Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
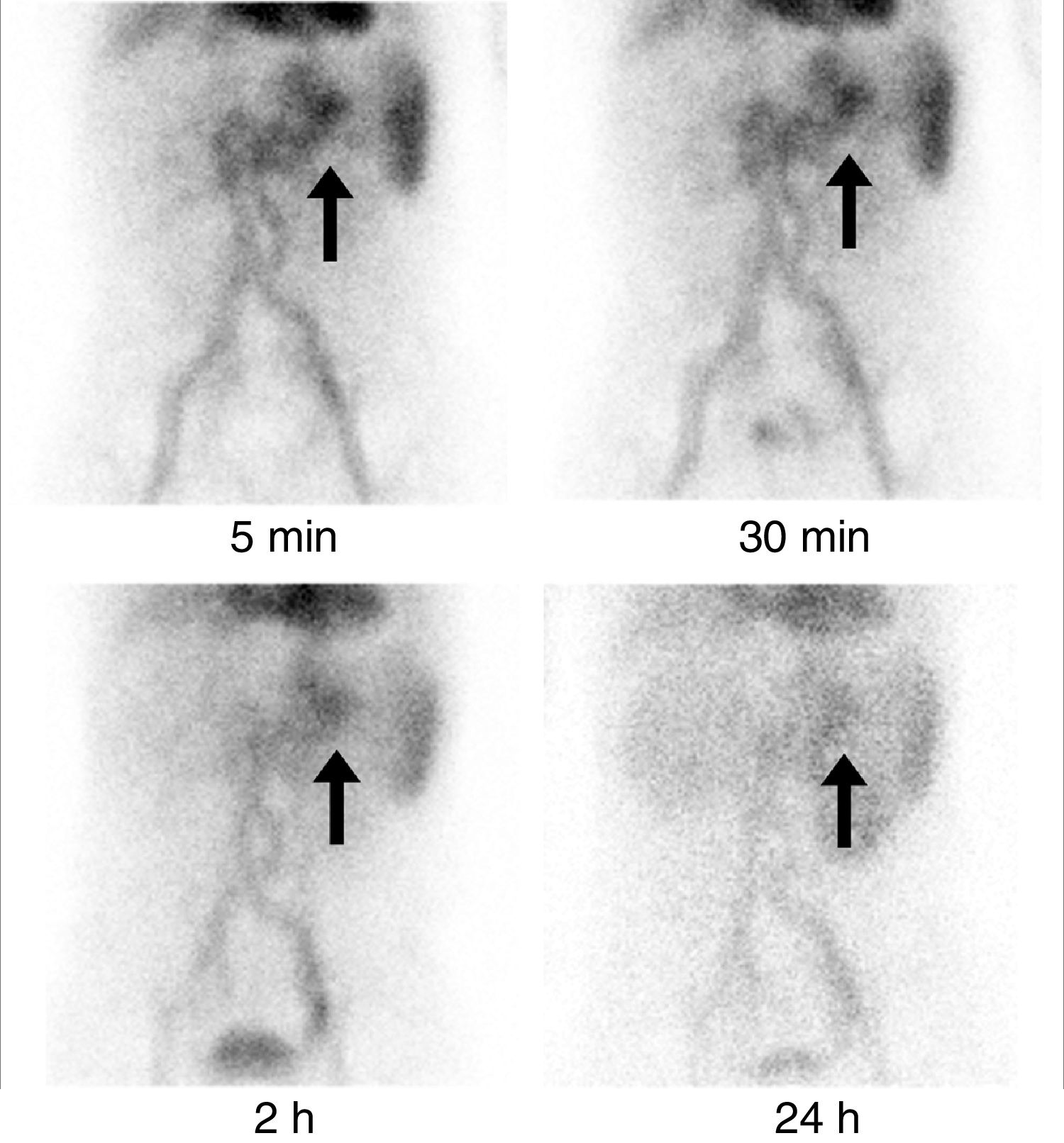
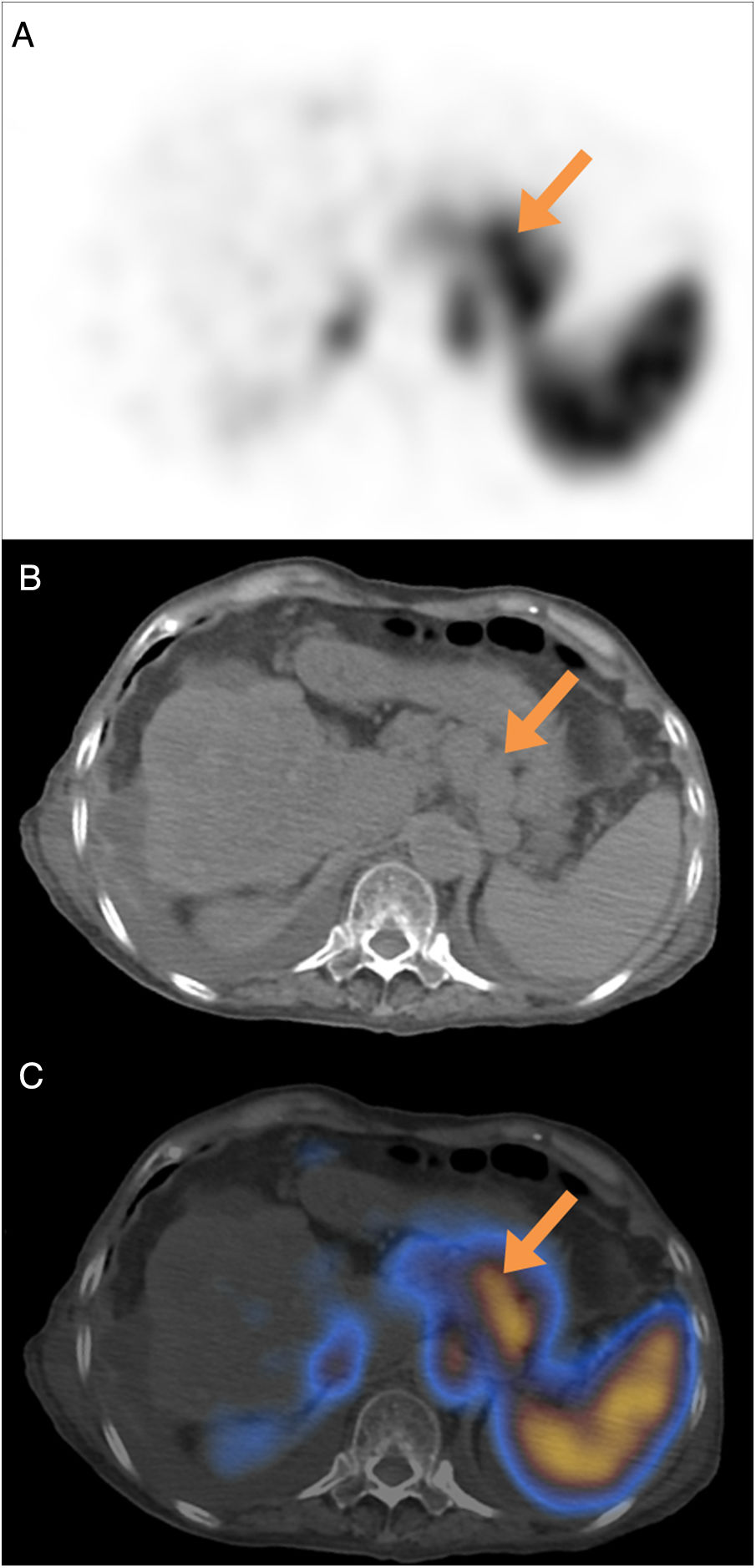
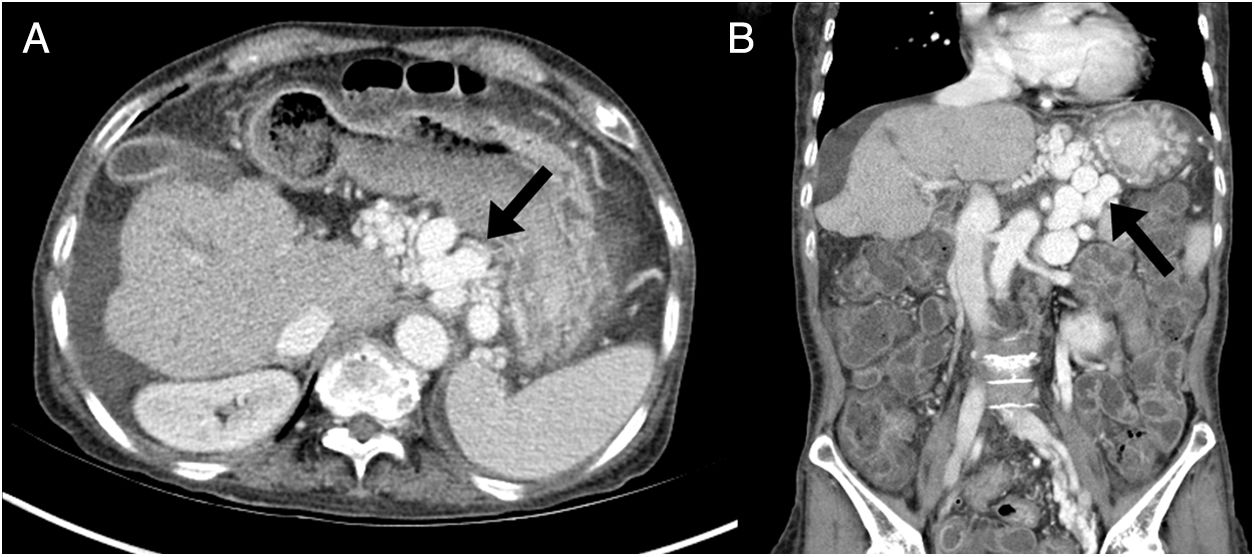
array:24 [ "pii" => "S2253808918300594" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.07.006" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-05-01" "aid" => "1005" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "copyrightAnyo" => "2018" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:186-7" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 4 "formatos" => array:2 [ "HTML" => 2 "PDF" => 2 ] ] "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2253654X18301173" "issn" => "2253654X" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2018.07.001" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-05-01" "aid" => "1005" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:186-7" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 40 "formatos" => array:2 [ "HTML" => 26 "PDF" => 14 ] ] "es" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Imágenes de interés</span>" "titulo" => "Varices perigástricas detectadas en un estudio de hemorragia digestiva mediante SPECT/TC con hematíes marcados con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc" "tienePdf" => "es" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "es" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "186" "paginaFinal" => "187" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "en" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Perigastric varices detected in a gastrointestinal bleeding study with <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-labeled red blood cells SPECT/CT" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0015" "etiqueta" => "Figura 3" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr3.jpeg" "Alto" => 557 "Ancho" => 1255 "Tamanyo" => 110029 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "es" => "<p id="spar0015" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Las imágenes axial (A) y coronal (B) de la TC abdominal con contraste realizada posteriormente mostraron venas aumentadas y tortuosas (flechas) en el área perigástrica. Estas venas son la vena gástrica izquierda, responsable de la circulación colateral portosistémica. El hígado estaba atrófico, con una superficie nodular y se observó una pequeña cantidad de ascitis.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "M.H. Kim, S-A. Park, D-W. Kim" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "M.H." "apellidos" => "Kim" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "S-A." "apellidos" => "Park" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "D-W." "apellidos" => "Kim" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "en" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253808918300594" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.07.006" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808918300594?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X18301173?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/2253654X/0000003800000003/v2_202009160717/S2253654X18301173/v2_202009160717/es/main.assets" ] ] "itemSiguiente" => array:18 [ "pii" => "S2253808918300776" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.10.007" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-05-01" "aid" => "1019" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:188-9" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 2 "PDF" => 2 ] "en" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Interesting images</span>" "titulo" => "Cutaneous metastasis from Hürthle cell follicular thyroid carcinoma" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "188" "paginaFinal" => "189" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Metástasis cutánea de carcinoma tiroideo folicular de células de Hürthle" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1012 "Ancho" => 1935 "Tamanyo" => 289296 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">(A) Anterior and posterior projections of 131-iodine wholebody scan without pathologic findings. (B) MIP and axial slices of <span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET/CT in which, in addition to a hypermetabolic pulmonary nodular lesion (arrow-head), a 30<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>×<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>36<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mm soft tissue density nodular lesion (arrow) located subcutaneous on the left flank with high metabolic activity (SUVmax: 77.45) was observed.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Francisco Javier García-Gómez, Teresa Cambil-Molina, Tomás Martín-Hernández, Gertrudis Sabatel-Hernández, María de la Cinta Calvo-Morón, Juan Castro-Montaño" "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Francisco Javier" "apellidos" => "García-Gómez" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Teresa" "apellidos" => "Cambil-Molina" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Tomás" "apellidos" => "Martín-Hernández" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Gertrudis" "apellidos" => "Sabatel-Hernández" ] 4 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "María de la Cinta" "apellidos" => "Calvo-Morón" ] 5 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Juan" "apellidos" => "Castro-Montaño" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253654X18301458" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2018.09.002" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X18301458?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808918300776?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/22538089/0000003800000003/v1_201905020850/S2253808918300776/v1_201905020850/en/main.assets" ] "itemAnterior" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2253808918301113" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.11.001" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-05-01" "aid" => "1017" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "crp" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:183-5" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 2 "PDF" => 2 ] "en" => array:13 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Clinical note</span>" "titulo" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET/CT in a patient with atypical presentation of cardiac angiosarcoma" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "tieneResumen" => array:2 [ 0 => "en" 1 => "es" ] "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "183" "paginaFinal" => "185" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "PET/TC con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG en paciente con presentación atípica de angiosarcoma cardiaco" ] ] "contieneResumen" => array:2 [ "en" => true "es" => true ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0015" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 3" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr3.jpeg" "Alto" => 671 "Ancho" => 900 "Tamanyo" => 46930 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0035" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET/TC. Axial fusion PET/CT image. Pathological FDG deposit in the right subhilum corresponding to the right pericardial pulmonary venous recess.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "J. Mestres-Marti, E. Llinares-Tello, A. Sabaté-Llobera, L. Gràcia-Sánchez, J. Robles-Barba, C. Gámez-Cenzano" "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "J." "apellidos" => "Mestres-Marti" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "E." "apellidos" => "Llinares-Tello" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "A." "apellidos" => "Sabaté-Llobera" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "L." "apellidos" => "Gràcia-Sánchez" ] 4 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "J." "apellidos" => "Robles-Barba" ] 5 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "C." "apellidos" => "Gámez-Cenzano" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253654X18301069" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2018.08.006" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X18301069?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808918301113?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/22538089/0000003800000003/v1_201905020850/S2253808918301113/v1_201905020850/en/main.assets" ] "en" => array:17 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Interesting images</span>" "titulo" => "Perigastric varices detected in a gastrointestinal bleeding study with <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-labeled red blood cells SPECT/CT" "tieneTextoCompleto" => true "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "186" "paginaFinal" => "187" ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "autoresLista" => "Myoung Hyoun Kim, Soon-Ah Park, Dae-Weung Kim" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Myoung Hyoun" "apellidos" => "Kim" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Soon-Ah" "apellidos" => "Park" ] 2 => array:4 [ "nombre" => "Dae-Weung" "apellidos" => "Kim" "email" => array:1 [ 0 => "akaxan@nate.com" ] "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">*</span>" "identificador" => "cor0005" ] ] ] ] "afiliaciones" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "entidad" => "Department of Nuclear Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine and Institute of Wonkwang Medical Science, Iksan, Republic of Korea" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] ] "correspondencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "cor0005" "etiqueta" => "⁎" "correspondencia" => "Corresponding author." ] ] ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Varices perigástricas detectadas en un estudio de hemorragia digestiva mediante SPECT/TC con hematíes marcados con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc" ] ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Figure 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 1878 "Ancho" => 905 "Tamanyo" => 121742 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">SPECT/CT was performed at 1 hour after injection of <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-RBC. Axial SPECT (A), corresponding CT (B) and fusion (C) images of SPECT/CT demonstrated focal increased activity in the perigastric area (arrows), but not in the stomach.</p>" ] ] ] "textoCompleto" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSections"><p id="par0005" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">A 66-year-old female with a 6-year history of liver cirrhosis (Child-Turcotte-Pugh class C) complained of drowsiness, intermittent hematochezia and melena. She received endoscopic injection sclerotherapy for gastroesophageal varices two years ago. Her hemoglobin level was 7.5<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>g/dL (reference range, 12.0–15.9<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>g/dL) and gastrointestinal bleeding was suspected. An upper gastrointestinal endoscopy showed gastric and duodenal ulcers without active bleeding. On colonoscopy, large amount of bleeding was showed, but exact bleeding focus was not demonstrated. The patient was referred for a gastrointestinal bleeding scintigraphy with <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-labeled red blood cells (<span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-RBC) to identify and localize the gastrointestinal bleeding.</p><p id="par0010" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Serial gastrointestinal bleeding scintigraphy showed <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-RBC activity restricted to the perigastric area (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0005">Fig. 1</a>, arrows). The activity of perigastric area did not show anterograde nor retrograde migration. There was no other evidence of gastrointestinal bleeding until 24<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>hours after injection. Additional SPECT/CT was performed for differential diagnosis at 1 hour after injection of <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-RBC. SPECT/CT demonstrated focal increased activity in the perigastric area, but not in the stomach (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0010">Fig. 2</a>). Subsequent contrast-enhanced abdomen CT showed tortuous and enlarged veins in the perigastric area (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0015">Fig. 3</a>). These veins are the left gastric vein, which is responsible for the portosystemic collateral. The liver was atrophied, showed nodular surface, and was accompanied by small amount of ascites.</p><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0005"></elsevierMultimedia><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0010"></elsevierMultimedia><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0015"></elsevierMultimedia><p id="par0015" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Esophageal and gastric varices result from portal hypertension and increased collateral venous flow in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis. Acute variceal bleeding is one of the most fatal complications of cirrhosis and is responsible for about one-third of cirrhosis-related deaths. Although gastric varices have less frequent bleeding than esophageal varices, once bleeding occurs, they can cause massive bleeding and have higher mortality. Therefore, it is very important to confirm the presence of bleeding in the gastric varices and to identify the bleeding focus.</p><p id="par0020" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Gastrointestinal bleeding scintigraphy performed with <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-RBC or <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-sulfur colloid has been a clinically useful tool since the 1970s. The study is useful to confirm active bleeding and to aid angiographers/surgeons in localization and treatment planning. Recently, SPECT/CT has been applied to further define the location of bleeding, and Dolezal et al. reported that SPECT or SPECT/CT can increase the sensitivity and specificity.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0020"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">1</span></a> Although gastrointestinal bleeding scintigraphy with <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-RBC is useful for localization of the active bleeding focus, multiple false positive findings have been described including abdominal/gluteal hematomas, aortic aneurysms and hemangiomas.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0025"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">2</span></a> Also, mesenteric and ileal varices mimicking an acute gastrointestinal hemorrhage have been reported.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0030"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">3</span></a> Therefore, nuclear medicine physicians should be aware of potential false positives in order to improve diagnostic accuracy.</p><p id="par0025" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">To the best of our knowledge this is the first documented case of <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-RBC SPECT/CT findings in a patient with gastric varices. This case highlights the usefulness of SPECT/CT to differentiate false positive cases in a patient with uncertain findings on the gastrointestinal bleeding scans.</p></span>" "pdfFichero" => "main.pdf" "tienePdf" => true "fechaRecibido" => "2018-06-05" "fechaAceptado" => "2018-07-09" "NotaPie" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "☆" "nota" => "<p class="elsevierStyleNotepara" id="npar0005">Please cite this article as: Kim MH, Park S-A, Kim D-W. Varices perigástricas detectadas en un estudio de hemorragia digestiva mediante SPECT/TC con hematíes marcados con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:186–187.</p>" ] ] "multimedia" => array:3 [ 0 => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figure 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1612 "Ancho" => 1500 "Tamanyo" => 178414 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Gastrointestinal bleeding scintigraphy showed <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-RBC activity restricted to the perigastric area (arrows). On the serial images, the activity of perigastric area neither show anterograde nor retrograde migration. There was no other evidence of gastrointestinal bleeding until 24<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>h after injection.</p>" ] ] 1 => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Figure 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 1878 "Ancho" => 905 "Tamanyo" => 121742 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">SPECT/CT was performed at 1 hour after injection of <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-RBC. Axial SPECT (A), corresponding CT (B) and fusion (C) images of SPECT/CT demonstrated focal increased activity in the perigastric area (arrows), but not in the stomach.</p>" ] ] 2 => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0015" "etiqueta" => "Figure 3" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr3.jpeg" "Alto" => 557 "Ancho" => 1255 "Tamanyo" => 109990 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0015" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Axial (A) and coronal (B) images of subsequent contrast-enhanced abdomen CT showed tortuous and enlarged veins (arrows) in the perigastric area. These veins are the left gastric vein, which is responsible for the portosystemic collateral. The liver was atrophied with nodular surface, and small amount of ascites was detected.</p>" ] ] ] "bibliografia" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "References" "seccion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "bibs0015" "bibliografiaReferencia" => array:3 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0020" "etiqueta" => "1" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Single-photon emission computed tomography enhanced Tc-99m-pertechnetate disodium-labelled red blood cell scintigraphy in the localization of small intestine bleeding: a single-centre twelve-year study" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => "J. Dolezal" 1 => "J. Vizda" 2 => "M. Kopacova" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:5 [ "tituloSerie" => "Digestion" "fecha" => "2011" "volumen" => "84" "paginaInicial" => "207" "paginaFinal" => "211" ] ] ] ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0025" "etiqueta" => "2" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Pitfalls of gastrointestinal bleeding studies with 99mTc-labeled RBCs" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "M.L. Lecklitner" 1 => "J.J. Hughes" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:5 [ "tituloSerie" => "Semin Nucl Med" "fecha" => "1986" "volumen" => "16" "paginaInicial" => "151" "paginaFinal" => "154" ] ] ] ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0030" "etiqueta" => "3" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "False positive GI bleed on Tc-99m RBC scintigraphy due to ileal varices" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "P.N. Chen" 1 => "R.K. Brown" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:5 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Radiol Case Rep" "fecha" => "2012" "volumen" => "6" "paginaInicial" => "23" "paginaFinal" => "28" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] "agradecimientos" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "identificador" => "xack404832" "titulo" => "Acknowledgement" "texto" => "<p id="par0030" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">This study was supported by Wonkwang University in 2018.</p>" "vista" => "all" ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "url" => "/22538089/0000003800000003/v1_201905020850/S2253808918300594/v1_201905020850/en/main.assets" "Apartado" => array:4 [ "identificador" => "47121" "tipo" => "SECCION" "en" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Interesting image" "idiomaDefecto" => true ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" ] "PDF" => "https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/22538089/0000003800000003/v1_201905020850/S2253808918300594/v1_201905020850/en/main.pdf?idApp=UINPBA00004N&text.app=https://www.elsevier.es/" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808918300594?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ]
Consulte los artículos y contenidos publicados en éste medio, además de los e-sumarios de las revistas científicas en el mismo momento de publicación
Esté informado en todo momento gracias a las alertas y novedades
Acceda a promociones exclusivas en suscripciones, lanzamientos y cursos acreditados
The Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (Spanish Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging), was founded in 1982, and is the official journal of the Spanish Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, which has more than 700 members. The Journal, which publishes 6 regular issues per year, has the promotion of research and continuing education in all fields of Nuclear Medicine as its main aim. For this, its principal sections are Originals, Clinical Notes, Images of Interest, and Special Collaboration articles. The works may be submitted in Spanish or English and are subjected to a peer review process. In 2009, it became the leading Spanish journal in the field of Medical Imaging on having an Impact Factor , awarded by the Journal Citation Reports.
Science Citation Index Expander, Medline, IME, Bibliomed, EMBASE/Excerpta Medica, Healthstar, Cancerlit, Toxine, Inside Conferences, Scopus
See moreThe Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2022
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more
Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)

¿Es usted profesional sanitario apto para prescribir o dispensar medicamentos?
Are you a health professional able to prescribe or dispense drugs?
Você é um profissional de saúde habilitado a prescrever ou dispensar medicamentos