This note constitutes the first report of the Guadalupe fur seal (Arctocephalus townsendi) for Oaxaca. This subadult male was found stranded on a beach in Cerro Hermoso, in the Lagunas de Chacahua National Park (PNLC). This record is highly relevant because the normal range for this fur seal is farther north, in Guadalupe Island and a recolonization site in the San Benito Archipelago, more than 1,300km from the stranding location. This is the southernmost report for A. townsendi and the first case for Oaxaca, increasing the number of known marine mammal species for this area in the Mexican South Pacific. Because of the current population growth of this otariid, we highlight the necessity of tracking these atypical sightings over time.
Se registra por primera vez la presencia de un lobo fino de Guadalupe (Artocephalus townsendi) en la costa de Oaxaca, mediante el varamiento de un macho subadulto en la comunidad de Cerro Hermoso, dentro del Parque Nacional Lagunas de Chacahua. Se evidencia la importancia de este registro ya que el área de distribución de la especie se encuentra restringida al norte de México en la Isla Guadalupe, con recolonización del Archipiélago San Benito, a más de 1,300km de la zona del varamiento. Esta nota representa el registro más sureño de lobo fino de Guadalupe y el primer caso para Oaxaca, lo que incrementa el número de especies conocidas de mamíferos marinos para el estado. Debido al actual crecimiento de la población de este otárido, resaltamos la necesidad de continuar con el esfuerzo de monitorización y seguir generando conocimiento de esta población, incluyendo el análisis de eventos de dispersión atípica como este.
To date, the California sea lion, Zalophus californianus (Guerrero and Oaxaca); the Galapagos fur seal, Arctocephalus galapagoensis (Guerrero and Chiapas); the Steller sea lion, Eumetopias jubatus (Colima); and the Galapagos sea lion, Zalophus wollebaeki (Chiapas) have been sighted or reported stranded in the Mexican South Pacific (Aurioles-Gamboa, Schramm, & Mesnick, 2004; Ceballos, Pompa, Espinoza, & García, 2010; Gallo-Reynoso & Solórzano-Velasco, 1991). Since there are no pinniped colonies around this region, these events are considered atypical. In the state of Oaxaca, California sea lions have been recorded on Isla Roca Blanca in San Pedro Pochutla (Gallo-Reynoso & Solórzano-Velasco, 1991) and near the La Ventanilla Beach in Santa María Tonameca and Bahía Riscalillo in Santa María Huatulco (Meraz-Hernando, 2003).
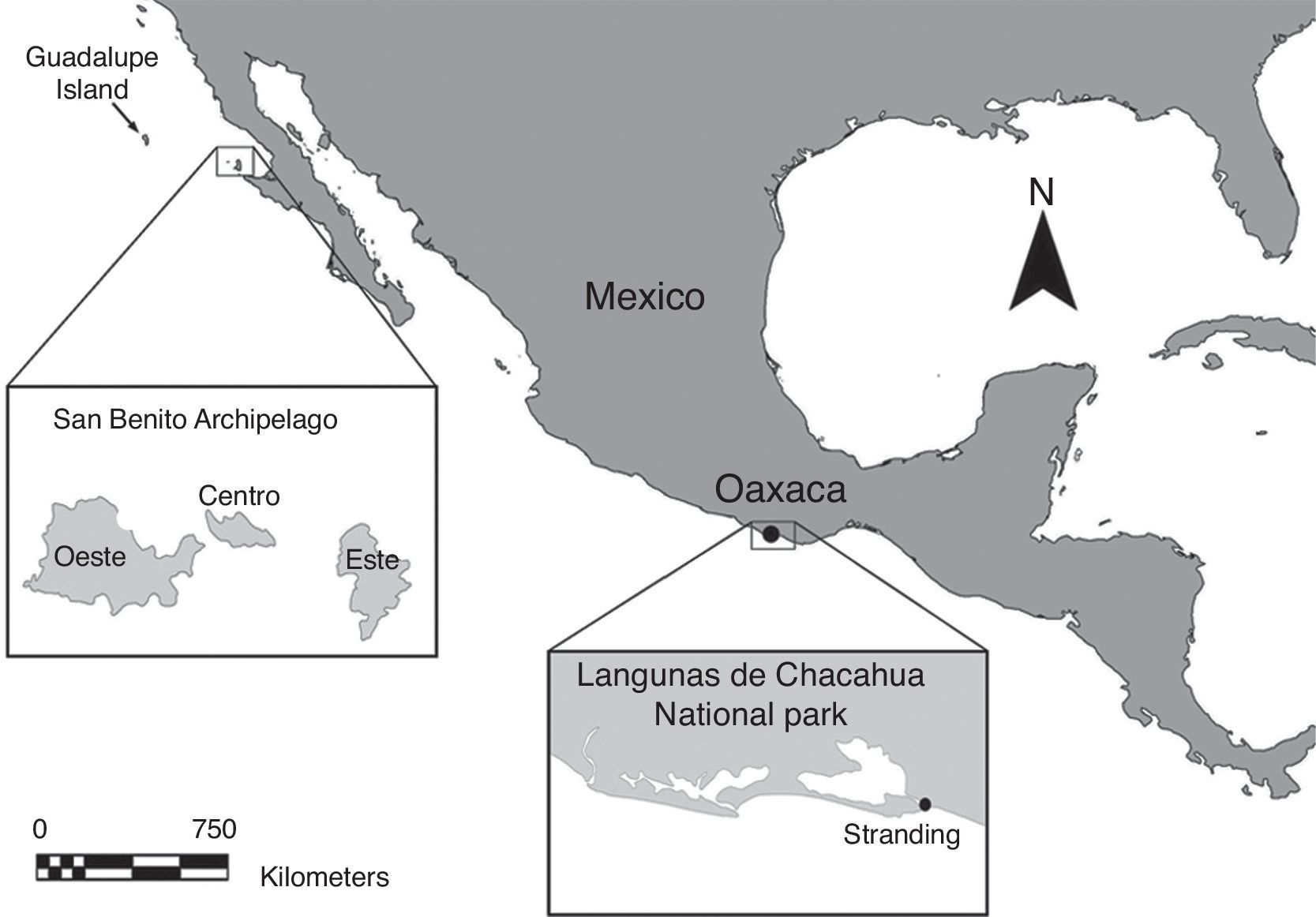
This note constitutes the first report of a Guadalupe fur seal in Oaxaca and the southernmost published to date. This species, Arctocephalus townsendi was reported stranded on October 15, 2012 on a beach in Cerro Hermoso (15°58′N, 97°32′W) in the PNLC, in the Villa de Tututepec de Melchor Ocampo municipality of Oaxaca, Mexico. Local residents notified PNLC staff and inspectors from the Procuraduría Federal de Protección al Ambiente (PROFEPA; Federal Attorney for Environmental Protection) who transported the individual to the Centro Mexicano de la Tortuga (CMT) in Mazunte, Santa María Tonameca. There, the animal's health was assessed and appropriate treatment was administered, which consisted of an intravenous application of restorative serum, antibiotic (enrofloxacina) and ranitidine, as well as a vitamin B complex; the individual was placed under observation. External inspection did not yield evidence of any wounds or contusions. The subadult male was identified to the species level following the identification guide by Reeves, Brent, Clapham, Powell, and Folkens (2002). The individual weighed 70kg and measured 190cm from nose to tail, indicating poor body condition (Fig. 1); adult males are usually 220cm long and typically weigh 220kg (Reeves et al., 2002). The specimen showed no improvement after 12 days of treatment and died on October 24, 2012. The complete skeleton and skin are currently housed in the Colección Osteológica de Mamíferos Marinos, Universidad del Mar (UMAR) under registration numbers COMMUMAR-130013AT1 and 130013AT1P, respectively, and in accordance with PROFEPA permit PFPA/26.3/2C.7.3/12 for the deposition of biological material.
In Mexico, the distribution of the Guadalupe fur seal is limited to Guadalupe Island, although the species is gradually recolonizing the San Benito Archipelago (Fig. 2) (Aurioles-Gamboa, Elorriaga-Verplancken, & Hernández-Camacho, 2010; Esperón-Rodríguez & Gallo-Reynoso, 2012). This note represents the southernmost report of the species published to date, with the specimen having been stranded some 1,300km from the species’ normal range of distribution around the San Benito Archipelago (28°18′N, 115°32′W) (Fig. 2).
Such sightings, as the one reported here, are of particular interest. Specifically, this report of A. townsendi is important because the species has made a significant recovery – from few dozen individuals from the 1950s to ∼17,000 today – with an annual increase of 13.7% (IUCN, 2015). Conditions have changed within the Guadalupe fur seal population, creating the need to monitor established breeding (Guadalupe Island) and recolonization (San Benito) sites as well as atypical sightings such as the one reported here. Rare sightings may become more frequent and these movements, which may be part of the current population growth, should be tracked and analyzed.
The authors thank C.A. Montalvo, E.M. López, M. Harfush and M. Rodríguez of the Centro Mexicano de la Tortuga for facilitating data collection; the Universidad del Mar for financial support for processing the skeleton and skin. We are grateful to the anonymous reviewers whose thoughtful recommendations improved this work. Finally, FREV wishes to thank the Instituto Politécnico Nacional for financial support received through the Programa de Contratación por Excelencia.
Peer Review under the responsibility of Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México.