < 0.001). En los G3 la realización de ambas exploraciones permitió detectar enfermedad en el 100% de este subgrupo. La sensibilidad de la PET/TC con [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC y con [18F]FDG se correlaciona significativamente con el índice proliferativo Ki-67. En los pacientes G2 el número de lesiones detectadas con el [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC fue superior a la [18F]FDG.
ConclusionesLa sensibilidad conjunta de ambas PET/TC es mayor que la del [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC y [18F]FDG por separado y permite demostrar la heterogeidad molecular de los TNE metástásicos, sobre todo en aquellos pacientes G2 y G3.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)