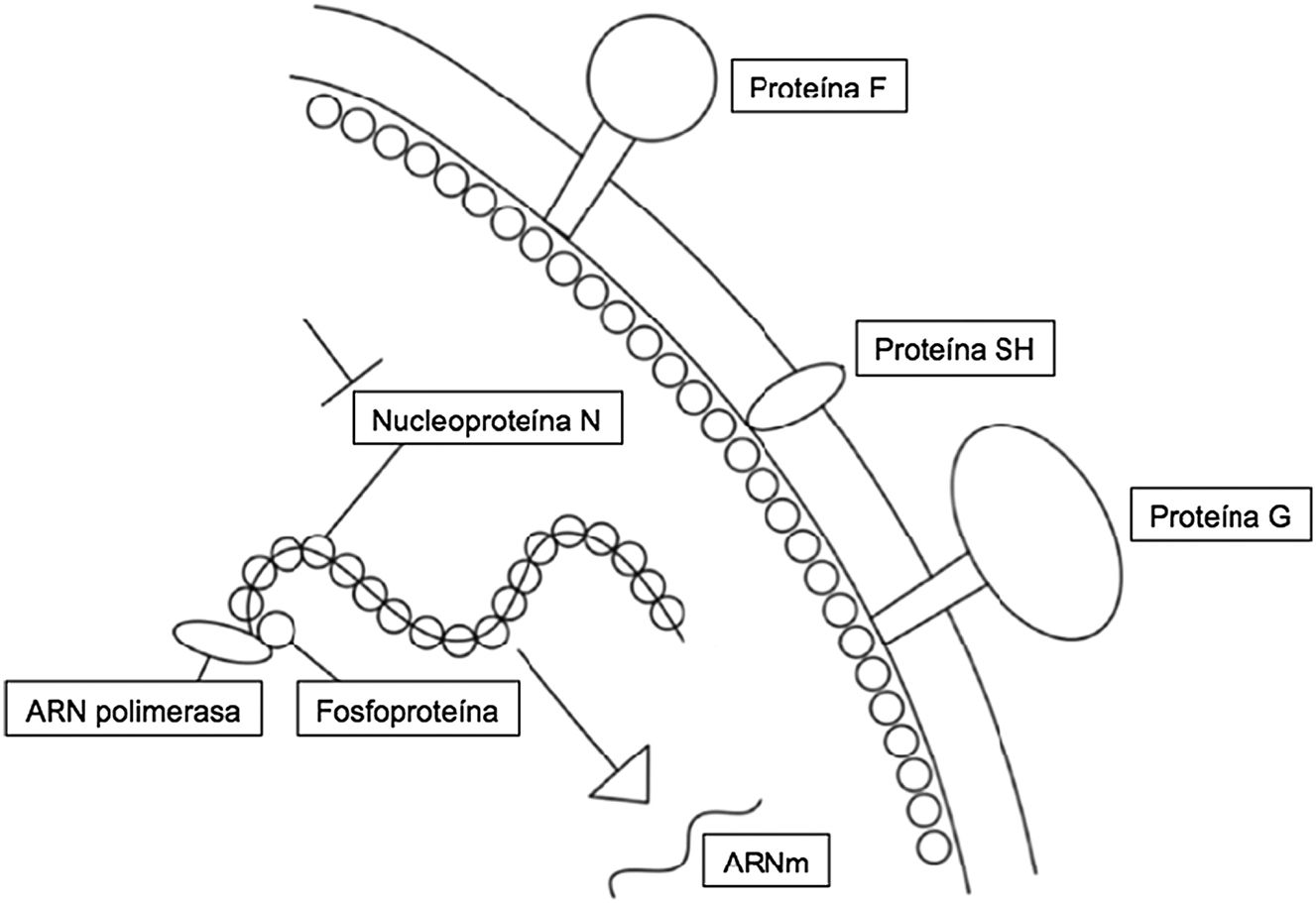
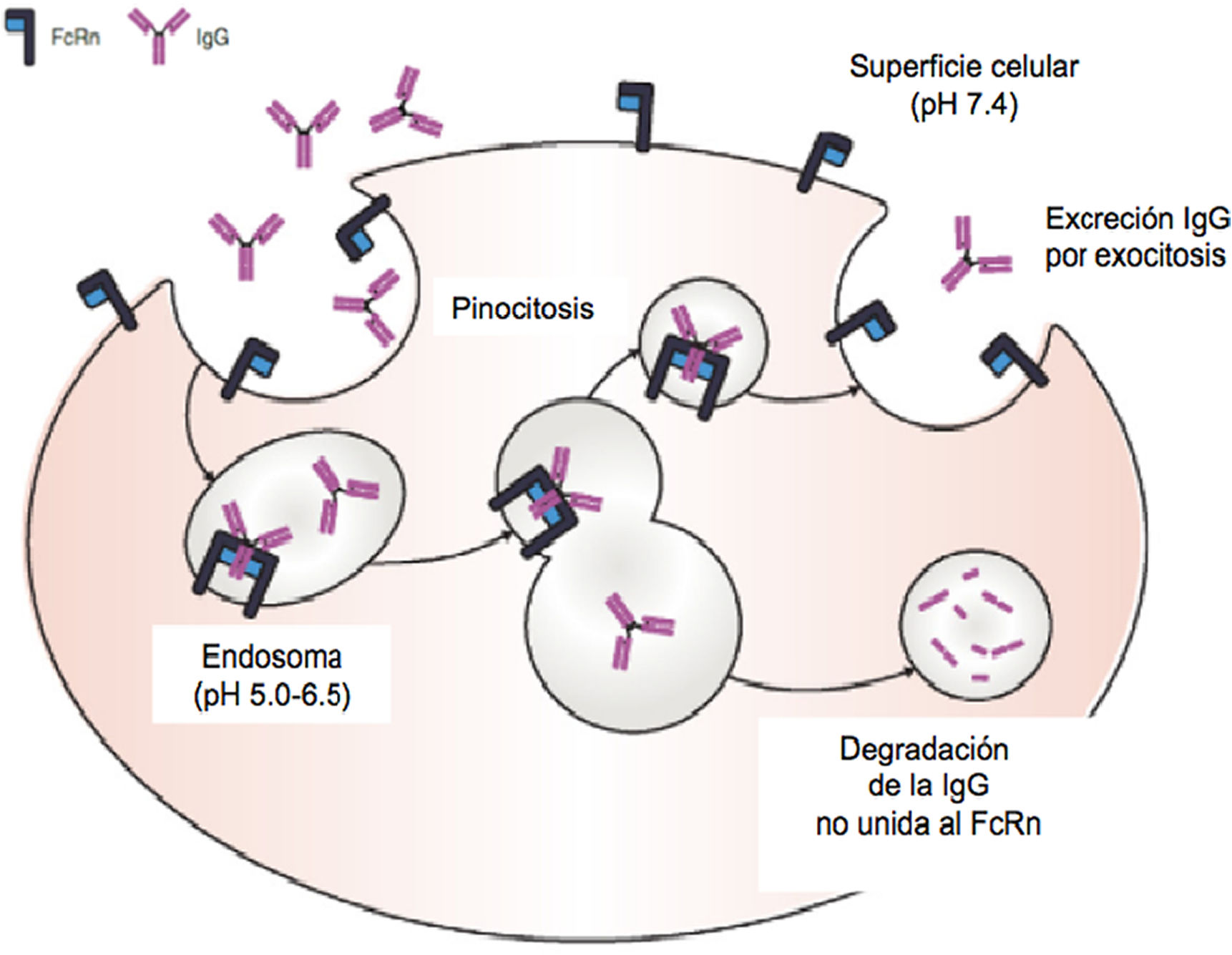
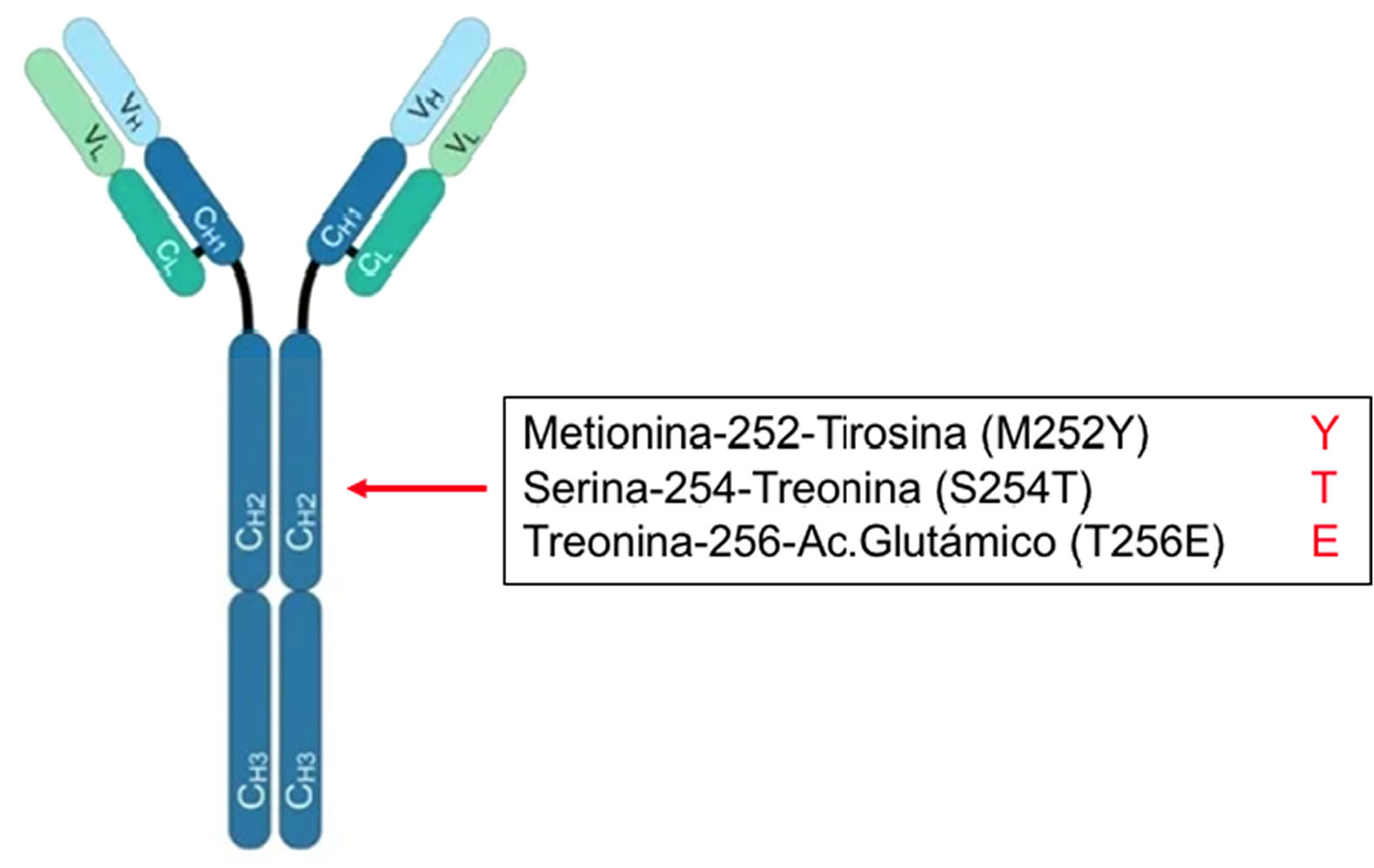
El virus respiratorio sincitial (VRS) es el causante de enfermedades respiratorias agudas epidémicas. Actualmente no existe una vacuna eficaz frente a este virus. Una alternativa para prevenir la enfermedad por VRS es la inmunoprofilaxis pasiva mediante la administración de anticuerpos neutralizantes. En 2002 se aprobó el palivizumab para los niños de riesgo frente al VRS. Sin embargo, el elevado coste y su administración mensual, no permite utilizarlo como profilaxis universal. En 2017 se describió el monoclonal nirsevimab, que presenta una potencia y actividad 50 veces superior al palivizumab con una vida media de como mínimo 5 meses. Los ensayos clínicos han mostrado la eficacia y seguridad de nirsevimab en la prevención tanto de la enfermedad como en los ingresos hospitalarios asociados al VRS de los prematuros y nacidos a término, tanto sanos como con enfermedades cardiopulmonares previas. Con este monoclonal podría realizarse una inmunización universal (vaccine-like strategy).
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes epidemic acute respiratory pathologies especially in young children and the elderly. There is currently no effective vaccine against this virus. An alternative to prevent RSV disease is passive immunoprophylaxis through the administration of neutralizing antibodies. In 2002, palivizumab was approved for children at risk of RSV. However, its high cost and its monthly administration do not allow it to be used as universal prophylaxis. In 2017, the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab, which has a power and activity 50 times higher than palivizumab, was described as having a half-life of at least 5 months. Clinical trials have shown the efficacy and safety of nirsevimab in preventing both the disease and hospital admissions associated with RSV in premature and full-term infants, both healthy and with previous cardiopulmonary pathologies. With this monoclonal antibody, universal immunization is feasible (vaccine-like strategy).