The aim of this study is to assess the relationship between structural, remodeling, synchrony, and systolic left ventricular (LV) function parameters using gated-SPECT myocardial-perfusion-images (gSPECT-MPI). In addition, obtaining the cut-off values for end-diastolic LV-shape-index (EDLVsi), end-systolic LV-shape-index (ESLVsi), ECC (eccentricity-index) and PER, and developing a new index to evaluate different patterns of the LV systolic function.
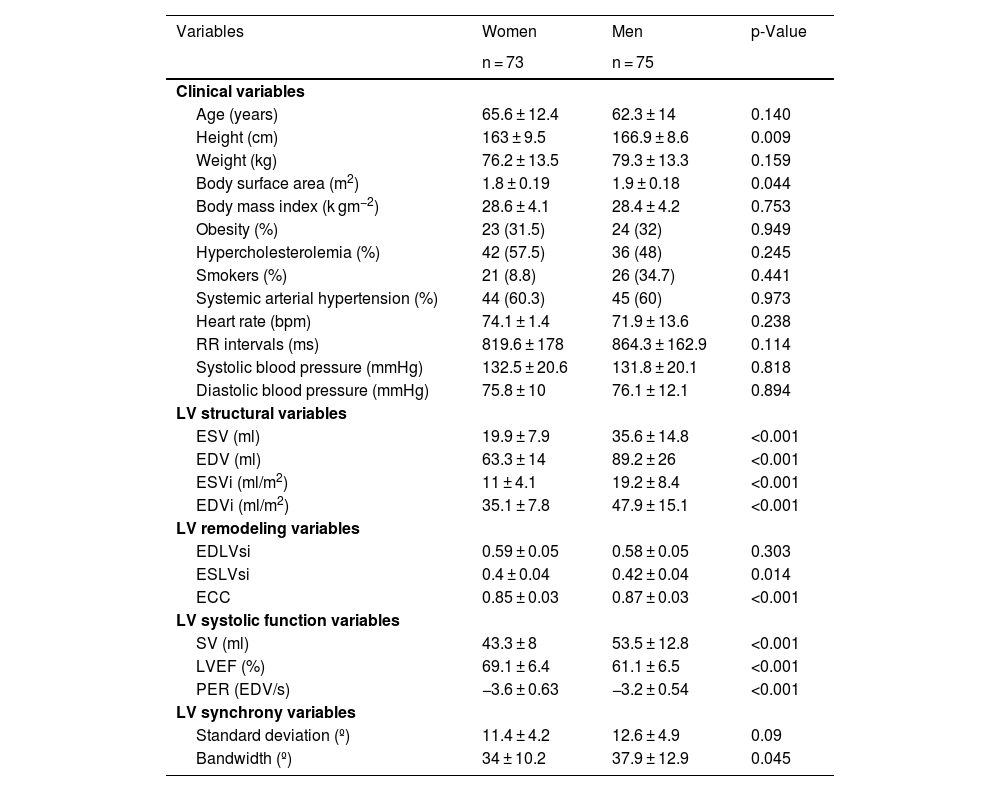
MethodsThe study was approved by the Hospital’s Ethical-Committee (PR[AG]168.2010), and all patients gave their informed consent. We analyzed prospectively 238 patients (age 63.4 ± 13 years) who underwent stress-rest gSPECT-MPI (control-group, n = 148; patients with previous myocardial infarction [MI], n = 90).
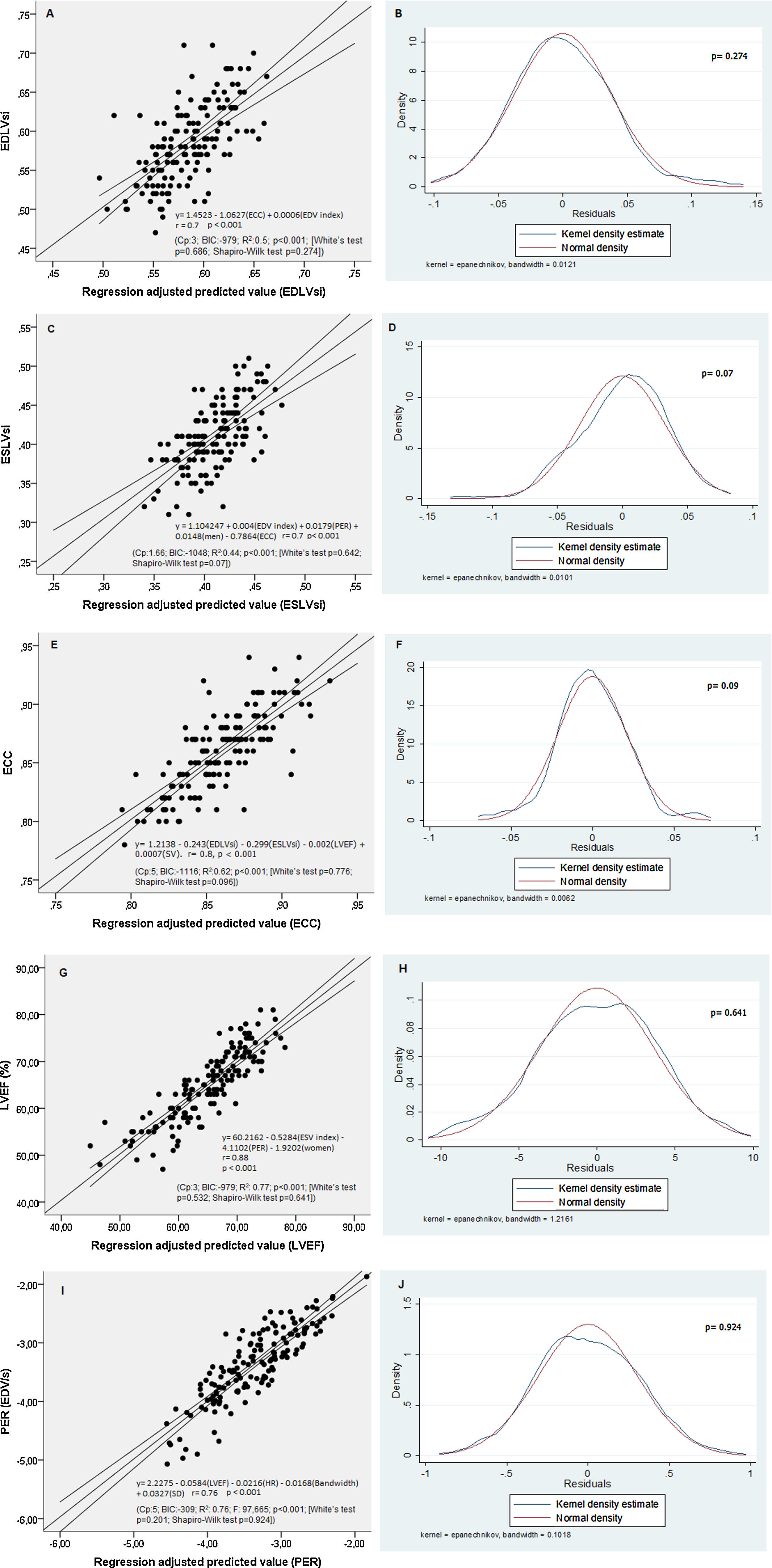
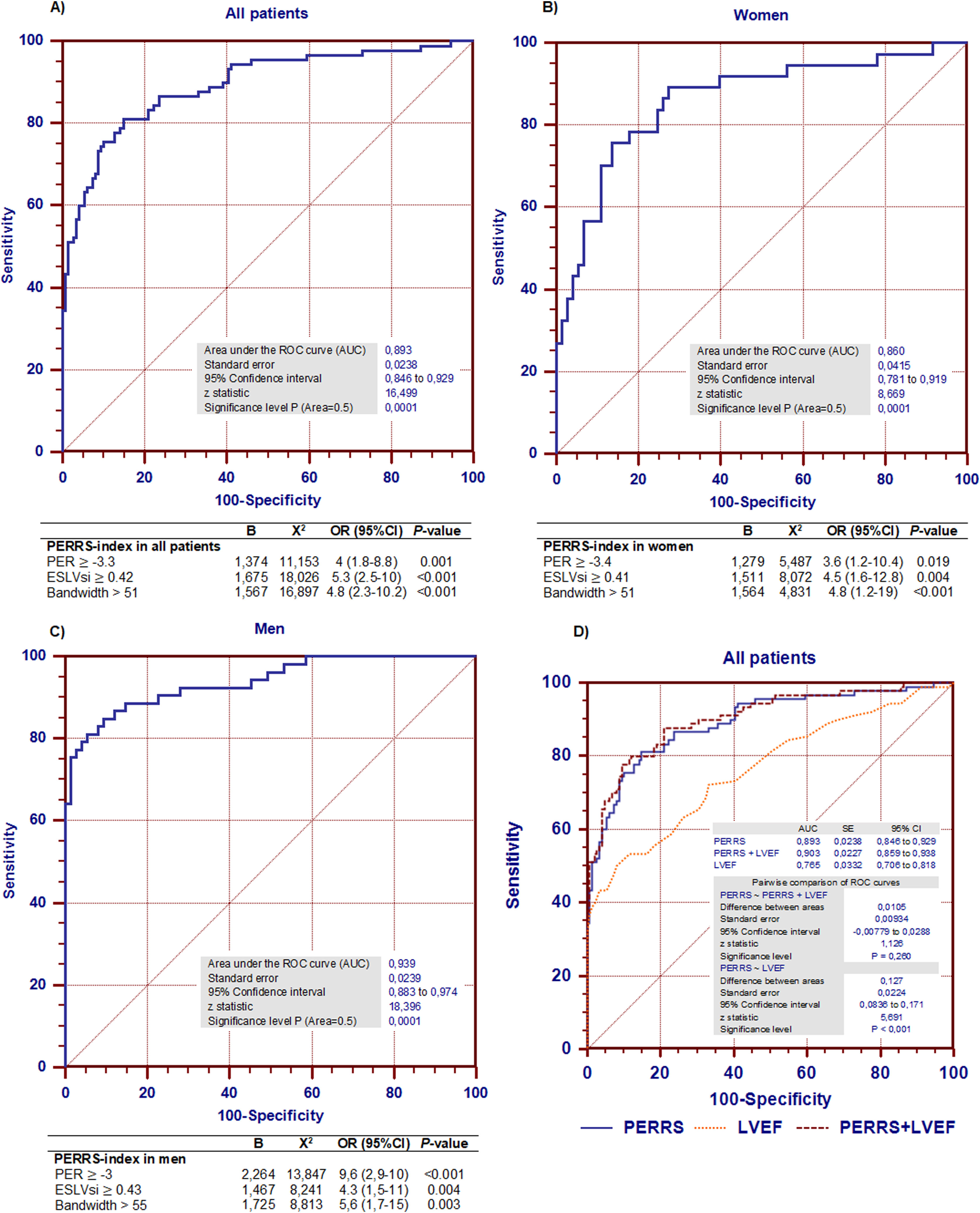
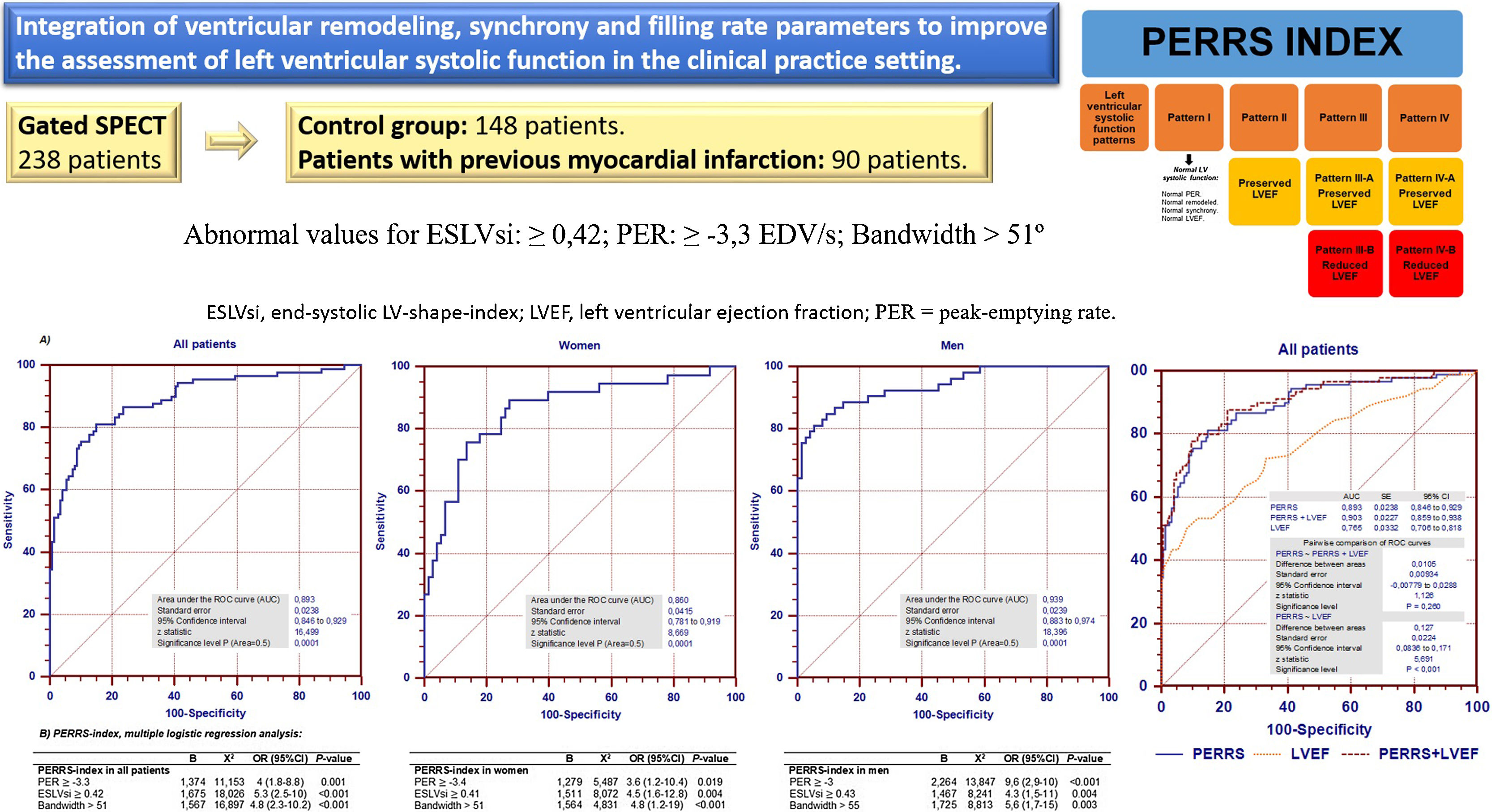
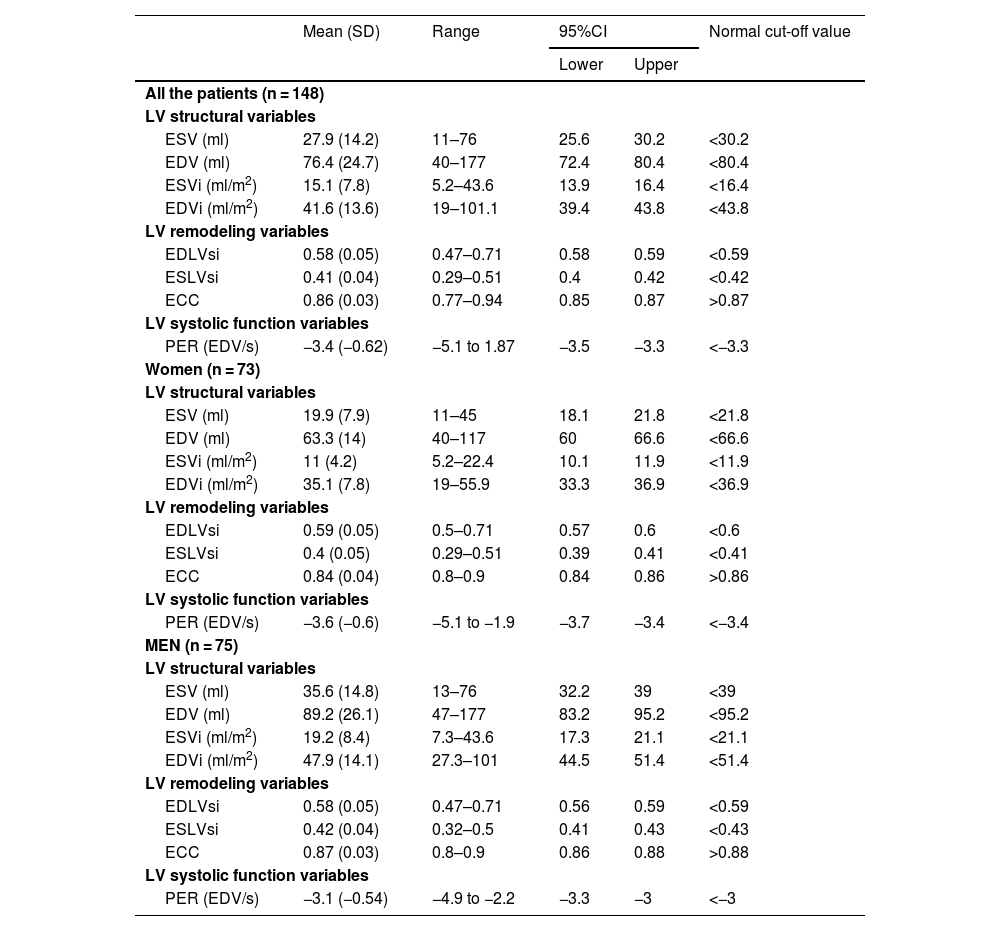
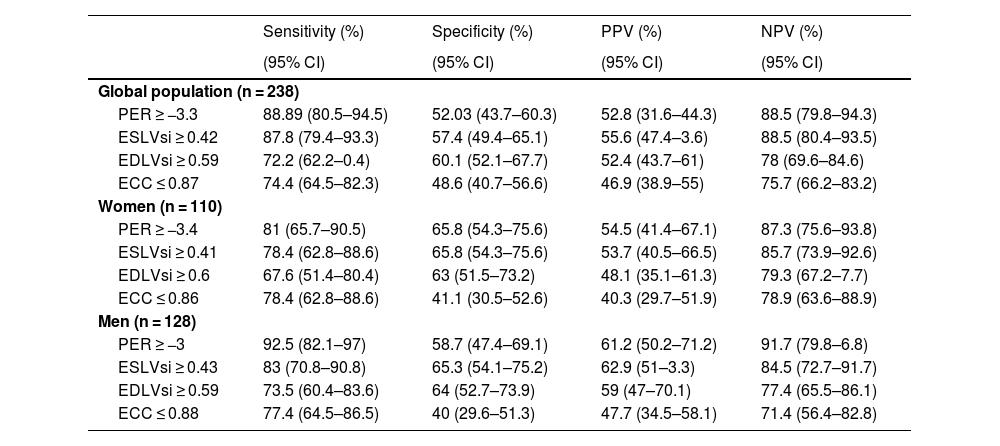
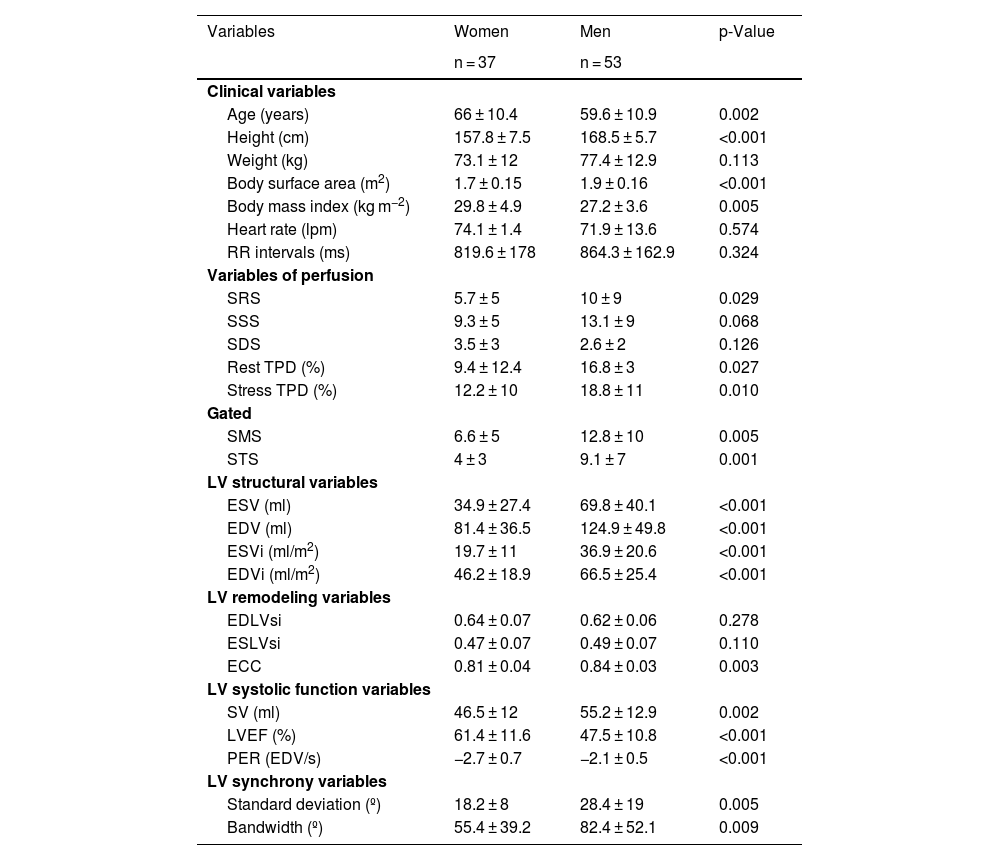
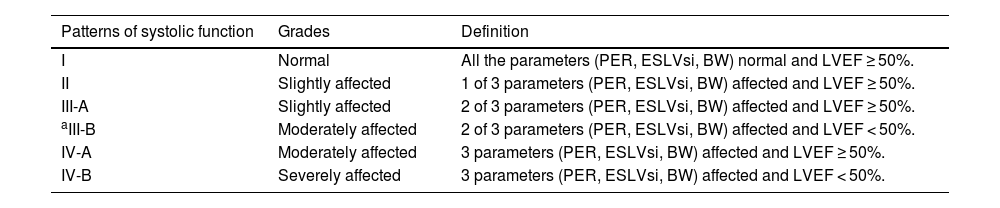
ResultsIn the control group, with regard to remodeling parameters: the end-diastolic-volume-index (EDV) and the ECC were the parameters that influenced the EDLVsi (r2: 0.52, p < 0.001). EDV, PER, men, and the ECC were the parameters (r2: 0.44; p < 0.001) which influenced the ESLVsi. EDLVsi, ESLVsi, LVEF and the stroke-volume were the parameters (r2: 0.62; p < 0.001) which influenced the ECC. With regards to PER: LVEF, heart-rate, bandwidth, and the standard-deviation were the influencing parameters (r2: 0.76; p < 0.001). The cut-off values for EDLVsi, ESLVsi, ECC, and PER were 0.59, 0.42, 0.87, and 3.3, respectively. The PER, the ESLVsi and the bandwidth were the parameters related to patients with previous MI (AUC: 0.89); and they allow the assessment of different patterns of systolic function (PERRS-index: peak-emptying-rate, left ventricular-remodeling and synchrony).
ConclusionsThe remodeling, synchrony and the systolic function parameters of the LV should be interpreted together (PERRS-index). In this way, we obtain different patterns of LV systolic function.
El objetivo es estudiar la relación entre los parámetros estructurales, de remodelado, de sincronía y de función sistólica del ventrículo izquierdo (VI) mediante gSPECT. Obtener los valores de corte del VI para el índice de la forma telediastólica (iFTD), el índice de la forma telesistólica (iFTS), el índice de excentricidad (iEX) y la velocidad máxima de vaciado (VMV). Desarrollar un nuevo índice para evaluar diferentes patrones de función sistólica del VI.
Material y métodosAnalizamos prospectivamente 238 pacientes (edad: 63,4 ± 13 años) estudiados mediante gSPECT de esfuerzo-reposo (grupo-control, n = 148; pacientes con infarto de miocardio [IM] previo, n = 90). Estudio aprobado por el Comité de Ética del Hospital (PR[AG]168.2010).
ResultadosEn el grupo-control, el índice del volumen telediastólico (iVTD) y el iEX influyeron en el iFTD (r2: 0,52, p < 0,001). El iVTD, la VMV, ser varones y el iEX (r2: 0,44; p < 0,001) influyeron en el iFTS. El iFTD, iFTS, la fracción de eyección VI (FEVI) y el volumen de eyección sistólica (r2: 0,62; p < 0,001) influyeron en el iEX. La FEVI, la frecuencia cardíaca, el ancho de banda (AB) y la desviación estándar influyeron (r2: 0,76; p < 0,001) en la VMV. Los valores de corte para iFTD, iFTS, iEX y VMV fueron 0,59, 0,42, 0,87 y −3,3 respectivamente. La VMV, el iFTS y el AB fueron los parámetros mejor relacionados con los pacientes con IM previo (AUC: 0,89), y sumados a la FEVI permitieron obtener distintos patrones de función sistólica (índice PERRS).
ConclusionesLos parámetros de remodelado, sincronía y función sistólica del VI deben interpretarse simultáneamente, ya que esto permite obtener distintos patrones de función sistólica del VI.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)