The fungus ball is the most frequent type of fungal rhino-sinusitis. The objective of this study is to analyse the clinical and surgical features of our patients.
MethodsRetrospective analysis of 35 patients with fungus ball treated in our centre between 2006 and 2014.
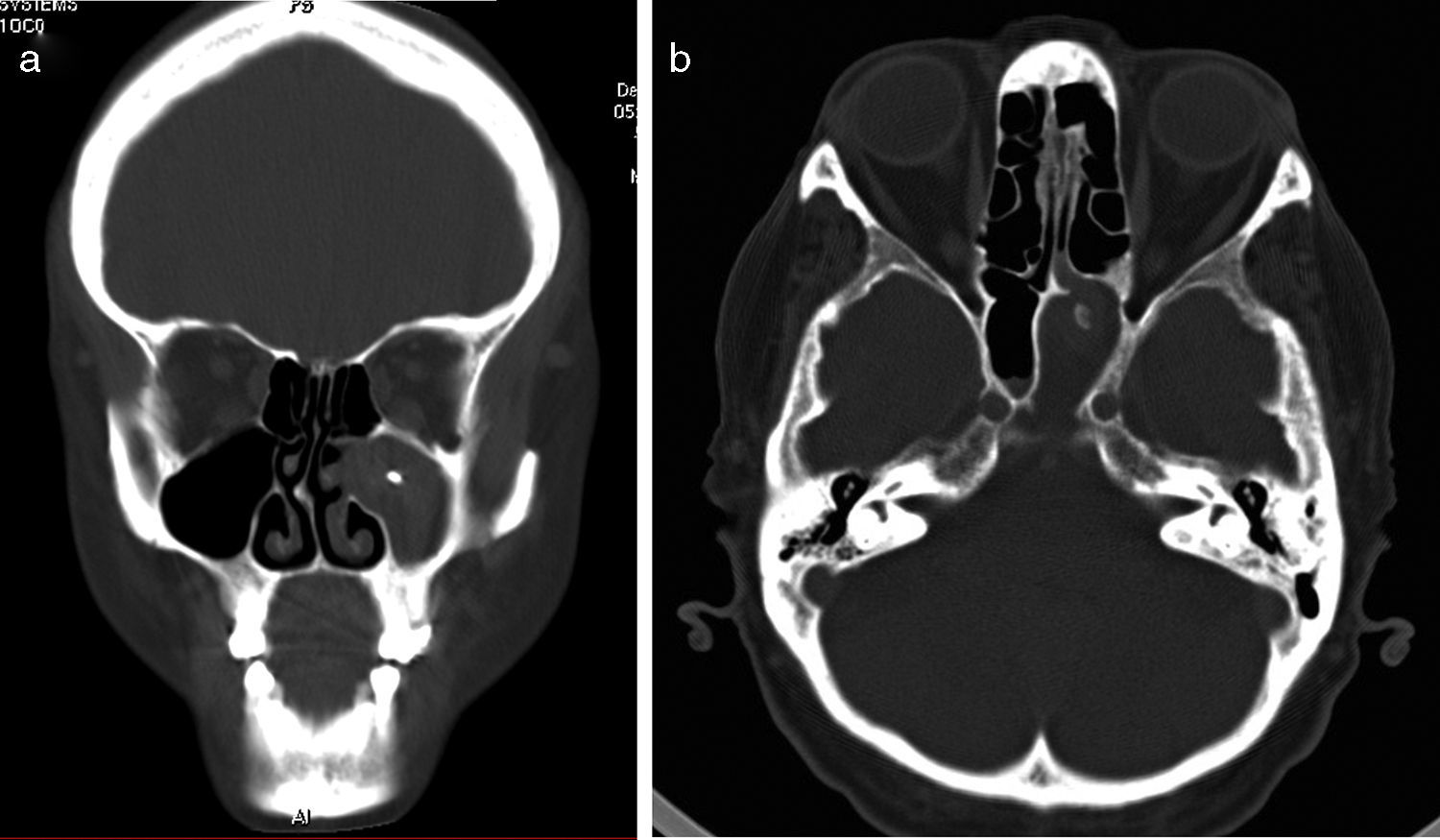
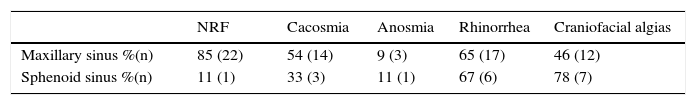
ResultsMean age was 55 years old. 49% were men and 51% women. 75% involved the maxillary sinus, whereas 25% involved the sphenoid. 69% of our patients showed microcalcifications in the CT study. All the patients were surgically treated, with no cases of recurrence.
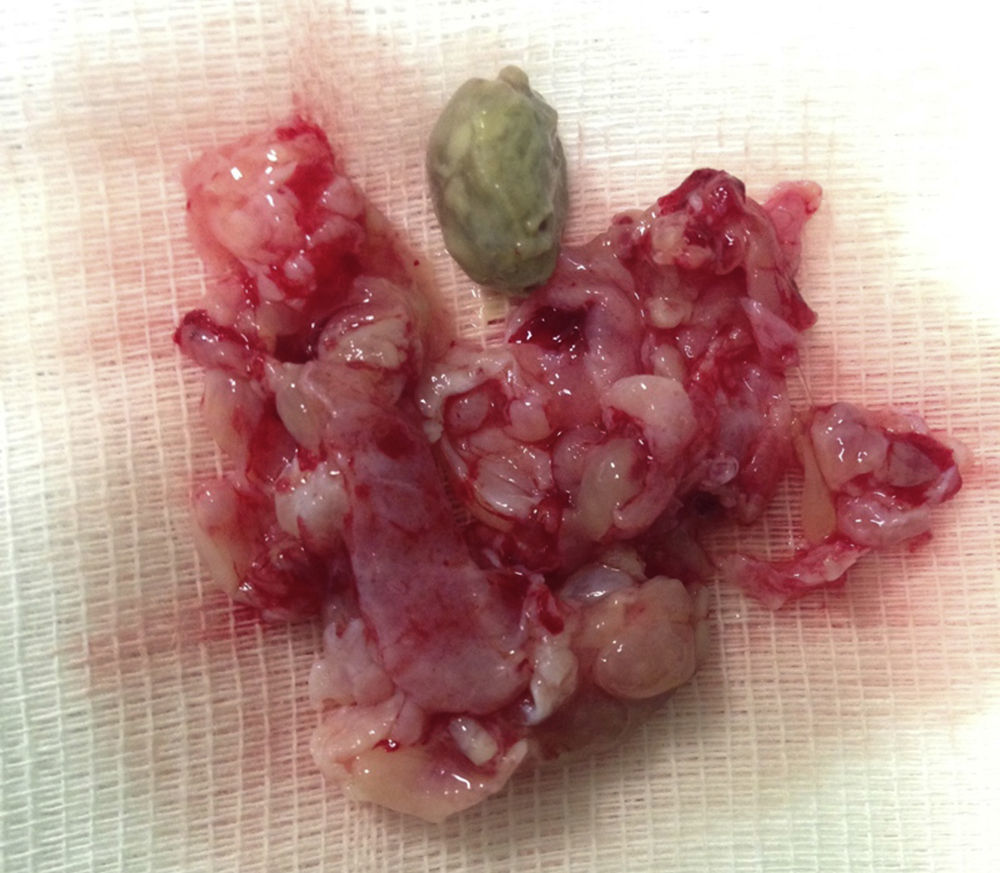
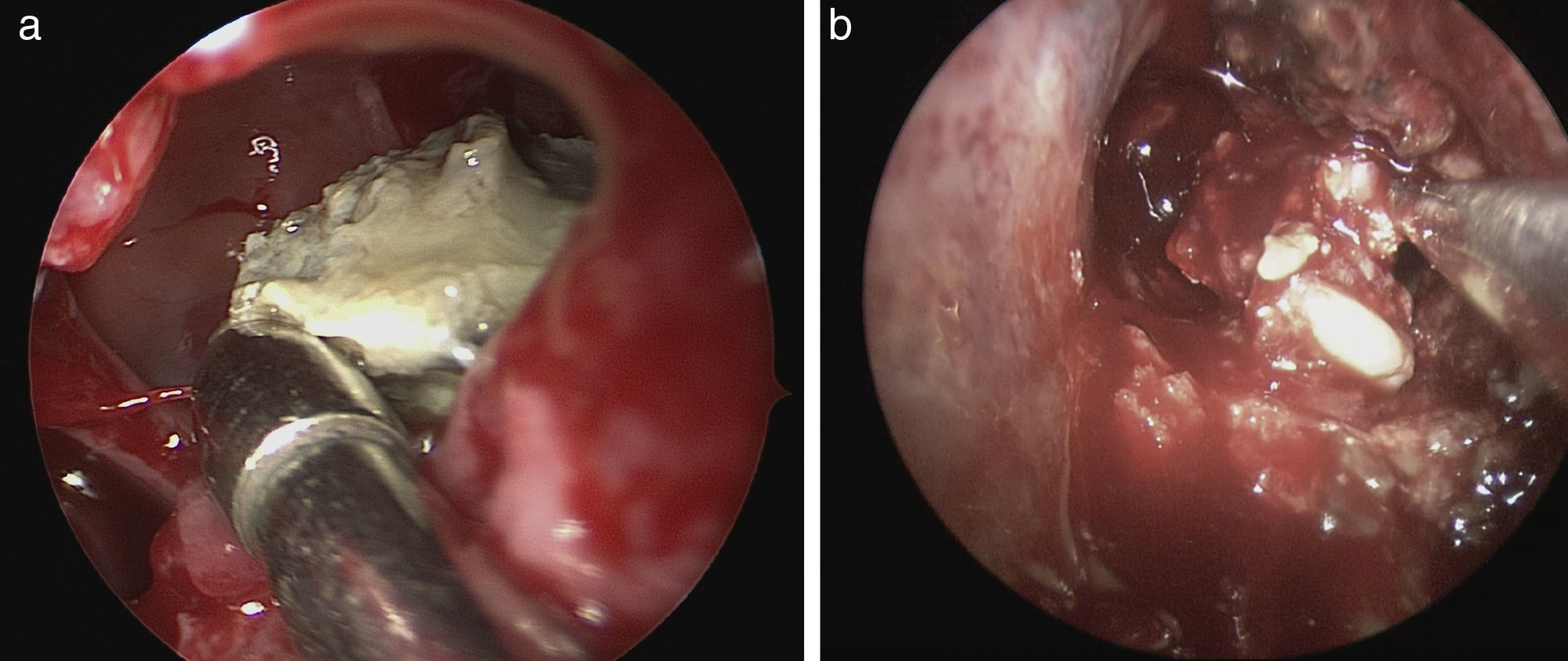
ConclusionsClinical manifestations of fungus ball are non-specific, therefore endoscopy and image study are mandatory. The definitive diagnosis is made by histopathological study of the lesion. Endoscopic sinus surgery is the treatment of choice, with opening of the diseased sinus and complete removal of the fungus ball. The frequency of complications is very low. No oral or topical antimycotic treatments are necessary.
La bola fúngica es la forma más frecuente de rinosinusitis fúngica. El objetivo de nuestro estudio es analizar las características clínicas y los resultados de la cirugía en nuestra serie de pacientes.
MétodosSe analizaron retrospectivamente 35 pacientes con bola fúngica tratados en nuestro centro entre 2006 y 2014.
ResultadosLa edad media fue de 55 años. El 49% de los pacientes fueron varones y el 51% mujeres. El 75% se localizaron en el seno maxilar y el 25% restante en el seno esfenoidal. La clínica más frecuente fue obstrucción nasal, rinorrea y algias craneofaciales. El 69% de pacientes mostró microcalcificaciones intrasinusales en la tomografía computerizada. Todos los pacientes fueron intervenidos quirúrgicamente, sin registrarse recidivas.
ConclusionesLas manifestaciones clínicas de la bola fúngica son muy inespecíficas, por lo que el diagnóstico de sospecha se hace mediante endoscopia y estudio de imagen. El estudio histopatológico confirma el diagnóstico. La cirugía endoscópica nasosinusal es la base del tratamiento de la bola fúngica, limitándose a la apertura del seno (o senos) afecto, y exéresis completa de la lesión. La tasa de complicaciones postoperatorias es muy baja, y no es necesario tratamiento antifúngico oral o tópico concomitante.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora