Obsessive compulsive disorder is associated with affected executive functioning, including memory, cognitive flexibility, and organizational strategies. As it was reported in previous studies, patients with preserved executive functions respond better to pharmacological treatment, while others need to keep trying different pharmacological strategies.
Material and methodsIn this work we used machine learning techniques to predict pharmacological response (OCD patients’ symptomatology reduction) based on executive functioning and clinical variables. Among those variables we used anxiety, depression and obsessive-compulsive symptoms scores by applying State-Trait Anxiety Inventory, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale respectively, while Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test was used to assess organisation skills and non-verbal memory; Digits’ subtests from Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-IV were used to assess short-term memory and working memory; and Raven's Progressive Matrices were applied to assess problem solving and abstract reasoning.
ResultsAs a result of our analyses, we created a reliable algorithm that predicts Y-BOCS score after 12 weeks based on patients’ clinical characteristics (sex at birth, age, pharmacological strategy, depressive and obsessive-compulsive symptoms, years passed since diagnostic and Raven's Progressive Matrices score) and Digits’ scores. A high correlation (0.846) was achieved in predicted and true values.
ConclusionsThe present study proves the viability to predict if a patient would respond or not to a certain pharmacological strategy with high reliability based on sociodemographics, clinical variables and cognitive functions as short-term memory and working memory. These results are promising to develop future prediction models to help clinical decision making.
Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) is a severe, chronic mental disorder that affects up to 2–3% of the population and causes significant global impairment. Despite being typified by two primary symptoms, namely obsessions and compulsions,1 the manifestation of these symptoms varies widely among individual sufferers, demonstrating a heterogeneous expression within the disorder's subtypes.
Recent literature has observed a growing body of evidence indicating altered cognitive functions such as flexibility, short- and long-term memory, inhibitory control, and planning in individuals with OCD.2–6 Furthermore, several neuropsychological impairments characteristic of OCD have been noted in unaffected relatives, particularly pertaining to organizational abilities and working memory.7–10 Notably, certain studies suggest a potential link between executive dysfunctions in OCD and responsiveness to pharmacological interventions such as selective and non-selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRI and SSRI) and/or cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).11–13 These findings release investigations into personalized pharmacological treatments tailored to individual patient characteristics.
Research has identified working memory and fluid intelligence as predictors of treatment response, independent of symptom severity,14 with organizational skills specifically cited as predictive of response to SSRIs, a frontline treatment for OCD.15 First-line therapies exhibit efficacy in only 40% of patients, necessitating alternative pharmacological strategies such as augmentation with atypical antipsychotics for the remaining individuals.16 Augmentation approaches require personalized dosage adjustments to mitigate adverse effects and the selection of optimal pharmacological strategies, identifying potential predictors of treatment response at baseline – ranging from demographic to cognitive factors14 – becomes imperative. While previous studies have hinted at the relationship between various executive functions and response to conventional pharmacological strategies, robust and reliable methodologies must be established before implementing such predictions in clinical practice.
Supervised machine learning, a technique wherein algorithms are trained on labeled datasets comprising input (predictors or features) and output (predicted) data, offers a promising avenue for predicting treatment response in OCD patients. By discerning patterns and relationships within the data, these algorithms learn to map input data to corresponding output data, thereby facilitating predictions on new, unlabeled data.17,18 The application of machine learning techniques holds considerable promise in the realm of health and personalized medicine,19–22 with several uses across diverse psychiatric domains22–24 and specifically within the context of OCD.25–28
Our study aims to assess the reliability of predictive models for treatment response in OCD patients undergoing different pharmacological strategies, using supervised machine learning algorithms. We aim to analyse a combination of sociodemographic, clinical, and neurocognitive data to develop and validate the most robust algorithm for predicting treatment outcomes. Building upon prior work,14 our research aims to employ innovative techniques with potential clinical utility in the analysis of pharmacological treatment response in OCD.
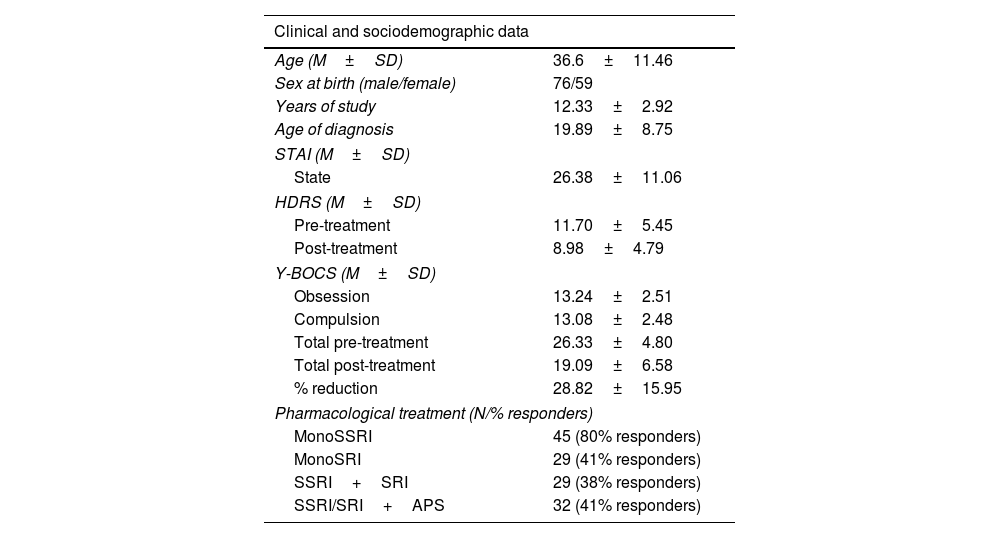
MethodsParticipantsOur study included 135 OCD-diagnosed patients (59 females), aged 18–63 years old. Participants were sequentially recruited from 2006 to 2012 at the OCD Clinical and Research Unit of the Department of Psychiatry, Hospital de Bellvitge (Spain). An initial sample of 150 patients agreed to take part in the study. At the end of the follow-up, 135 provided their pharmacological response. Fifteen participants did not make the final sample due to dropping out of the study (10 participants) and dropping out of the follow-up (5 participants). All patients met the diagnostic criteria for OCD according to the DSM in use at the time of diagnosis (DSM-IV, DSM-IV-TR or DSM-5). The assessments were carried out by qualified clinicians, who see and assess patients for a minimum of 10 years’ experience working in the OCD Clinical and Research Unit at Bellvitge Hospital, to which patients are referred from different regions of the country. There was no missing data while carrying out pre- and post-treatment assessments. Post-treatment assessments were carried out by the same professional who assessed each participant at pre-treatment stage. Exclusion criteria included substance abuse within the previous six months, psychotic disorder and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Bellvitge Hospital and the Galician Research Ethics Committee. Written consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki was formally recorded for each participant. Please refer to Table 1 for a summary of the main characteristics of the sample.
Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of the sample.
| Clinical and sociodemographic data | |
|---|---|
| Age (M±SD) | 36.6±11.46 |
| Sex at birth (male/female) | 76/59 |
| Years of study | 12.33±2.92 |
| Age of diagnosis | 19.89±8.75 |
| STAI (M±SD) | |
| State | 26.38±11.06 |
| HDRS (M±SD) | |
| Pre-treatment | 11.70±5.45 |
| Post-treatment | 8.98±4.79 |
| Y-BOCS (M±SD) | |
| Obsession | 13.24±2.51 |
| Compulsion | 13.08±2.48 |
| Total pre-treatment | 26.33±4.80 |
| Total post-treatment | 19.09±6.58 |
| % reduction | 28.82±15.95 |
| Pharmacological treatment (N/% responders) | |
| MonoSSRI | 45 (80% responders) |
| MonoSRI | 29 (41% responders) |
| SSRI+SRI | 29 (38% responders) |
| SSRI/SRI+APS | 32 (41% responders) |
Abbreviations: HDRS: Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; MonoSSRI: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor monotherapy; MonoSRI: serotonin reuptake inhibitor monotherapy; ROCFT: Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test; SSRI+SRI: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor+serotonin reuptake inhibitor combined therapy; SSRI/SRI+APS: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor/serotonin reuptake inhibitor+antipsychotic combined therapy; STAI: State-Trait Anxiety Inventory; Y-BOCS: Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale.
Experienced clinicians conducted a clinical and neuropsychological assessment of each participant before starting the 12-week sustained pharmacological treatment strategy.
The Anxiety-State Subtest of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI),29 The Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS),30 and the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS)31 were applied to measure anxiety level, OCD severity, and intensity of depressive symptoms, respectively. Both Y-BOCS and HDRS were also applied at baseline and after 12 weeks of sustained pharmacological treatment.
Regarding neuropsychological assessment, the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test (ROCFT)32,33 was used to assess organizational ability, immediate and delayed recall and recognition of non-verbal memory. The ROCFT is based on a complex geometric figure that individuals are asked to copy as accurately as possible. After a delay of 3 and 30min, they are asked to reproduce the figure from memory to assess immediate and delayed recall, respectively. At the end of the evaluation, and as a measure of recognition, subjects are presented with a fixed number (24) of figures, of which only some (12) were part of the original figure copied.34 Organization was assessed by dividing the figure into five segments, according to Savage et al.5 Non-verbal memory was measured using the system of Meyers and Meyers,34 dividing the figure into 18 segments, and scoring it according to the accuracy and placement of each segment.
The forward and backward forms of the Digits subtest of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-IV, WAIS-IV35 were also applied. Digits’ subtests provide an assessment of short-term memory (forward form) and working memory ability (backward form). Raven's Progressive Matrices36 were applied to quantify problem solving and abstract and analytical reasoning.
Pharmacological response assessmentAll patients were under pharmacological treatment when they were referred to our Unit, and 66.6% had undergone CBT prior to the study, except only those taking SSRIs in monotherapy. After clinical and neuropsychological evaluation, pharmacological treatment (SSRI, SRI, SSRI+SRI or SSRI/SRI+antipsychotics) was prescribed to participants for at least 12 weeks of sustained dose. The choice of the current treatment was made according to the recommendations of international guidelines for OCD considering the resistance shown by patients to previous treatments.37
During clinical assessment, all patients completed the Y-BOCS scale to assess their OCD symptoms in a baseline. Patients completed 12 weeks of sustained pharmacological treatment and were re-assessed with the Y-BOCS scale to compare with the baseline scores.
Patients who experienced a reduction of, at least, 35% in the Y-BOCS were considered as responders. Table 1 shows the type of treatment prescribed in the sample, including the number of considered responders and non-responders to the four pharmacological strategies reflected in this study.
Statistical analysesStatistical analyses were performed using the IBM Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS), version 27 for Windows (IBM Inc.). Pearson correlation analyses were performed to determine the correlation between sociodemographic, clinical, and the cognitive functions assessed. Values of p≤0.05 were considered significant.
Algorithm developmentThis study used a collection of 22 supervised machine learning models to predict the treatment response to different pharmacological strategies in OCD patients. The variable Y-BOCS scores after 12 weeks of sustained pharmacological treatment (labelled as “end Y-BOCS”) was predicted. As the output has continuous values, its prediction is a regression problem. Supplementary Material Table 1 lists these models (regressors), that belong to different families of learners such as linear, regularised linear and kernel ridge regression, support vector regression, Gaussian processes, regression trees, gradient descent, nearest neighbours, ensembles and neural networks. The selected models were those with leading performance in the experimental comparison performed by Fernández-Delgado et al.38
The features used for the prediction included sociodemographic, clinical, and neuropsychological variables as reported in Supplementary Material Table 2. The features were grouped into several datasets, and each dataset was used to create predictive models.
Common information dataset
- •
sex at birth: man/woman
- •
age: age of the patient, in years
- •
treatment: SSRI monotherapy, SRI monotherapy, SRI+SSRI, SRI/SSRI+antipsychotic
- •
HDRS: pre-treatment HDRS score
- •
Y-BOCS: pre-treatment Y-BOCS score
- •
years: years passed since diagnostic
- •
mraven: Raven's Progressive Matrices score
Digits test (WAIS-IV) dataset
- •
digitdir: score in forward form
- •
digitind: score in backward form
ROCFT dataset
- •
reycop: copy score
- •
reyrim: immediate recall score
- •
reytard: long-term recall score
- •
totalrec: recognition score
- •
orgcop: organization score
The continuous input variables were standardized (i.e. scaled and translated to have zero mean and standard deviation equal to one) before being used by these models. These models included different combinations of input variables as it follows:
- -
common: the model uses only the variables from the common information above.
- -
common-digits: the model includes variables from common information and digits.
- -
common-ROCFT: only common information and ROCFT datasets.
- -
common-digits-ROCFT: analogous with the first three datasets.
The automatic prediction of end Y-BOCS using supervised machine learning used the above sociodemographic, clinical and neuropsychological variables. Due to the reduced number of patients, this study used a special case of cross-validation, named “two-layer leave-one-patient-out”. There are as many cross-validation trials as available patients (in our case, 135). In each trial, we exclude one patient, and the remaining dataset is used to train the machine learning model for regression and to perform hyperparameter tuning. Specifically, this dataset is divided in two equally-sized sets: the training set, for model training, and the validation set, to evaluate the performance of the trained model for each hyperparameter value (listed in the Supplementary Material Table 1 for each regressor). Both sets include data with output values distributed over the whole output range. Once the model is trained on the training set, it is used to predict the output for the data in the validation set. This process is repeated for each hyperparameter value. The value that achieves the highest prediction performance, i.e. the least average difference between predicted and true labels over the validation set, is selected. The model is trained using both training and validation sets and the selected hyperparameter value. Then, the trained model is used to predict the output for the excluded patient. The process is repeated for all the trials (each excluding a different patient), and the test performance is evaluated by averaging the difference between the true and predicted values over all the patients.
To measure the models’ reliability, we used the root mean square error (RMSE), Pearson correlation coefficient (R), mean absolute error (MAE), and weighted average percentage error (WAPE). They measure in several ways the difference between true and predicted values over the whole dataset, and are defined in Supplementary Equations 1–4.
ResultsClinical resultsAccording to the anxious and depressive assessments, patients showed a mild level of anxious (STAI-state mean=26.38, SD=11.06) and emotional symptomatology (HDRS mean=11.70, SD=5.45). Regarding obsessive-compulsive symptoms, the application of the Y-BOCS reported mean scores of 26.33 (SD=4.80). The mean obsessive-compulsive score of the sample was reduced 28.82% (SD=15.95) after 12 weeks of sustained pharmacological treatment. Final mean scores of the sample on the Y-BOCS were 19.09 (SD=6.58).
The prescription of pharmacological groups in the total sample included in this study was distributed as reported in Table 2, increasing refractoriness order.39
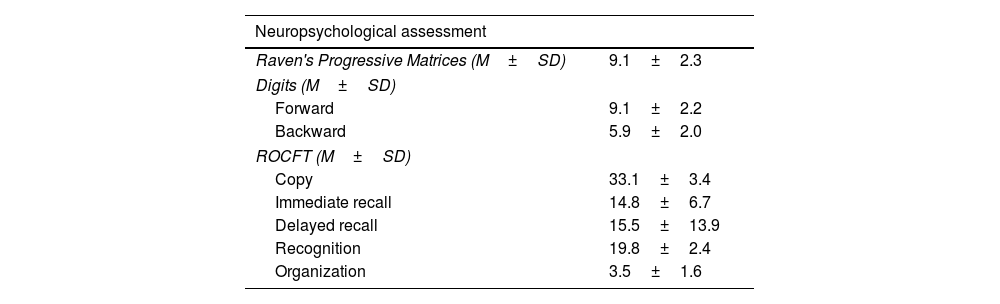
Neuropsychological characteristics of the sample.
| Neuropsychological assessment | |
|---|---|
| Raven's Progressive Matrices (M±SD) | 9.1±2.3 |
| Digits (M±SD) | |
| Forward | 9.1±2.2 |
| Backward | 5.9±2.0 |
| ROCFT (M±SD) | |
| Copy | 33.1±3.4 |
| Immediate recall | 14.8±6.7 |
| Delayed recall | 15.5±13.9 |
| Recognition | 19.8±2.4 |
| Organization | 3.5±1.6 |
Abbreviations: M: mean; ROCFT: Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test; SD: standard deviation.
Twelve weeks of pharmacological treatment that included, at least, an antidepressant, were useful to reduce depressive symptoms on the sample. By mean, HDRS scores after treatment resulted in 8.98 (SD=4.79). After 12 weeks of sustained treatment 72 patients responded to the pharmacological group and dose, while 63 did not achieve a Y-BOCS reduction equal or higher than 35%.
Neuropsychological resultsNeuropsychological results are summarized in Table 2. They were presented and discussed in a previous study conducted by our research group.14
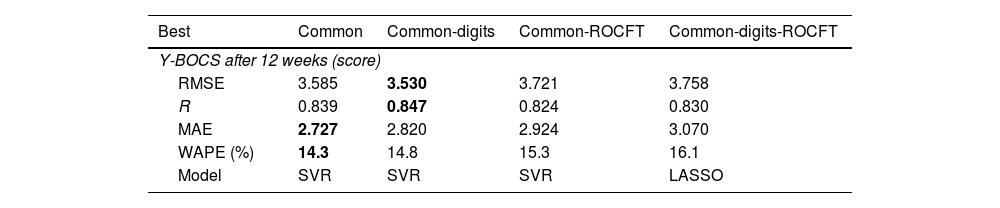
Prediction of end Y-BOCSSupplementary Material Table 3 reports the RMSE values achieved by all the previous regressors and datasets, using the leave-one-patient-out cross-validation methodology, for the prediction of end Y-BOCS. The lowest RMSE (3.530) and highest correlation R (0.847) are achieved by the support vector regression (SVR) model using the common-digits dataset, as presented in bold in Table 3. The RMSE is the squared root of the squared difference between predicted and true values averaged over all the patients. Since the standard deviation of end Y-BOCS is 6.58, that is also the average squared difference between the values and their mean, a RMSE value of 3.530 is about half the standard deviation, so it is a low difference with respect to the true values. Even considering the lowest MAE and WAPE (2.727 and 14.3%, respectively) the best result is also achieved by the SVR but on the common dataset. Therefore, using both criteria the best performance is achieved using the smallest datasets, either common-digits or common, with only the first 9 or 7 features, so that a reduced number of features are required for a reliable prediction.
Best RMSE and model in the prediction of end Y-BOCS for each dataset, alongside with the values of R, MAE and WAPE achieved.
| Best | Common | Common-digits | Common-ROCFT | Common-digits-ROCFT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y-BOCS after 12 weeks (score) | ||||
| RMSE | 3.585 | 3.530 | 3.721 | 3.758 |
| R | 0.839 | 0.847 | 0.824 | 0.830 |
| MAE | 2.727 | 2.820 | 2.924 | 3.070 |
| WAPE (%) | 14.3 | 14.8 | 15.3 | 16.1 |
| Model | SVR | SVR | SVR | LASSO |
Abbreviations: MAE: mean absolute error; R: Pearson correlation coefficient; RMSE: root mean square error; ROCFT: Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test; SVR: support vector regression; WAPE: weighted average percentage error; Y-BOCS: Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale.
The best RMSE, R, MAE and WAPE values are bolded.
Using the SVR regressor on the common-digits dataset, the correlation value (R) is 0.847 (see Table 3), that, according to Colton,40 reflects a “strong relation” between true and predicted end Y-BOCS. Values of R slightly lower (with RMSE slightly higher), but still “strong”, are also achieved by datasets common and common-ROCFT, that include 7 of 9 features of common-digits (see Supplementary Table 2), and by common-digits-ROCFT, that includes these nine features. This means that the information conveyed by the features in common-digits is the one that provides the best performance, and the remaining datasets achieve poorer performance either because they miss the two digits features (common and common-ROCFT) and/or because the additional features (in common-ROCFT and common-digits-ROCFT) reduce the performance.
Table 3 also reports a low MAE (2.820), so the predicted value is expected to be inside a narrow band around the true value. In fact, the mean of the absolute difference between end Y-BOCS and its mean is 5.331, that is nearly twice the MAE. Thus, the deviation of true end Y-BOCS values around its mean is twice the deviation of predicted vs. true values. According to the WAPE, this difference means a 14.8% of the value to be predicted, since end Y-BOCS ranges from 5 to 34.
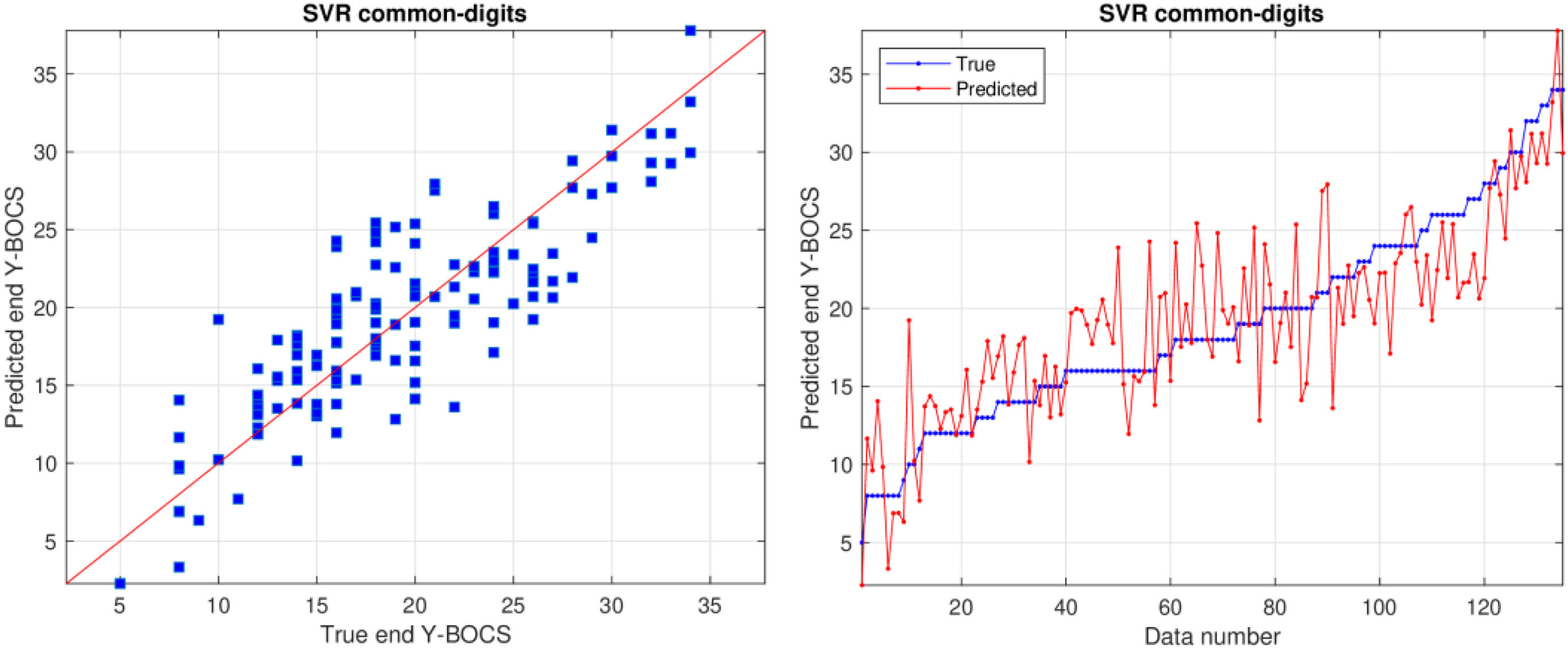
Fig. 1 plots predicted and true values using the SVR model on the common-digits’ dataset. The left panel plots predicted vs. true end Y-BOCS, while the right panel plots both values for each patient, sorted by increasing true values. In these plots, predicted and true values are near, either for low and high values. The right panel also shows clearly that the difference between blue and red line is never large, even in the left and right ends of the plot. This difference is often in a ±5 threshold and, as each Y-BOCS range includes 7 scores, the predicted value will always be near to the true range.
Note that other regressors achieve similar results, as reported in the Supplementary Material Fig. 1. This figure shows the value of RMSE for the 22 regressors and the best dataset (common-digits), sorted by increasing values. The best results are achieved by SVR, GPR, linear regression (LR, ridge, enet and LASSO), followed by ELM, GBM, SGD and KRR. On the contrary, the poorest results are achieved by KNN, the remaining ensembles (lsboost, bagging, adaboost, extratrees and random forest) and neural networks (GRNN and MLP). Supplementary Material Figs. 2 and 3 show how the results perform with respect to regressors and datasets. Supplementary Material Fig. 2 plots the RMSE values over datasets for each regressor, sorted increasingly by the median of the regressor over datasets. Despite they are sorted by increasing median, the sorting is very similar to the one in Supplementary Material Fig. 1. This proves that the behavior of each regressor is similar over datasets, i.e., the best, or the worst, regressors are the same on all datasets. Supplementary Material Fig. 3 plots of RMSE values over regressors for each dataset. The lowest box is achieved by common-digits, with the lowest minimum and median values, providing the most reliable prediction. The common dataset is slightly above it, but the remaining datasets common-ROCFT and common-digits-ROCFT are clearly far above them, proving that they are less related to the Y-BOCS output and provide a less reliable prediction, not helping the automatic prediction.
Supplementary Material Fig. 4 displays, for dataset common-digits, the importance of each feature for the prediction of end Y-BOCS, calculated by the Importance function of the Rminer package (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rminer/index.html) of the R statistical computing language. This function uses one-dimensional sensitivity analysis (1D-SA) and a radial basis function kernel support vector machine classifier (KSVM) to calculate the importance of each feature.41 According to this metric, the most important feature is pre-treatment Y-BOCS, which is expectable since the model predicts the end Y-BOCS. The second most important feature is years and HDRS, with lower importance, followed by mraven. The remaining features (digitdir, treatment, age, sex and digitind) have low importance.
DiscussionTo our knowledge, this is the first study to analyse predictors of clinical response to different pharmacological strategies in OCD using machine learning techniques. Among the different algorithms analysed, the one that includes severity of obsessive-compulsive symptoms and depression, sociodemographic variables and cognitive functions assessed with the Digits’ subtests (forward and backward forms) and Raven's Progressive Matrices demonstrated higher predictive reliability on the response to a specific pharmacological treatment.
Therapeutic guides37 systematically list the pharmacological strategies to be followed. They start with “milder” therapies and pharmacological treatment such as CBT and SSRI, and end with surgical interventions.40 OCD pharmacological treatment includes a wide range of therapeutic strategies, useful in reducing the symptoms associated with this disorder.
More than 50% of patients are resistant to first-line treatments,15 so they need to advance in therapeutic complexity until they achieve an effective treatment for their situation.41 On the other hand, the minimum period to assess clinical response in OCD is 12 weeks under sustained pharmacological doses, so the time to reach an effective treatment may be prolonged in resistant patients.
In our study, the possibility of predicting the clinical situation of each patient before starting treatment has been considered. In the scientific literature, numerous studies demonstrate the viability of supervised machine learning algorithms within the field of psychiatry.19–22 Those algorithms were proved helpful in predicting the prognosis of individual patients based on known information. In literature, it can be also found that these algorithms can provide reliable predictions at an early stage. Each regressor has been trained using different sets of input variables, with the aim of locating the set of information that offers the most reliable prediction.
In regard to predicting Y-BOCS after 12 weeks of treatment, it has been determined that the most reliable algorithm includes sociodemographic and clinical information and cognitive data assessed with the Digit subtest from the Wechsler scale. Clinical information includes details about the treatment type, severity of OCD and depressive symptoms. Recent studies, including Tubío-Fungueiriño et al.14 and D’Alcante et al.,11 have reported that the baseline Y-BOCS score and HDRS can predict pharmacological response. The present study's findings support previous research that employs machine learning techniques to analyse predictors of CBT response, emphasizing the significance of clinical and sociodemographic variables.25
The algorithm we trained predicts automatically the Y-BOCS score at 12 weeks with a Pearson correlation R of 0.847, that is considered in the literature40 as a “strong coincidence” with the exact Y-BOCS score. The mean absolute error (MAE) between exact and predicted Y-BOCS is 2.82 points above or below each patient's score. Since Y-BOCS ranges from 0 to 40, this means that the reliability of the automatic prediction is 92.95%, calculated as 100 (1–2.82/40). We have also found that the variable with the highest predictive significance is the baseline Y-BOCS score, followed by the amount of years passed since the OCD diagnosis, and scores for depressive symptomatology and intelligence as measured by the HDRS and Raven's Matrices scales, respectively. Our results align with previous literature that reported the Y-BOCS baseline score as one of the most important variables in predicting OCD prognosis using supervised machine learning techniques.27,42,43 In the cases that the output is not related to OCD prognosis (i.e. develop suicide behaviors in OCD patients), Y-BOCS scores tend to weight less in the algorithm and sociodemographic variables emerge as important in the prediction.26,44
Although the prediction of Y-BOCS score after 12 weeks of treatment is not perfect, it serves as an early warning of potential outcomes for each patient. The algorithm includes the type of pharmacological treatment as an input variable, enabling clinicians to input the four different therapeutic strategies from this study and compare each patient's predicted outcome after 12 weeks of each strategy. This provides an early indication of the most suitable approach to take, facilitating more personalized care based on each patient's characteristics, as expected for novel strategies.45 The model shortens the process of testing various therapeutic strategies and achieves symptomatology improvements earlier.
Studying information from other disciplines such as neurophysiological,46,47 neuroimaging measures48,49 and genetics50-52 could be useful to train the most reliable algorithm for the prediction of pharmacological treatment response. As some of these suggestions were reported in literature to identify neuroimaging markers for OCD diagnosis,53 prediction of OCD severity54 and a deep understanding of the disorder,55 the development of multidisciplinary investigations need to be carried out to collect diverse information. To improve the accuracy of predictive algorithms, future studies should consider experimenting with a larger number of patients diagnosed with OCD. The patients in our study attend a tertiary hospital where, although patients come from all over the country, it is difficult to generalise to the general obsessive-compulsive population. The algorithms we obtained in our research should be also replicated in OCD related disorders,56 or it should be considered developing new algorithms that explore different variables and information. The ultimate goal will be to provide mental health professionals with tools that can facilitate personalized care for each patient, reducing the amount of trial and error in various therapeutic strategies, and shortening the time it takes to achieve an effective therapeutic response.
This study focused on developing predictive algorithms to determine response to four pharmacological strategies in OCD patients. The response was measured as Y-BOCS score at 12 weeks of treatment as a function of a series of sociodemographic, clinical, and executive functioning variables. We have succeeded in creating a reliable algorithm that predicts the Y-BOCS score at 12 weeks using sociodemographic variables and scores on the Digits subtest of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale. The Y-BOCS predicted by the support vector regressor (SVR) achieves a correlation of 0.847 with the true label, with mean absolute error of 2.820. These preliminary results demonstrate the viability of machine learning to predict treatment response, and they are encouraging to achieve personalized medicine in Psychiatry.
FundingThis work has received financial support from the Consellería de Educación, Universidade e Formación Profesional (accreditation 2019-2022 ED431G-2019/04) and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), which acknowledges the CiTIUS – Centro Singular de Investigación en Tecnoloxías Intelixentes da Universidade de Santiago de Compostela as a Research Center of the Galician University System. SB was supported by Río Hortega grant CM21/00278. This study has been funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III through the grants PI16/00950, PI18/00856, PI19/01184, PI22/00752 and CM21/00278 (co-funded by European Social Fund. ESF investing in your future).
Conflicts of interestNothing to declare.
Data availabilityThe data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
MTF, AC and MFP acknowledge Fundación María José Jove for the support of this research. SB, ER, JMM, PA and CS thank CERCA Programme/Generalitat de Catalunya for institutional support.
The following are the supplementary data to this article:
All supplementary materials referred in this manuscript can be consulted, including: the collection of input variables for supervised machine learning models; the collection of regressors used in this research, with the values of their tunable hyperparameters; predictors included in each dataset; performance metrics; RMSE values achieved by each regressor and dataset; RMSE values for all the regressors and the best dataset common-digits; boxplots of performance values by dataset and regressor; plot of predictor importances for the best dataset.