Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
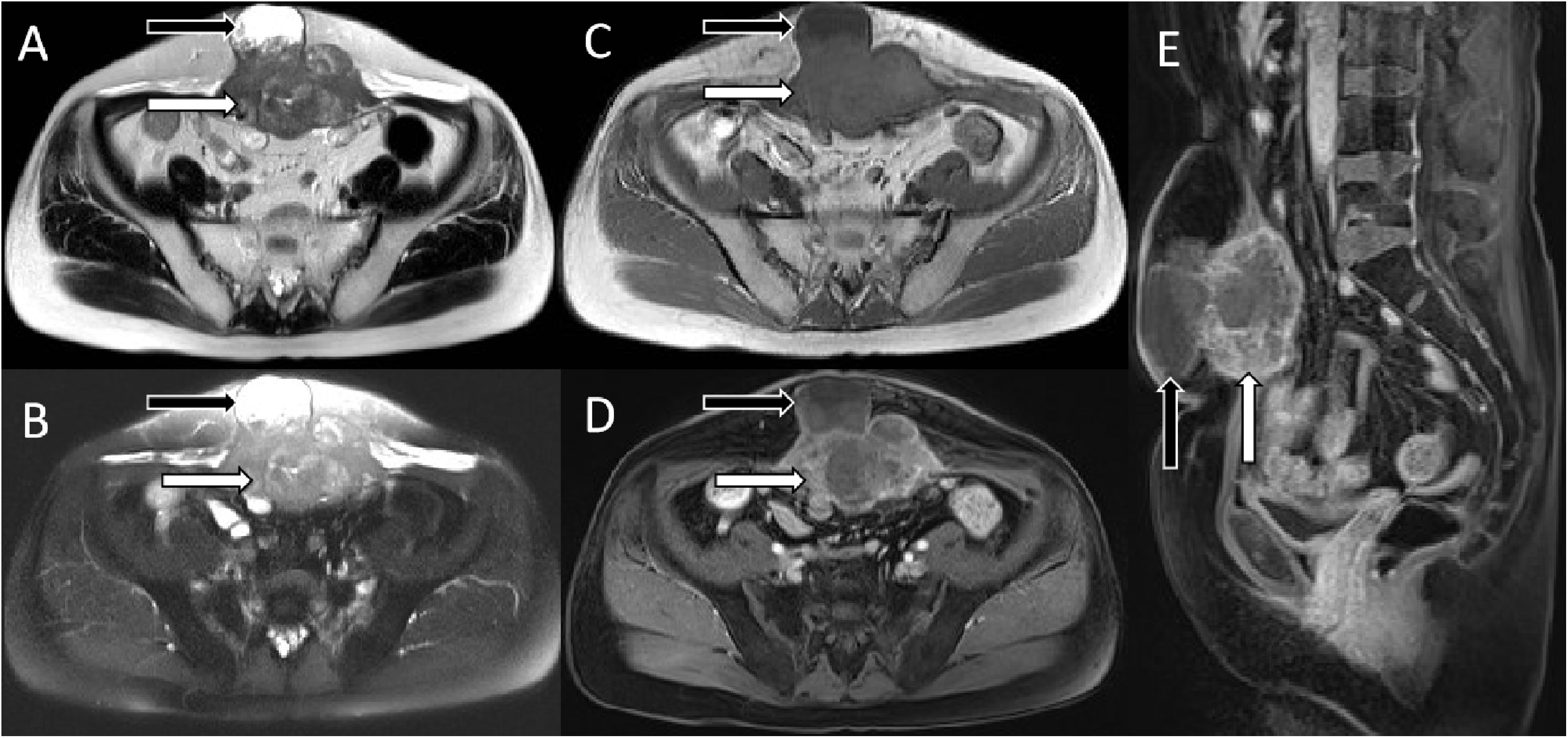
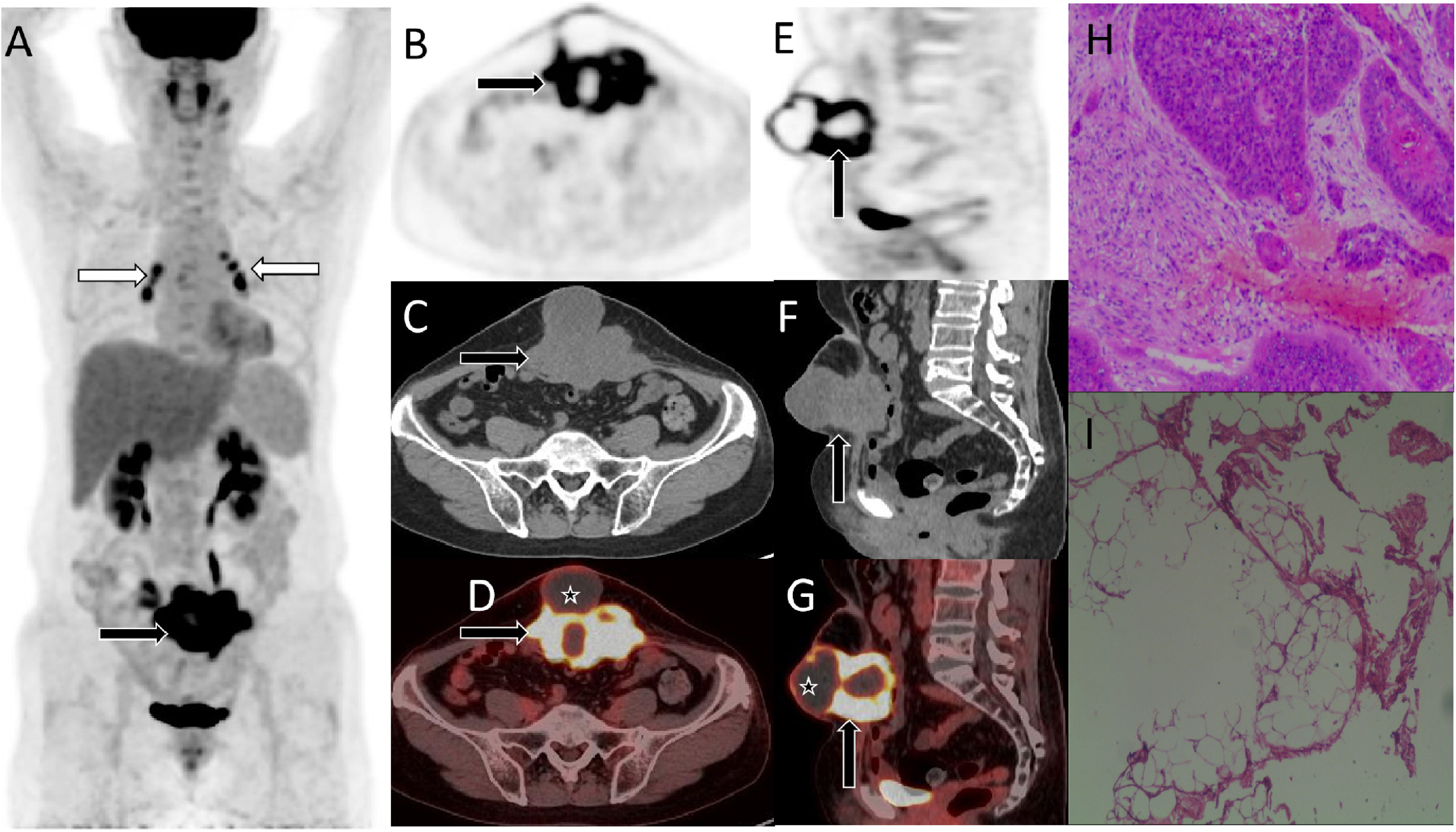
array:23 [ "pii" => "S2253808921001579" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2021.10.007" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2022-11-01" "aid" => "1341" "copyrightAnyo" => "2021" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2022;41:383-4" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:18 [ "pii" => "S2253654X21001748" "issn" => "2253654X" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2021.09.007" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2022-11-01" "aid" => "1341" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2022;41:383-4" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "es" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Imágenes de interés</span>" "titulo" => "Metástasis solitaria en músculo abdominal después de la cirugía de un cáncer cervical imitando un sarcoma mesenquimal en la imagen de RM y<span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET / TC" "tienePdf" => "es" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "es" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "383" "paginaFinal" => "384" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "en" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Solitary abdominal muscle metastasis of cervical cancer after surgery mimicking mesenchymal sarcoma on MRI and<span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET/CTimaging" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figura 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 941 "Ancho" => 2002 "Tamanyo" => 220616 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "es" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Resonancia magnética (RM). Las imágenes potenciadas en secuencia T2 A), en secuencia de supresión grasa B) y las imágenes potenciadas en T1 C) mostraron que el tumor presentaba una señal isomuscular (flechas blancas), y se observó la formación de un absceso con señal larga en T1 y T2 (flechas negras) por delante de la masa tumoral. Después de la inyección de contraste, la masa de partes blandas de la pared abdominal mostró un evidente realce en forma de roseta en las imágenes potenciadas en T1 (D, corte axial, E, corte sagital, flecha blanca), mientras que el absceso no presentó realce evidente (flecha negra). Basándose en los hallazgos anteriores descritos de la RM, los radiólogos consideraron tumores mesenquimales como el rabdomiosarcoma y el fibrosarcoma.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "D. Li, X. Hu" "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "D." "apellidos" => "Li" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "X." "apellidos" => "Hu" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "en" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253808921001579" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2021.10.007" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808921001579?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X21001748?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/2253654X/0000004100000006/v1_202211060631/S2253654X21001748/v1_202211060631/es/main.assets" ] ] "itemSiguiente" => array:18 [ "pii" => "S2253808921001476" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2021.10.001" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2022-11-01" "aid" => "1312" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2022;41:385-6" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Interesting images</span>" "titulo" => "FDG PET/CT imaging of solitary lymphoma on right atrioventricular groove with elevated NSE and CA125" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "385" "paginaFinal" => "386" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Imagen de FDG PET/TC en linfoma solitario del surco atrioventricular derecho con aumento de la NSE y CA125" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:8 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Figure 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 2212 "Ancho" => 2507 "Tamanyo" => 306299 ] ] "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at0010" "detalle" => "Figure " "rol" => "short" ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">MIP image (A) and corresponding axial PET (B), CT (C), fusion image (D) showed a soft tissue mass in the right atrioventricular groove with SUVmax of 21.5. Small amount of pericardial and pleural effusion was seen.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Liu Xiao, Lin Li" "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Liu" "apellidos" => "Xiao" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Lin" "apellidos" => "Li" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253654X21001104" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2021.05.003" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X21001104?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808921001476?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/22538089/0000004100000006/v1_202211060529/S2253808921001476/v1_202211060529/en/main.assets" ] "itemAnterior" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2253808921001580" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2021.10.008" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2022-11-01" "aid" => "1342" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2022;41:380-2" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Interesting images</span>" "titulo" => "Intrathoracic accessory spleen mimicking pleural metastasis in <span class="elsevierStyleSup">68</span>Ga-PSMA PET/CT, confirmed with selective spleen scintigraphy" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "380" "paginaFinal" => "382" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Bazo accesorio intratorácico que imita la metástasis pleural en PET/TC con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">68</span>Ga-PSMA, confirmada con gammagrafía selectiva de bazo" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:8 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figure 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1824 "Ancho" => 2924 "Tamanyo" => 258192 ] ] "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at0005" "detalle" => "Figure " "rol" => "short" ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">68</span>Ga-PSMA PET/CT showed a spheric lesion with increased uptake, located adjacently to the diaphragmatic pleura of left hemi-thorax (arrows in A [maximum intensity projection], B [axial fusion] and C [coronal fusion]).</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Nazim Coskun, Berkay Cagdas, Mustafa Genc, Seyda Turkolmez" "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Nazim" "apellidos" => "Coskun" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Berkay" "apellidos" => "Cagdas" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Mustafa" "apellidos" => "Genc" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Seyda" "apellidos" => "Turkolmez" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253654X2100175X" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2021.09.008" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X2100175X?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808921001580?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/22538089/0000004100000006/v1_202211060529/S2253808921001580/v1_202211060529/en/main.assets" ] "en" => array:14 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Interesting images</span>" "titulo" => "Solitary abdominal muscle metastasis of cervical cancer after surgery mimicking mesenchymal sarcoma on MRI and <span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET/CT imaging" "tieneTextoCompleto" => true "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "383" "paginaFinal" => "384" ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "autoresLista" => "Dandan Li, Xianwen Hu" "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => array:4 [ "nombre" => "Dandan" "apellidos" => "Li" "email" => array:1 [ 0 => "807442003@qq.com" ] "referencia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">*</span>" "identificador" => "cor0005" ] ] ] 1 => array:4 [ "nombre" => "Xianwen" "apellidos" => "Hu" "email" => array:1 [ 0 => "541757091@qq.com" ] "referencia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">b</span>" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] 1 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">*</span>" "identificador" => "cor0005" ] ] ] ] "afiliaciones" => array:2 [ 0 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Department of Obstetrics, Zunyi Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou, People’s Republic of China" "etiqueta" => "a" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Department of Nuclear Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, People’s Republic of China" "etiqueta" => "b" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] "correspondencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "cor0005" "etiqueta" => "⁎" "correspondencia" => "Corresponding authors." ] ] ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Metástasis solitaria en músculo abdominal después de la cirugía de un cáncer cervical imitando un sarcoma mesenquimal en la imagen de RM y <span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET / TC" ] ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:8 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figure 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1572 "Ancho" => 3340 "Tamanyo" => 558660 ] ] "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at0005" "detalle" => "Figure " "rol" => "short" ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">A 53-year-old female patient was diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix in an outside hospital due to “contact vaginal bleeding” 2 years ago. She underwent extensive transabdominal resection of the uterus and bilateral appendages plus lymph node dissection, followed by 28 consecutive radiotherapy and chemotherapy 1 time. A mass on the lower abdominal wall appeared before four months, and it has gradually increased in the past two weeks, and the skin on the abdominal wall has not been ulcerated. No obvious abnormalities were found in tumor markers. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is recommended to determine the nature of the tumor and the extent of invasion. T2-weighted imaging sequence (A), fat suppression sequence (B), and T1-weighted imaging (C) showed that the tumor showed isomuscular signals (white arrows), and the formation of long T1 and long T2 signal abscess (black arrows) was seen in front of the tumor. After the injection of contrast agent, the abdominal wall soft tissue mass showed obvious rosette enhancement on T1-weighted imaging (D, axial position, E, sagittal position, white arrow), and the abscess had no obvious enhancement (black arrow). Based on the above MRI signs, imaging doctors consider mesenchymal tumors such as rhabdomyosarcoma and fibrosarcoma.</p>" ] ] ] "textoCompleto" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSections"><p id="par0005" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">We present the findings of isolated abdominal wall muscle metastases on MRI and <span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET/CT in a patient with cervical cancer after surgery. A woman was diagnosed with cervical cancer at the age of 51 because of irregular bleeding in her vagina, and she subsequently underwent surgery to remove the mass and local radiotherapy. Two years after the operation, the patient came to our hospital complaining that she had felt a hard mass on her abdominal wall 3 months earlier, which had increased significantly for nearly 1 month. Blood routine examination and tumor marker examination of the patient showed no significant abnormalities. She underwent abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess the origin, size, and nature of the lesion, which suggested a malignant mesenchymal tumor of muscular origin in the lower abdominal wall (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0005">Fig. 1</a>). In view of the concern, she underwent <span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET/CT 65 min after intravenous injection of 7.5 mCi <span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG, for evaluating the staging of the tumor and to plan surgery, and revealed that there was no significant FDG uptake in the rest of the body except for abnormally high metabolism in the mass in the muscles of the lower abdominal wall (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0010">Fig. 2</a>).</p><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0005"></elsevierMultimedia><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0010"></elsevierMultimedia><p id="par0010" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Distant metastasis of cervical cancer is more common in lymph nodes, lungs, liver and bone<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0005"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">1</span></a>, and metastases that occur in the muscles of the abdominal wall are extremely rare<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0010"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">2</span></a>. The possible mechanism of abdominal muscle metastasis after cervical cancer surgery is currently accepted by most researchers is related to iatrogenic, that is, implanted metastasis of tumor cells left behind in the abdominal wall incision<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0015"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">3</span></a>. Based on the parameters of PET/CT and the radiomic characteristics of MRI are of great significance to the postoperative management and prognosis of patients with cervical cancer. The current case suggests that solitary abdominal muscle metastasis of cervical cancer after surgery needs to be considered as one of the differential diagnosis of mesenchymal tumors.</p></span>" "pdfFichero" => "main.pdf" "tienePdf" => true "NotaPie" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "☆" "nota" => "<p class="elsevierStyleNotepara" id="npar0005">Please cite this article as: Li D, Hu X. Metástasis solitaria en músculos abdominales de cáncer de cuello uterino que imita el sarcoma mesenquimal en la MRI y la <span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET/CT. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2022;41:382–383.</p>" ] ] "multimedia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:8 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figure 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1572 "Ancho" => 3340 "Tamanyo" => 558660 ] ] "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at0005" "detalle" => "Figure " "rol" => "short" ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">A 53-year-old female patient was diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix in an outside hospital due to “contact vaginal bleeding” 2 years ago. She underwent extensive transabdominal resection of the uterus and bilateral appendages plus lymph node dissection, followed by 28 consecutive radiotherapy and chemotherapy 1 time. A mass on the lower abdominal wall appeared before four months, and it has gradually increased in the past two weeks, and the skin on the abdominal wall has not been ulcerated. No obvious abnormalities were found in tumor markers. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is recommended to determine the nature of the tumor and the extent of invasion. T2-weighted imaging sequence (A), fat suppression sequence (B), and T1-weighted imaging (C) showed that the tumor showed isomuscular signals (white arrows), and the formation of long T1 and long T2 signal abscess (black arrows) was seen in front of the tumor. After the injection of contrast agent, the abdominal wall soft tissue mass showed obvious rosette enhancement on T1-weighted imaging (D, axial position, E, sagittal position, white arrow), and the abscess had no obvious enhancement (black arrow). Based on the above MRI signs, imaging doctors consider mesenchymal tumors such as rhabdomyosarcoma and fibrosarcoma.</p>" ] ] 1 => array:8 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Figure 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 1908 "Ancho" => 3340 "Tamanyo" => 698957 ] ] "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at0010" "detalle" => "Figure " "rol" => "short" ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET/CT was subsequently performed to further evaluate the patient’s general conditions, and MIP image showed that there were no high metabolic foci in other areas except for the mass-like high radioactive uptake in the lower abdominal wall shows a mass with high metabolic uptake (A, black arrow), with a SUVmax of 18.9. Besides, bilateral hiliomediastinal deposits also had hypermetabolic uptake foci, with a SUVmax of 9.3 (white arrows), which were confirmed by biopsy to be inflammatory lymph nodes in the hilar region. The tomographic images present an isometric mass with high metabolic uptake (B, axial PET, C, axial CT, D, axial PET/CT fusion image, E, sagittal PET, F, sagittal CT, G, sagittal PET/CT fusion image, black arrows), there is no obvious radioactive uptake in the abscess anterior (asterisk arrows). The patient finally received surgical treatment, and the pathological results with immunohistochemical analysis confirmed that it was metastatic squamous cell carcinoma (H, hematoxylin-eosin staining, 20 times amplification; I, 400 times amplification).</p>" ] ] ] "bibliografia" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "References" "seccion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "bibs0005" "bibliografiaReferencia" => array:3 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0005" "etiqueta" => "1" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Incisional site metastasis in a patient with cervical carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "C Iavazzo" 1 => "K Madhuri" 2 => "A Tailor" 3 => "S. Butler-Manuel" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:3 [ "tituloSerie" => "Case Rep Obstet Gynecol" "fecha" => "2012" "volumen" => "12" ] ] ] ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0010" "etiqueta" => "2" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix in an abdominal incision 2.5 years after a radical hysterectomy" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => "D.C. Ding" 1 => "T.Y. Chu" 2 => "Y.H. Hsu" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/S1028-4559(08)60140-0" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol" "fecha" => "2008" "volumen" => "47" "paginaInicial" => "348" "paginaFinal" => "349" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18936005" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0015" "etiqueta" => "3" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "The rate of port-site metastases after 2251 laparoscopic procedures in women with underlying malignant disease" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "O. Zivanovic" 1 => "Y. Sonoda" 2 => "J.P. Diaz" 3 => "D.A. Levine" 4 => "C.L. Brown" 5 => "D.S. Chi" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.08.024" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Gynecol Oncol" "fecha" => "2008" "volumen" => "111" "paginaInicial" => "431" "paginaFinal" => "437" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18929404" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "url" => "/22538089/0000004100000006/v1_202211060529/S2253808921001579/v1_202211060529/en/main.assets" "Apartado" => array:4 [ "identificador" => "47121" "tipo" => "SECCION" "en" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Interesting image" "idiomaDefecto" => true ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" ] "PDF" => "https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/22538089/0000004100000006/v1_202211060529/S2253808921001579/v1_202211060529/en/main.pdf?idApp=UINPBA00004N&text.app=https://www.elsevier.es/" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808921001579?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ]
Consulte los artículos y contenidos publicados en éste medio, además de los e-sumarios de las revistas científicas en el mismo momento de publicación
Esté informado en todo momento gracias a las alertas y novedades
Acceda a promociones exclusivas en suscripciones, lanzamientos y cursos acreditados
The Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (Spanish Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging), was founded in 1982, and is the official journal of the Spanish Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, which has more than 700 members. The Journal, which publishes 6 regular issues per year, has the promotion of research and continuing education in all fields of Nuclear Medicine as its main aim. For this, its principal sections are Originals, Clinical Notes, Images of Interest, and Special Collaboration articles. The works may be submitted in Spanish or English and are subjected to a peer review process. In 2009, it became the leading Spanish journal in the field of Medical Imaging on having an Impact Factor , awarded by the Journal Citation Reports.
Science Citation Index Expander, Medline, IME, Bibliomed, EMBASE/Excerpta Medica, Healthstar, Cancerlit, Toxine, Inside Conferences, Scopus
See moreThe Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2022
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more
Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)

¿Es usted profesional sanitario apto para prescribir o dispensar medicamentos?
Are you a health professional able to prescribe or dispense drugs?
Você é um profissional de saúde habilitado a prescrever ou dispensar medicamentos