Prospective study of patients with nasal obstruction (NO) in order to measure therapeutic success by anterior active rhinomanometry (AAR), Nasal Obstruction Symptom Evaluation (NOSE) scale and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and to establish the correlation between these tests.
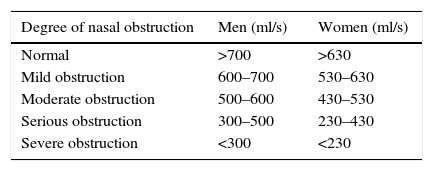
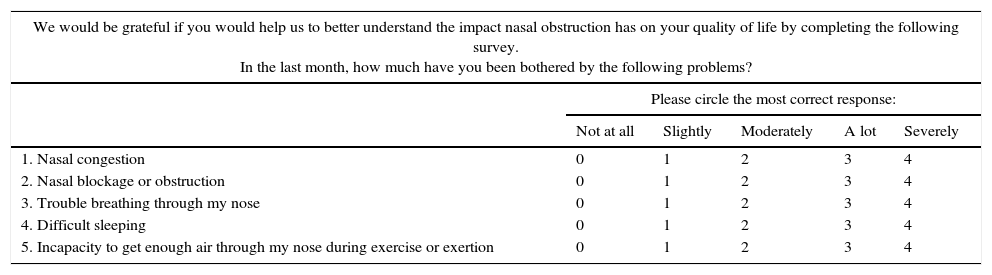
MethodsPatients with NO, on whom we performed an AAR, NOSE and VAS scales at baseline and after medical treatment (topical nasal steroid) or surgery (septoplasty, turbinoplasty or septoplasty and turbinoplasty). The nasal flow obtained by the AAR and the score of both subjective scales (NOSE and VAS) were compared and analysed.
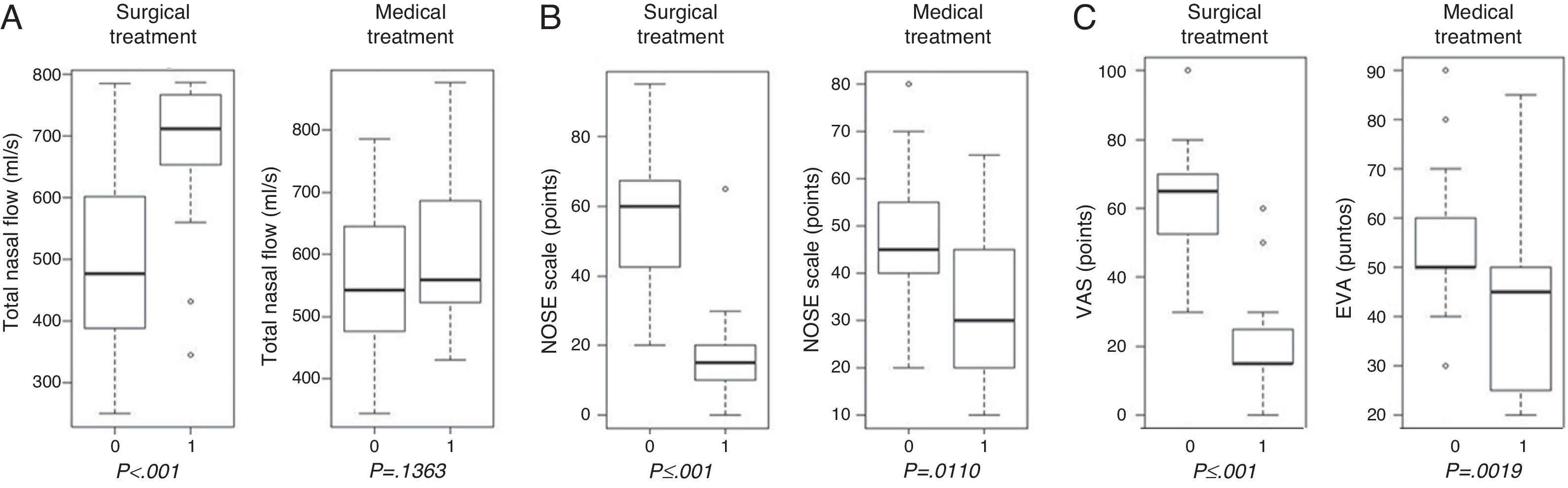
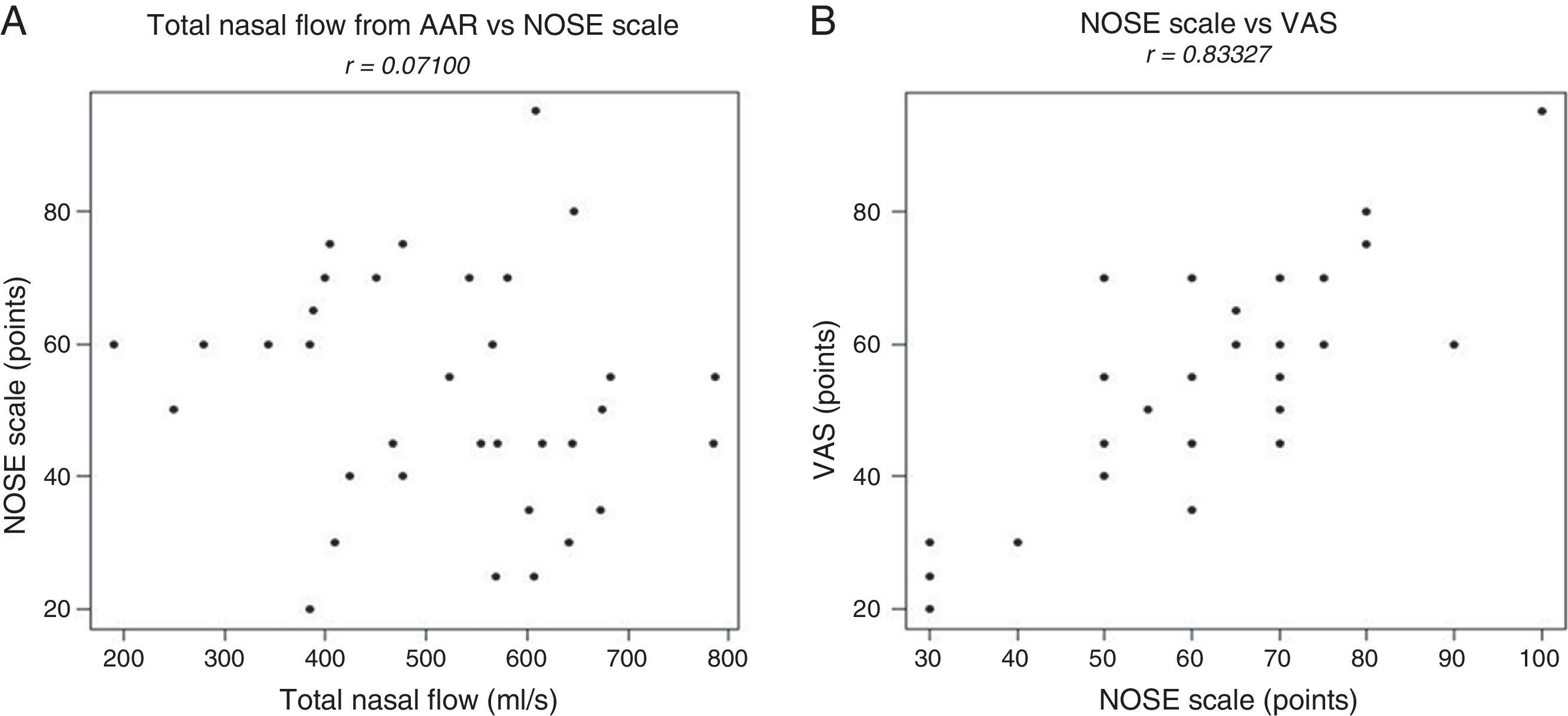
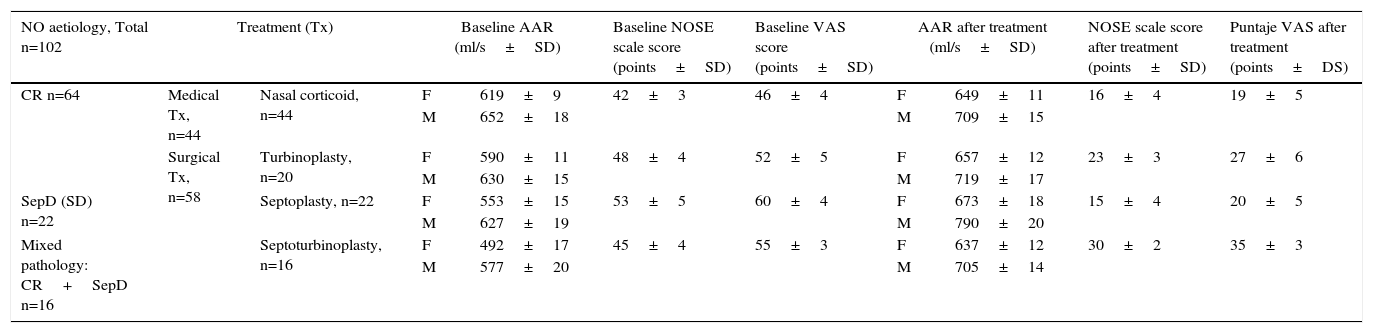
ResultsA total of 102 patients were included in the study. Surgical treatment resulted in statistically significant differences with the AAR and the subjective scales. While in patients with medical treatment there was an increase in the AAR nasal flow but without statistical significance (P=.1363). The correlation between the AAR, the NOSE and VAS scales was measured finding a strong correlation between the NOSE and VAS scales only (r=.83327).
ConclusionsThe patients with NO treated surgically have better results when these are evaluated by AAR or with subjective scales. There is no significant correlation between AAR, NOSE and VAS scales, this is considered to be because the AAR and subjective scales are complementary and measure different aspects of NO. The AAR and subjective scales are useful tools to be used together for the follow up of patients with NO.
Estudio prospectivo de pacientes con obstruccción nasal (ON) a fin de cuantificar el éxito terapéutico mediante una rinomanometría anterior activa (RAA), la escala de Evaluación de los Síntomas de Obstrucción Nasal (NOSE) y la Escala Visual Análoga (EVA), y determinar la correlación que existe entre las pruebas.
MétodosRealizamos RAA y valoración subjetiva mediante las escalas NOSE y EVA a pacientes con ON antes y después del tratamiento médico (corticoides tópicos) o quirúrgico (septoplastia, turbinoplastia o septoturbinoplastia). Comparamos y analizamos los resultados de las puntuaciones obtenidas en ambas escalas subjetivas (NOSE y VAS) con las mediciones en la RAA.
ResultadosUn total de 102 pacientes cumplieron los criterios de selección. Los resultados muestran que la mejoría de la ON, tras tratamiento quirúrgico, es evaluada más positivamente si la herramienta de medición es la RAA. Por el contrario, el tratamiento médico mejora el flujo nasal medido con la RAA, pero sin significación estadística (p=0,1363). Medimos la correlación entre RAA, escalas NOSE y EVA y hallamos solo una correlación positiva entre las escalas NOSE y EVA (r=0,83327).
ConclusionesLos pacientes quirúrgicamente tratados por ON presentan mejores resultados cuando estos se evalúan mediante RAA o con escalas subjetivas. No existe una correlación significativa entre RAA y las escalas NOSE y EVA; esto se considera debido a que la RAA y las escalas subjetivas son complementarias y miden diferentes aspectos de ON. La RAA y las escalas subjetivas son instrumentos útiles para emplearlos de forma conjunta en el seguimiento de pacientes con ON.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora