This study aimed to see how measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination affected the increase in SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin levels in individuals who had received the second dose of the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
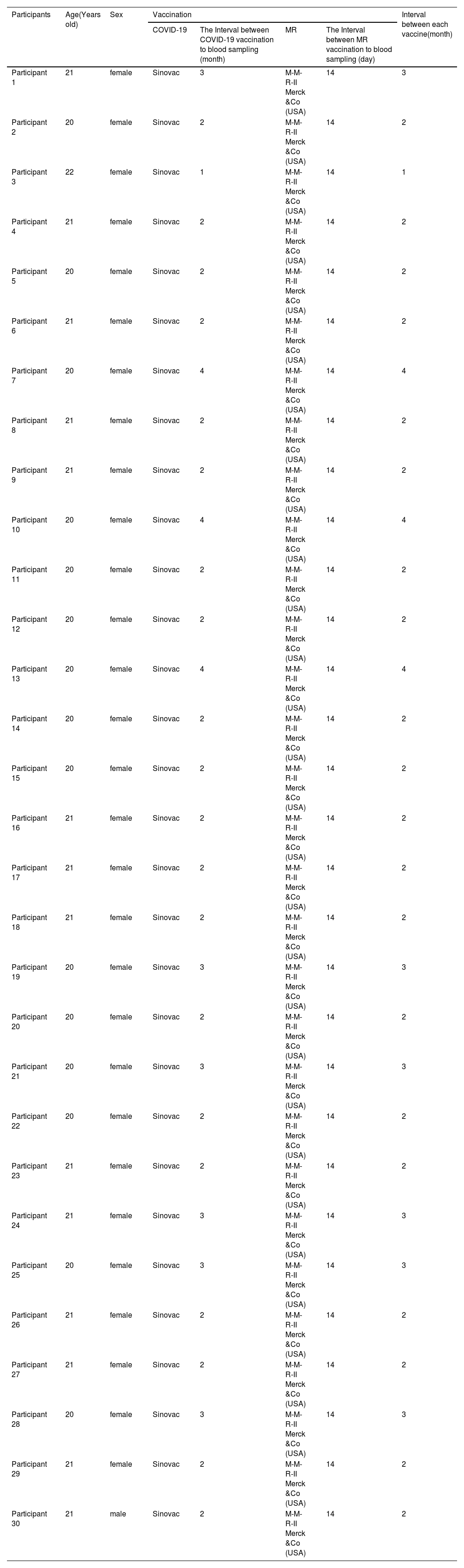
Material and methodThis research is a quasi-experimental type with a pre-post test design. The population studied were adults who had received the second dose of the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, consisting of 30 people.
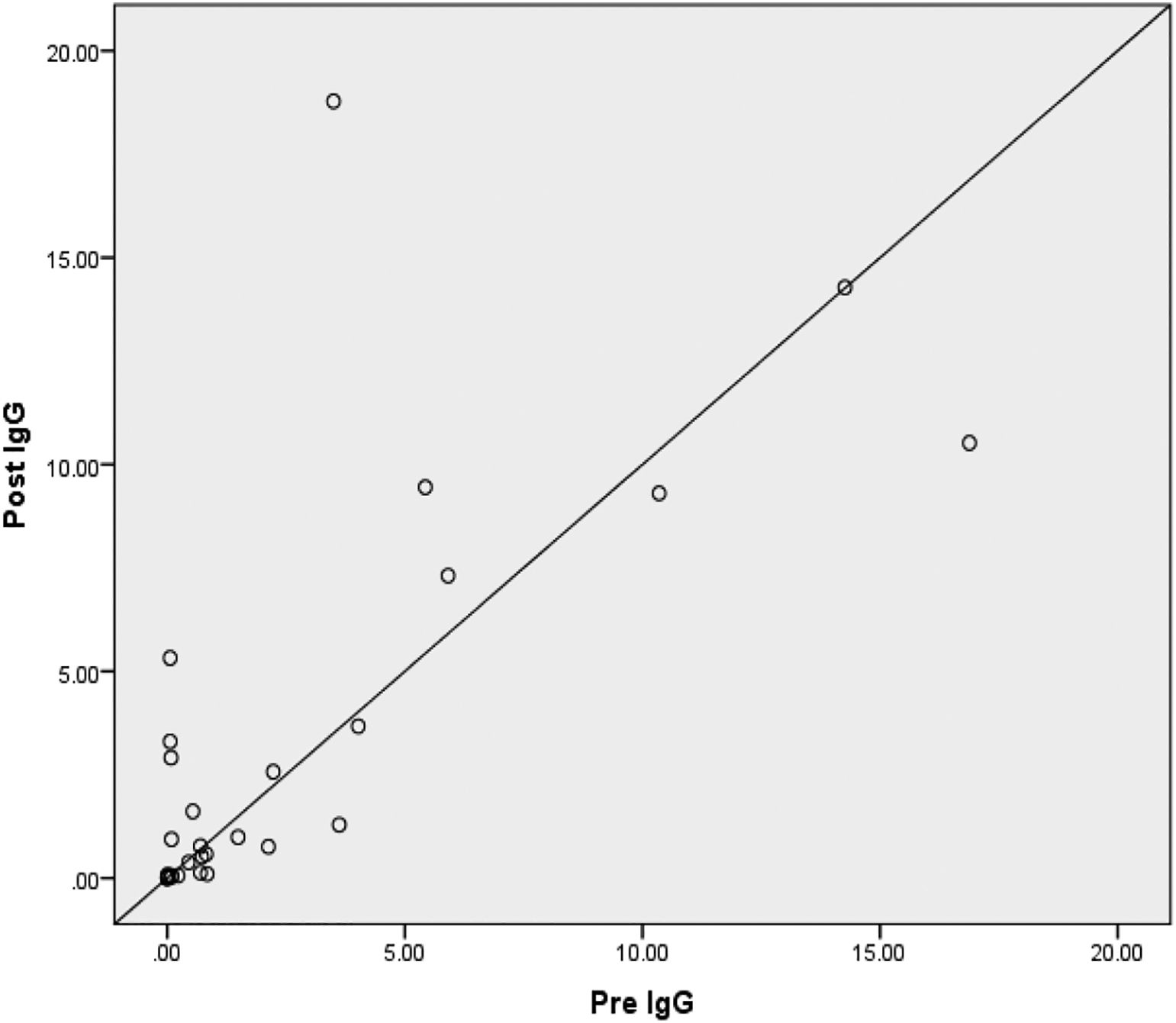
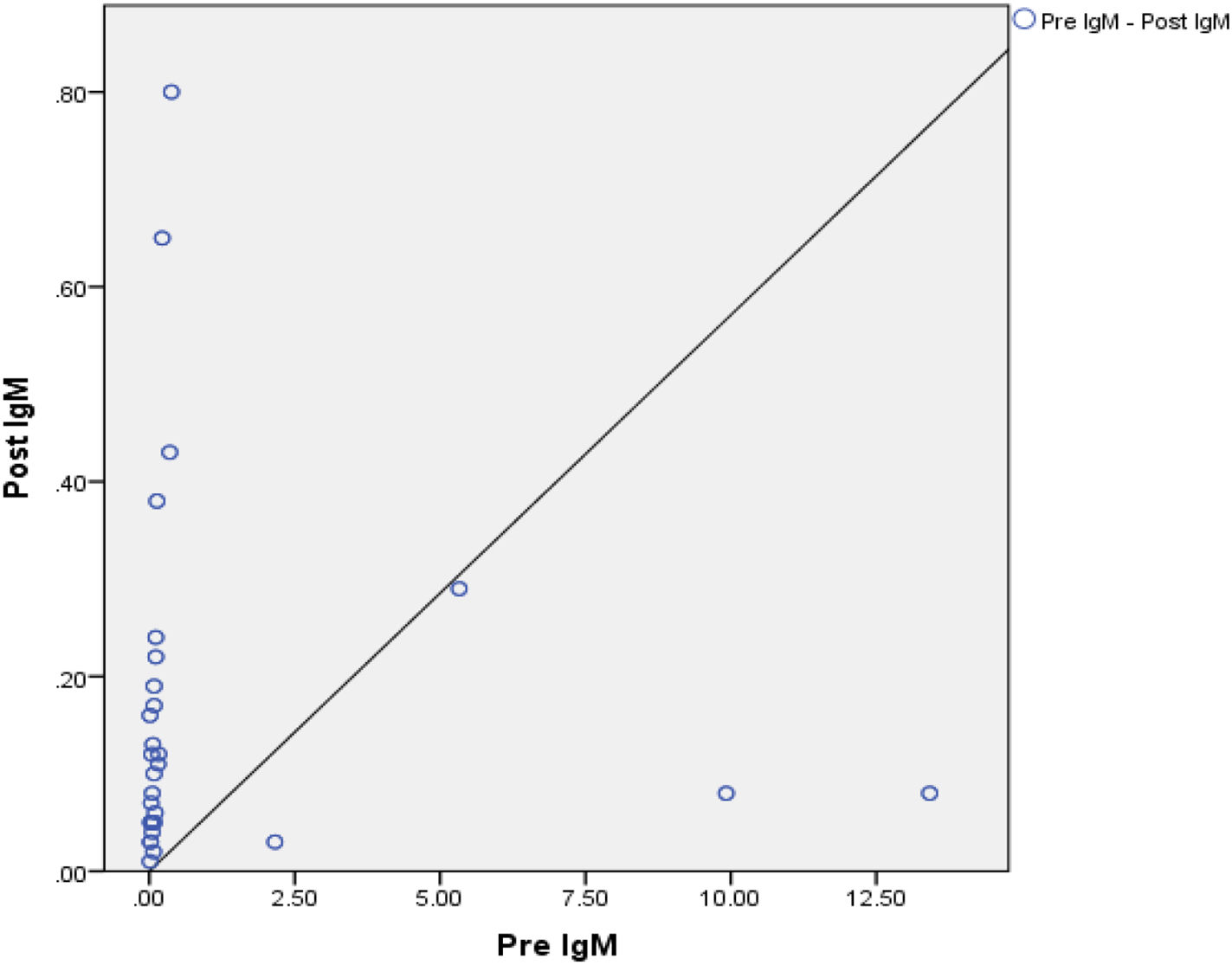
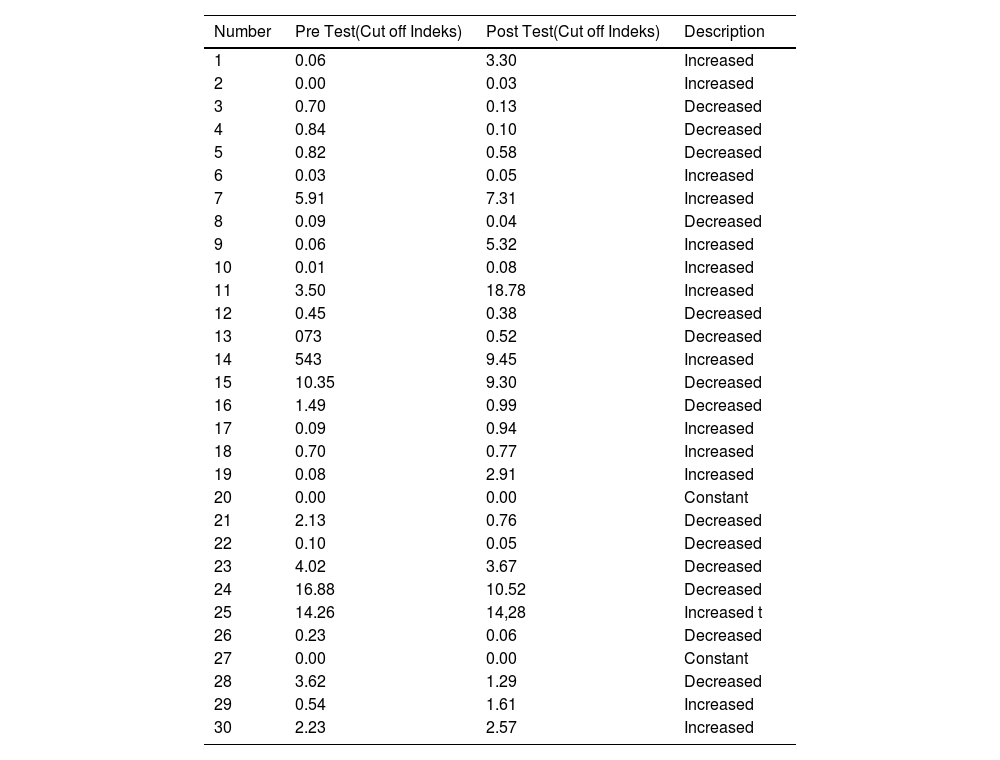
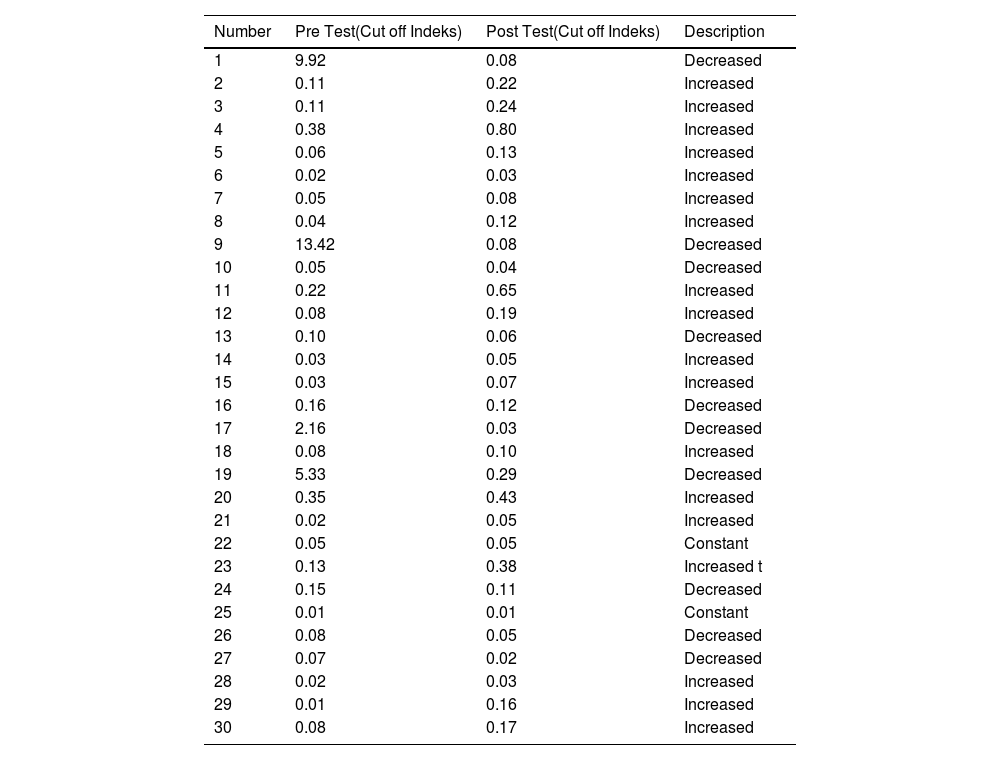
ResultsThe results of this study were that most (60%) research subjects experienced an increase in IgM and some subjects (46.6%) experienced an increase in anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG levels. The administration of the MR vaccination had no effect on increasing anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM levels. This happened because the increase in IgM and IgG levels in the pre and post-tests in most research subjects was relatively low.
ConclusionThe administration of the MR vaccine to adults who had received a second dose of the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine elicited a response with low levels of IgG and IgM SARS-CoV-2.
Este estudio tuvo como objetivo ver cómo la vacunación contra el sarampión, las paperas y la rubéola afectó el aumento de los niveles de inmunoglobulina contra el SARS-CoV-2 en personas que habían recibido la segunda dosis de la vacuna contra el SARS-CoV-2.
Material y MétodoEsta investigación es de tipo cuasi-experimental con un diseño pre-post test. La población estudiada fueron adultos que habían recibido la segunda dosis de la vacuna contra el SARS-CoV-2, conformada por 30 personas.
ResultadosLos resultados de este estudio fueron que la mayoría de los sujetos de investigación (60%) experimentaron un aumento de IgM y algunos sujetos (46,6%) experimentaron un aumento en los niveles de IgG anti-SARS-CoV-2. Según los resultados de la prueba T pareada, el valor de p fue superior a 0,05, lo que indica que no hubo cambios significativos en los niveles de IgG e IgM antes y después de la vacunación con MR. Esto sucedió porque el aumento en los niveles de IgM e IgG en las pruebas previas y posteriores en la mayoría de los sujetos de investigación fue relativamente bajo.
ConclusiónLa administración de la vacuna MR a adultos que habían recibido una segunda dosis de la vacuna SARS-CoV-2 provocó una respuesta con niveles bajos de IgG e IgM SARS-CoV-2.