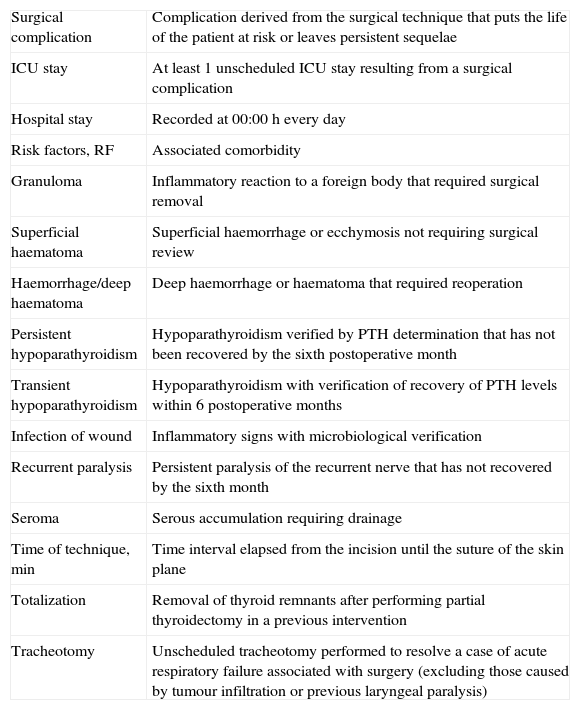
There have been significant technological advances for hemostasis in thyroid surgery, that allow more precise and safer vascular sealing than the traditional bond associated with mono- or bipolar electrocoagulation.
ObjectiveTo compare the complications in total thyroidectomy using traditional techniques (ligation and electrocoagulation, including LigaSure) compared to the exclusive use of the Ultracision Harmonic scalpel, performing dissection, cutting and hemostasis simultaneously.
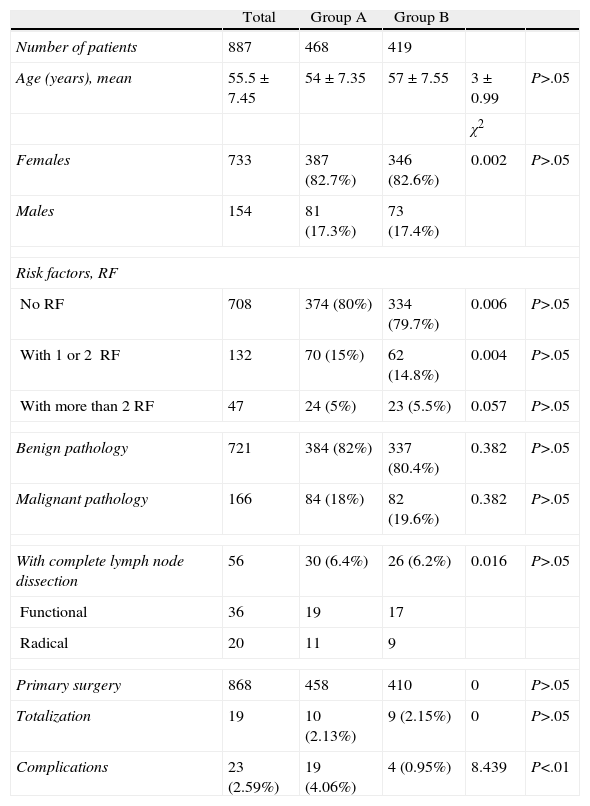
MethodsRetrospective descriptive non-randomised comparative study with 887 patients who underwent total thyroidectomy by the same surgeon. They were distributed into Group A (traditional techniques in 468 patients, January 1997 to September 2006) and Group B (Harmonic Ultracision in 419 patients, October 2006 to May 2010).
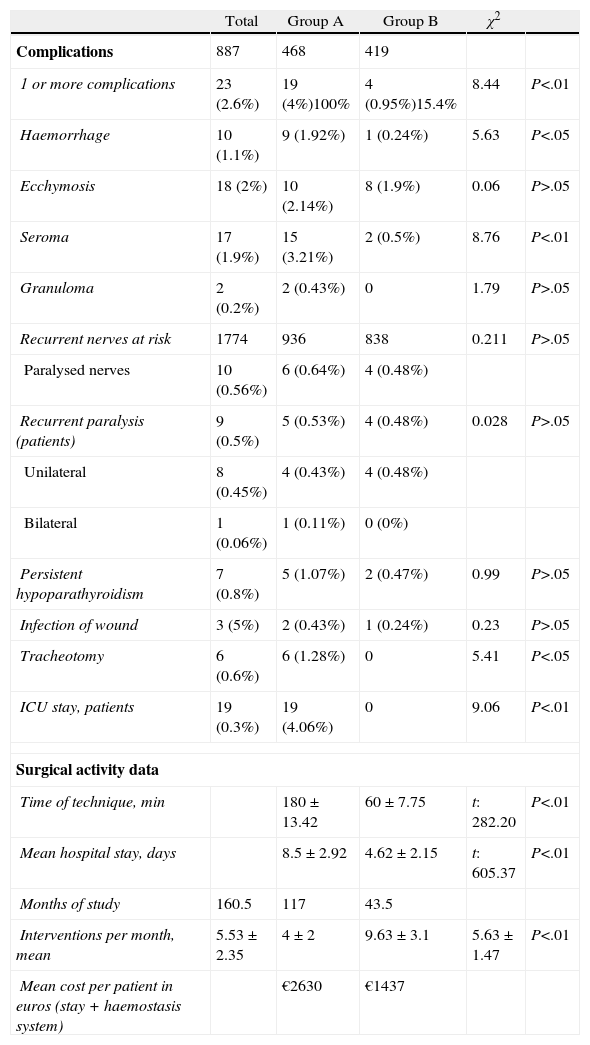
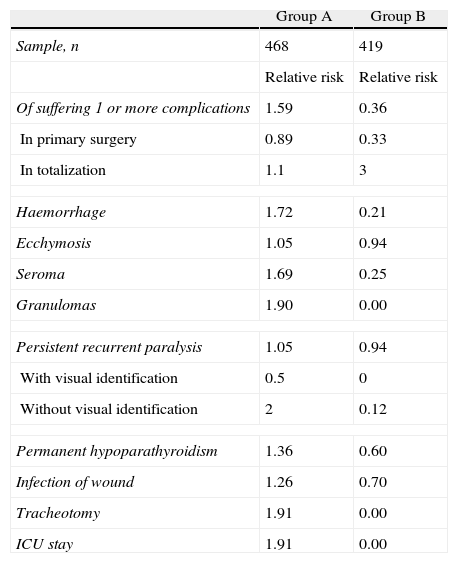
ResultsThere was a statistically significant lower incidence of complications in Group B (0.95% versus 4.06% in group A): bleeding (0.24% versus 1.92% in group A), tracheostomy (0% versus 1.28%) and intensive care unit stay (0% versus 4.06%). Improvement of surgical activity parameters was also significant for Group B: shorter operation time (60min versus 180min), fewer hospital stays (4.62 versus 8.5 stays) and increase in operations per month (9.63 versus 4 interventions). Persistent sequelae (recurrent paralysis [0.48%] and hypoparathyroidism [0.47%]) decreased in the second group but the difference was not statistically significant compared to Group A. The cost per patient was lower in Group B.
ConclusionsThe Ultracision Harmonic scalpel system is the technique of choice for thyroid surgery.
Los avances tecnológicos en hemostasia permiten el sellado vascular con mayor precisión y seguridad que la tradicional ligadura asociada a la electrocoagulación mono o bipolar.
ObjetivoComparar las complicaciones en tiroidectomía total mediante técnicas tradicionales (ligadura, electrocoagulación, incluido Ligasure), frente al uso exclusivo de Harmonic Ultracision que realiza disección, corte y hemostasia simultáneamente.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo, descriptivo, comparativo, no aleatorio en 887 pacientes sometidos a tiroidectomía total por el mismo cirujano. Se distribuyen en grupo A (técnicas tradicionales en 468 pacientes, enero de 1997 a septiembre de 2006) y grupo B (Harmonic Ultracision en 419 pacientes, octubre de 2006 a mayo de 2010).
ResultadosEn el grupo B se produjeron significativamente menos complicaciones (incidencia global de 0,95 frente al 4,06 en el grupo A): hemorragia (0,24 frente a 1,92% en grupo A), traqueotomía (0 frente a 1,28%) y estancia en UCI (0 frente a 4,06%). Hubo mejora de los parámetros de actividad: menor tiempo quirúrgico (60 frente a 180 minutos), menor estancia hospitalaria (4,62 frente a 8,5 estancias), incremento del número de intervenciones mensuales (9,63 frente a 4 intervenciones). Las secuelas persistentes en el grupo B (parálisis recurrencial −0,48%− e hipoparatiroidismo −0,47%−) disminuyeron pero sin diferencia estadísticamente significativa respecto al grupo A. El coste por paciente es inferior en el grupo B.
ConclusionesEl sistema Harmonic Ultracision es la técnica de elección en cirugía tiroidea.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora