Squamous cell carcinomas of the oropharynx are aggressive tumours usually diagnosed at advanced stage. Their optimal treatment has not been established. The aim of this study was to compare the oncological and functional outcomes in patients with carcinomas of the oropharynx treated by radiotherapy (with chemotherapy in advanced stages) vs surgery (with radiotherapy in advanced stages).
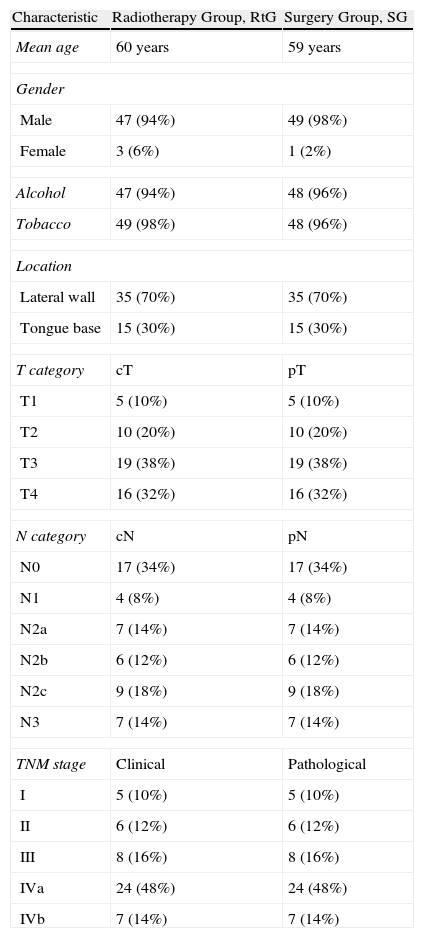
MethodsA retrospective study on 50 patients with squamous cell cancer of the oropharynx treated by radiotherapy (with or without chemotherapy) at our institution between 1998 and 2008 was carried out. The oncological and functional results were compared with patients with same cancer location and stage treated by surgery (with or without radiotherapy). In both groups, the patients were classified as follows: 10% Stage I, 12% Stage II, 16% Stage III, 48% Stage IVa and 14% Stage IVb.
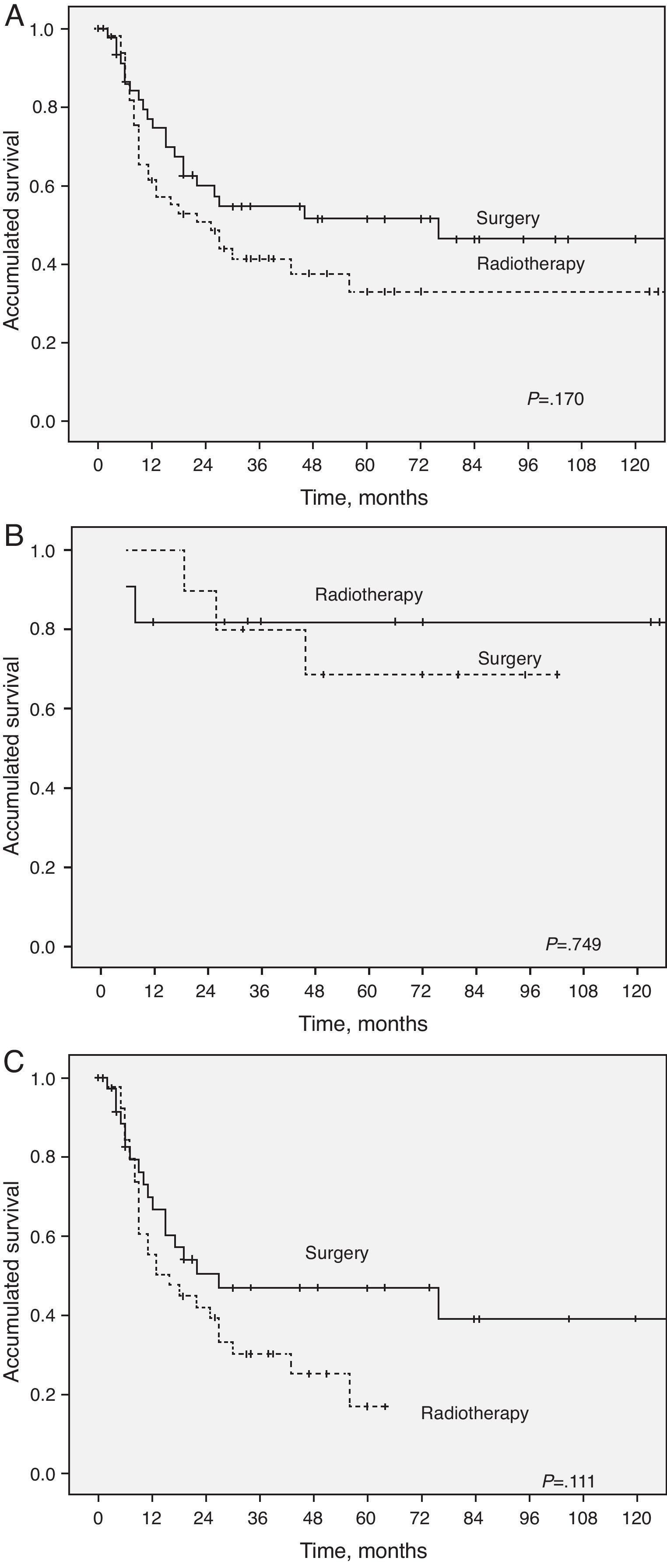
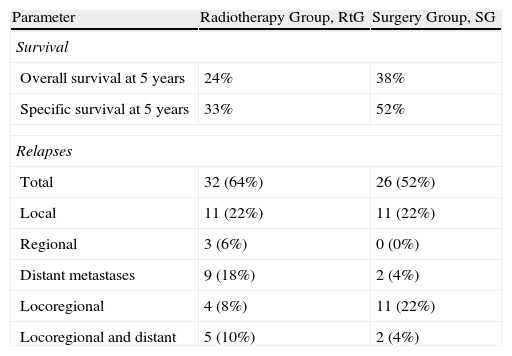
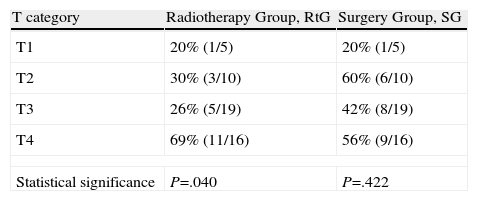
ResultsThe 5-year disease-specific survival was 33% in the radiotherapy group and 52% in the surgical group (P=.17). Five-year disease-specific survival for Stage I and II patients was 82% in the radiotherapy group and 70% in the surgical group. In Stages III and IV disease, 5-year disease-specific survival was higher in the surgical group (47% vs 17%). The functional results were similar; anatomical and functional preservation of the larynx was higher in the radiotherapy group but the successful return to oral food intake was higher in the surgical group.
ConclusionsThe prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx is poor. Oncological results in Stages I and II were similar for radiotherapy and surgical treatments. In advanced stages, the prognosis was better in patients treated by surgery with or without radiotherapy. Functional results were similar in both treatment modalities.
Los carcinomas de orofaringe son neoplasias agresivas habitualmente diagnosticadas en estadios avanzados, siendo su tratamiento óptimo controvertido. El objetivo de este estudio es comparar los resultados oncológicos y funcionales de pacientes tratados con radioterapia (± quimioterapia concomitante) con otros tratados mediante cirugía (± radioterapia complementaria).
MétodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo en 50 pacientes con carcinoma epidermoide de orofaringe tratados con radioterapia (más quimioterapia concomitante en casos avanzados) entre 1998 y 2008, comparándolos con pacientes con el mismo estadio y localización tratados con cirugía (más radioterapia complementaria en casos avanzados). Ambos grupos se clasificaron de la siguiente manera: 10% estadio I, 12% en estadio II, 16% en estadio III, 48% en estadio IVa y 14% en estadio IVb.
ResultadosLa supervivencia específica para la enfermedad a los 5 años fue del 33% para el grupo de radioterapia y del 52% para el grupo de cirugía (p=0,17). En tumores en estadios I y II, esta supervivencia específica fue del 82% en los tratados con radioterapia y del 70% en los tratados con cirugía. En estadios III y IV la supervivencia era mayor en los pacientes tratados con cirugía (47 vs 17%). Los resultados funcionales fueron similares en ambos grupos, presentando mayor preservación anatómica y funcional de la laringe el grupo de radioterapia, mientras que el grupo quirúrgico obtuvo mejores resultados para la alimentación oral.
ConclusionesEl pronóstico de los pacientes con carcinomas epidermoide de orofaringe es pobre. Los resultados oncológicos del tratamiento con radioterapia y cirugía son similares para los estadios I y II. En estadios III y IV la supervivencia es mayor en los pacientes tratados mediante cirugía. Los resultados funcionales son también similares en ambos grupos.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora