The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic affected the school-aged population because of the disease itself and due to the measures applied for prevention and control of the infection. The aim of the study was to evaluate the effect of population-based vaccination against COVID-19 on the incidence of infection in school settings.
Material and methodsA retrospective descriptive study of COVID-19 cases and school outbreaks was carried out at the province level. Students, teachers and staff from different educational stages of the schools were included. The outcome measure was the incidence according to educational stage, case profile and clinic during the first of the academic year 2020/2021 versus the same period 2021/2022.
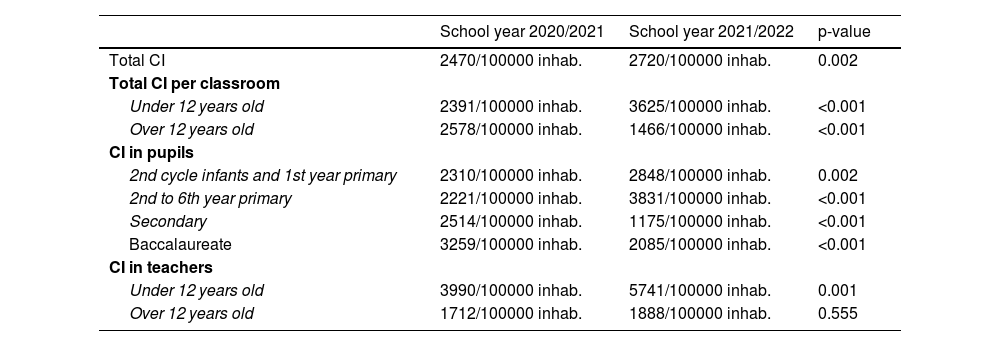
ResultsThe total incidence of SARS-CoV-2 in classrooms was 2470 cases per 100,000 population in the first trimester of the academic year 2020/2021 and 2720 cases per 100,000 population in the same period 2021/2022. The number of reported school outbreaks was 7 times higher in this second period; and the risk of infection in classrooms over 12 years of age (students and teachers) was reduced by 43.1% (vaccinated in high percentage).
ConclusionsThis study shows a reduction in transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection in students of higher educational stages (secondary and high school) during the first of the academic year 2021/2022 (group with high vaccination coverage at the beginning of the period) compared to the previous school year (without vaccination).
La pandemia por SARS-CoV-2 afectó a la población en edad escolar debido a la propia enfermedad y, al mismo tiempo, por las medidas aplicadas de prevención y control de la infección. El objetivo del estudio fue evaluar el efecto de la vacunación poblacional contra COVID-19 en la incidencia de infección en ámbito escolar
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un estudio descriptivo retrospectivo de casos y brotes escolares por COVID-19 a nivel provincial. Se incluyó alumnado, docentes y personal de diferentes etapas educativas de los centros. La medida principal de resultados fue la incidencia acumulada en función de etapa educativa, perfil del caso y clínica durante el primer trimestre del curso 2020/2021 frente al mismo periodo 2021/2022.
ResultadosLa incidencia total de infección por SARS-CoV-2 en las aulas fue de 2.470 casos por cada 100.000 habitantes en el primer trimestre del curso 2020/2021 y de 2.720 casos por cada 100.000 habitantes en el mismo periodo 2021/2022. El número de brotes escolares notificados fue 7 veces mayor en este segundo periodo; y, al mismo tiempo, el riesgo de infección en las aulas de mayores de 12 años (alumnos y docentes) se redujo un 43,1% (vacunados en elevado porcentaje).
ConclusionesEste estudio muestra menor transmisión de infección por SARS-CoV-2 en los alumnos de las etapas educativas superiores (Secundaria y Bachillerato) durante el primer trimestre escolar 2021/2022 (grupo con elevada cobertura vacunal al inicio del período) respecto al curso previo (sin vacunación).
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora