To compare the different endovesical therapeutic regimes in terms of clinical effectiveness based on glycosaminoglycan replenishment agents (RA-GAG) available on the market in Spain.
Material and methodsA bibliographic analysis was made of the studies published in Medline from 1996 to 2012 on RA-GAG of application in the bladder, placing emphasis on the clinical results. A post hoc comparison was made of the efficacy of this treatment in the studies conducted in patients with interstitial cystitis in different conditions by calculating the effect sizes to analyze improvement on the pain visual analogue scale (VAS) and clinical response rate. The number of patients needed to treat (NNT) for the different agents were calculated based on the odds ratio and associated economic implications.
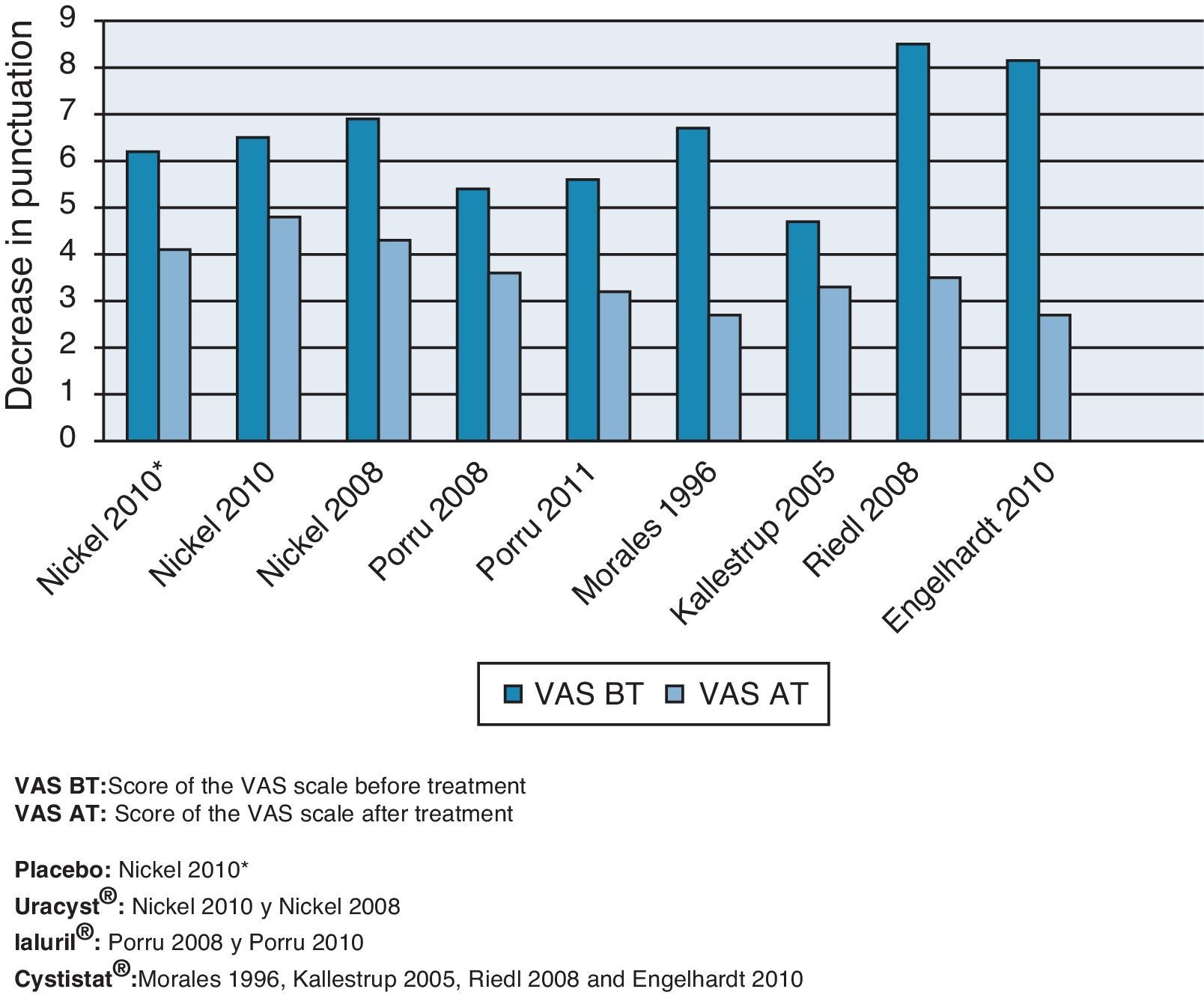
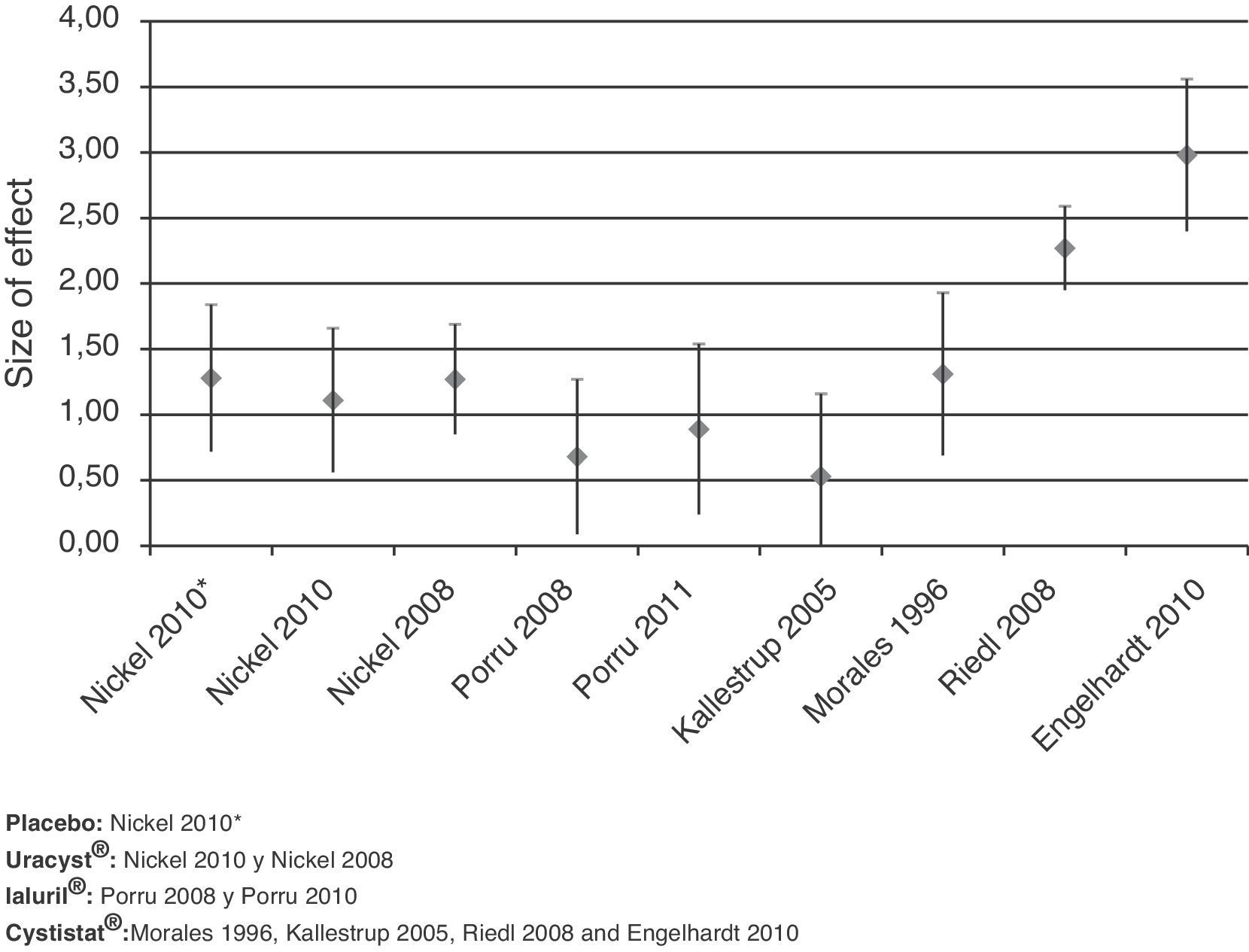
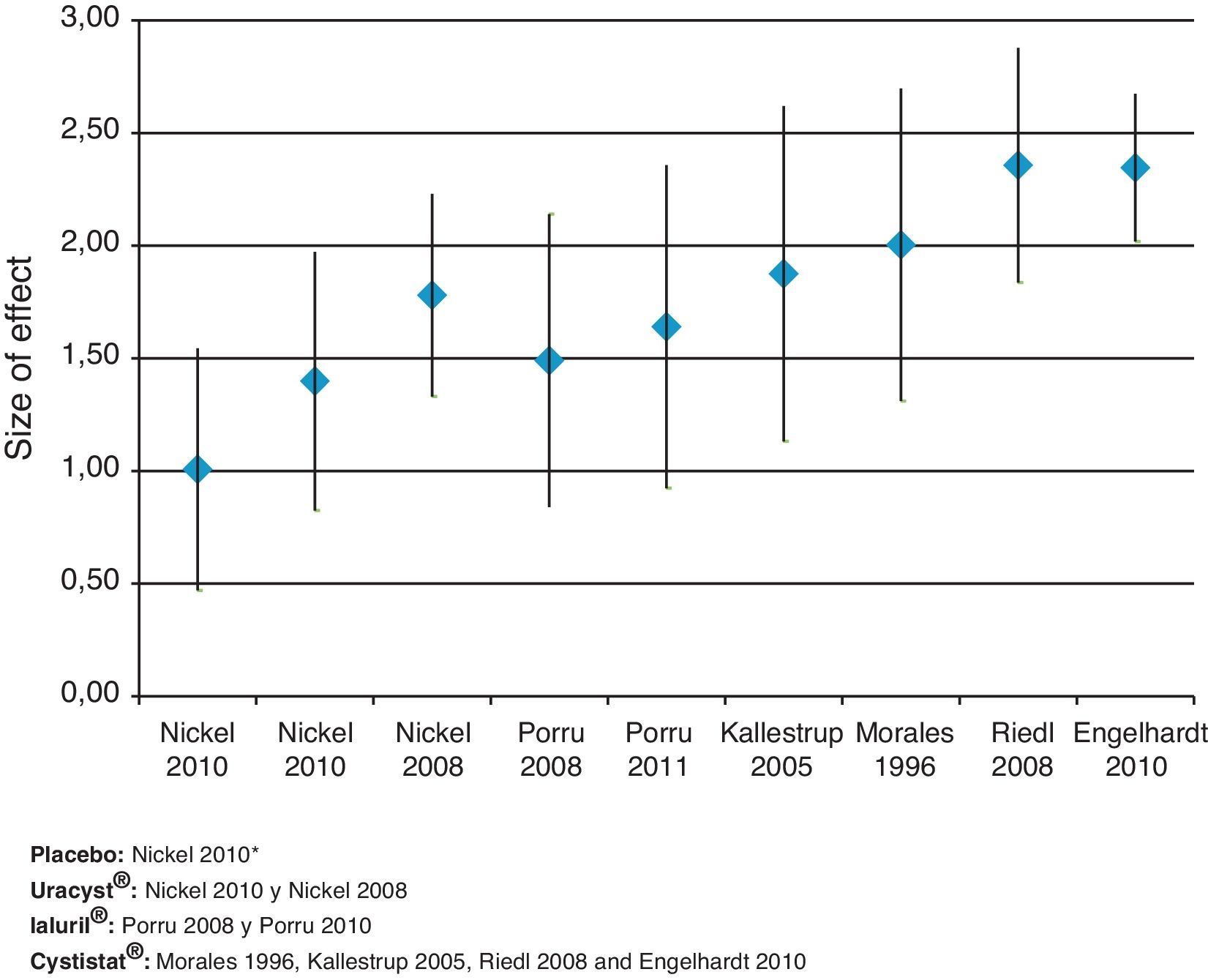
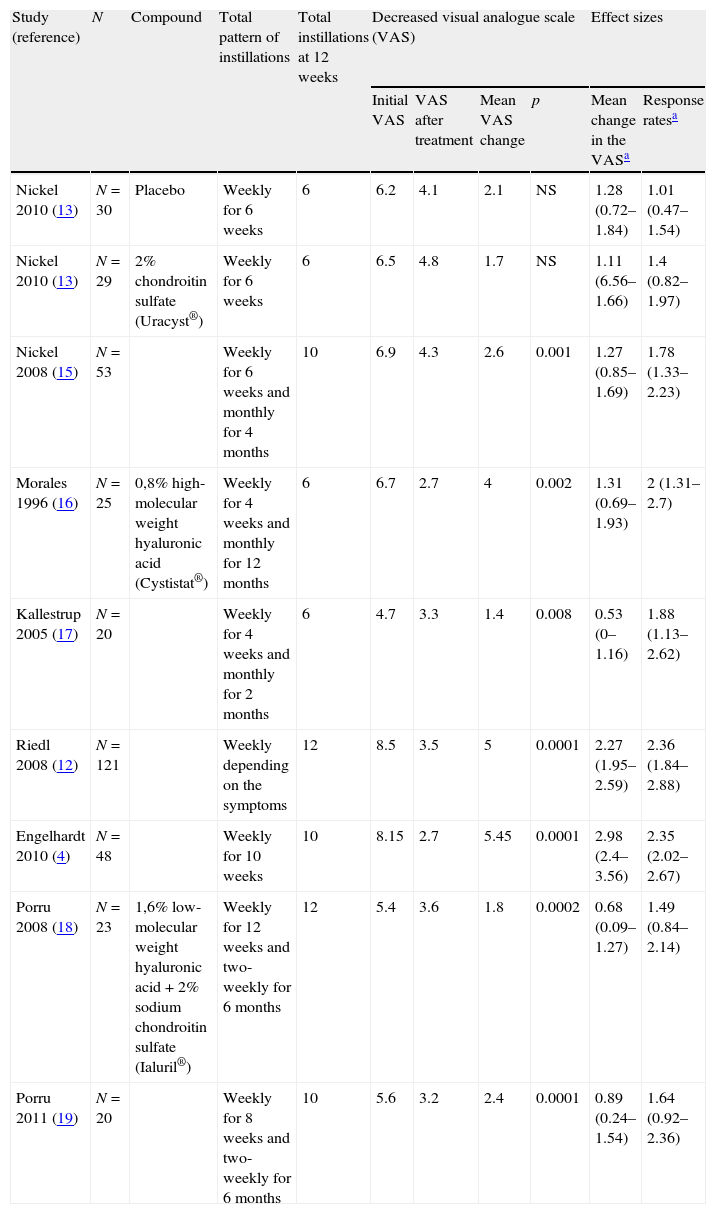
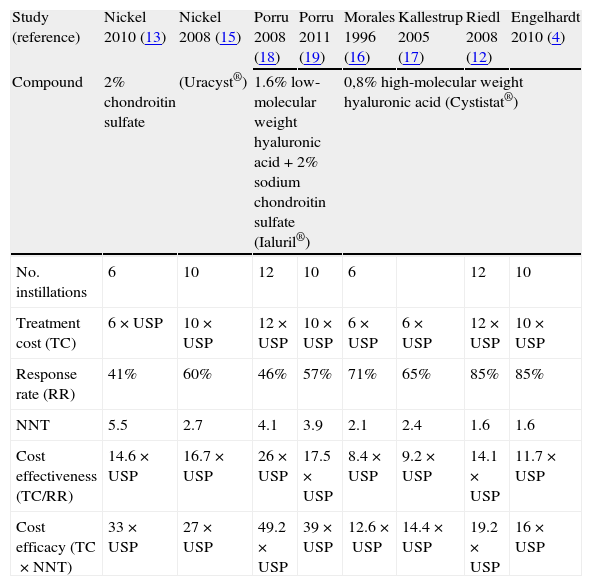
ResultsThe globally available evidence is scarce. There are 38 articles about RA-GAGs in different indications, 71 of them in interstitial cystitis and only 8 may assist in establishing a comparison between the results presented. The treatments used were placebo, 0.8% high molecular weight hyaluronic acid (Cystistat®), 2% chondroitin sulfate sodium (Uracyst®) and a combination of 1.6% low molecular weight hyaluronic acid plus 2% chondroitin sulfate (Ialuril®), between 6 and 12 instillations. Another low molecular weight hyaluronic acid preparation (Uromac®) lacks any scientific evidence. All the therapeutic elements studied show a mean score decrease on the pain VAS and increase in the rate of post-treatment response. The NNT for the treatments that are statistically more beneficial over placebo ranges from 1.6 to 4.1. The post hoc comparison of the response rates has established that Cystistat® 12 instillations (OR 18.8; 95% CI 6.4–57.2; p=.001) or 10 instillations (OR 19.2; 95% CI 5.3–75.3; p=.001) are the treatment regimes that obtain maximum effectiveness. In both cases, the NNT was 1.6.
ConclusionsThis study has multiple limitations inherent to the nature of the design. However, although the available literature is scarce, it shows that there are differences regarding the clinical effectiveness of the different agents and regimes used for endovesical treatment of interstitial cystitis. These differences also entail economic type implications.
Comparación de los diferentes regímenes terapéuticos endovesicales a base de agentes restituidores de glucosaminoglicanos (AR-GAG) comercialmente disponibles en España en términos de efectividad clínica.
Material y métodoAnálisis bibliográfico de los estudios publicados en Medline entre 1996 y 2012 sobre AR-GAG de aplicación vesical con énfasis en los resultados clínicos. Comparación post-hoc de la eficacia de dicho tratamiento en los estudios realizados en pacientes con cistitis intersticial en diferentes condiciones, mediante el cálculo de los tamaños de efecto para el análisis de mejora en la escala analógica visual (EAV) de dolor y la tasa de respuesta clínica. Cálculo del número necesario de pacientes a tratar (NNT) para los distintos agentes a partir de la odds ratio (OR) e implicaciones económicas asociadas.
ResultadosLa evidencia disponible es globalmente escasa. Un total de 38 artículos tratan de AR-GAG en diferentes indicaciones, 17 de ellos en cistitis intersticial y solamente 8 son subsidiarios de establecer comparación entre los resultados presentados. Los tratamientos empleados fueron placebo, ácido hialurónico de alto peso molecular al 0,8% (Cystistat®), condroitín sulfato sódico al 2% (Uracyst®) y una combinación de ácido hialurónico de bajo peso molecular al 1,6% más condroitín sulfato al 2% (Ialuril®), entre 6 y 12 instilaciones. Otro preparado de ácido hialurónico de bajo peso molecular (Uromac®) carece de evidencia científica alguna. Todos los elementos terapéuticos estudiados muestran disminución de la puntuación media de la EAV de dolor y aumento de la tasa de respuesta postratamiento. El NNT para los tratamientos estadísticamente ventajosos sobre placebo oscila entre 1,6 y 4,1. La comparación post-hoc de las tasas de respuesta establece que Cystistat® 12 instilaciones (OR: 18,8; IC 95%: 6,4-57,2; p=0,001) o 10 instilaciones (OR: 19,2; IC 95%: 5,3-75,3; p=0,001) son las pautas de tratamiento que obtienen máxima efectividad. En ambos casos el NNT fue 1,6.
ConclusionesEste estudio está sujeto a múltiples limitaciones inherentes a la naturaleza de su diseño; no obstante, muestra que, a pesar de que la literatura disponible es escasa, existen diferencias en cuanto a la efectividad clínica de los diferentes agentes y regímenes aplicados para el tratamiento endovesical de la cistitis intersticial. Estas diferencias conllevan también implicaciones de índole económica.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora