El diagnóstico y la estadificación molecular del cáncer vesical basados en la detección de ARNm de gelatinasas (MMP-2 y MMP-9) en células circulantes y mononucleares de sangre periférica han mostrado resultados prometedores. Analizamos si la determinación de los correspondientes productos de síntesis proteica permite diagnosticar y caracterizar pacientes con neoplasia vesical.
Material y métodoSe ha llevado a cabo la cuantificación de los niveles séricos de MMP-2, MMP-9 y TIMP-2 en una serie de 42 individuos (31 pacientes con cáncer vesical en diversos estadios y 11 controles sanos) mediante técnica de ELISA. Se compararon las determinaciones entre casos y controles (U Mann-Whitney), así como entre diferentes grupos de tumores (U Mann-Whitney o Kruskal-Wallis), según las características clínico-patológicas (edad, sexo, categoría T, categoría M o grado). Se evaluó el rendimiento diagnóstico de estos marcadores mediante análisis de curvas ROC.
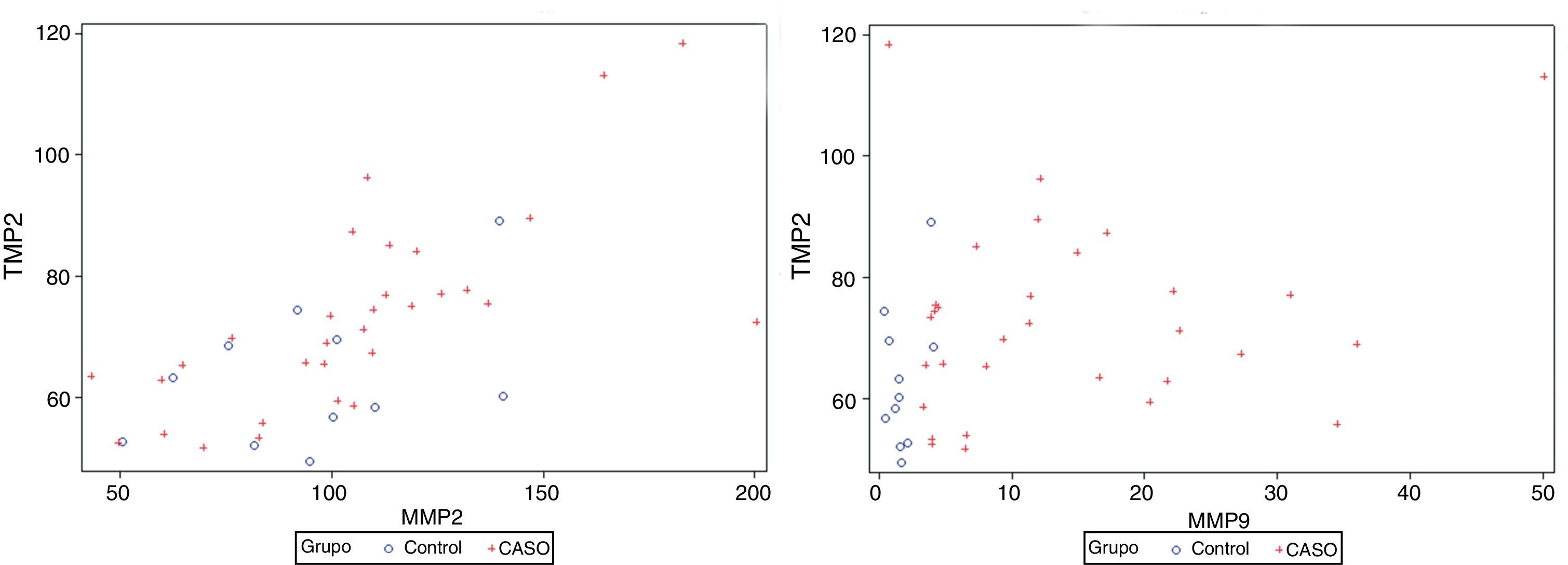
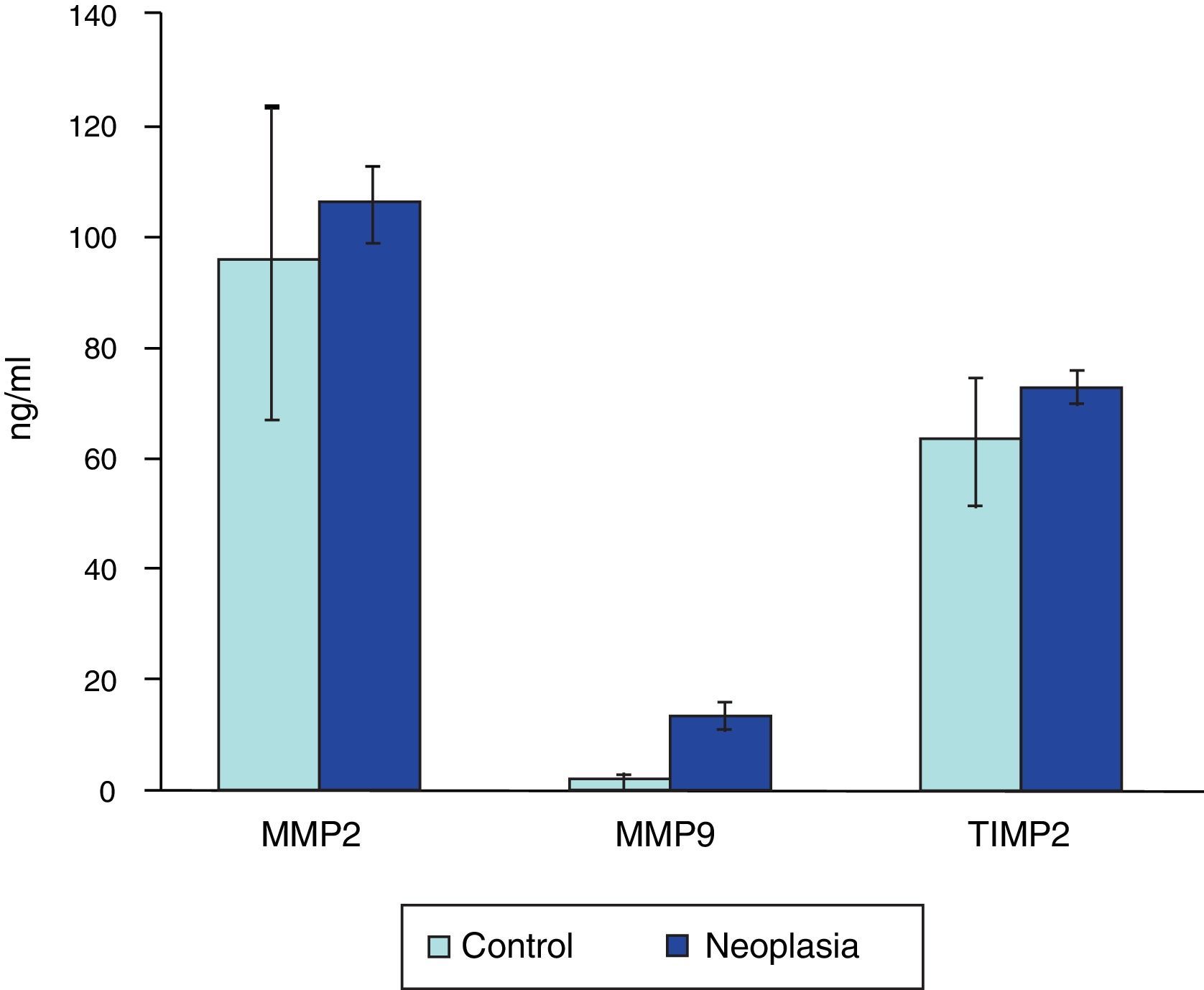
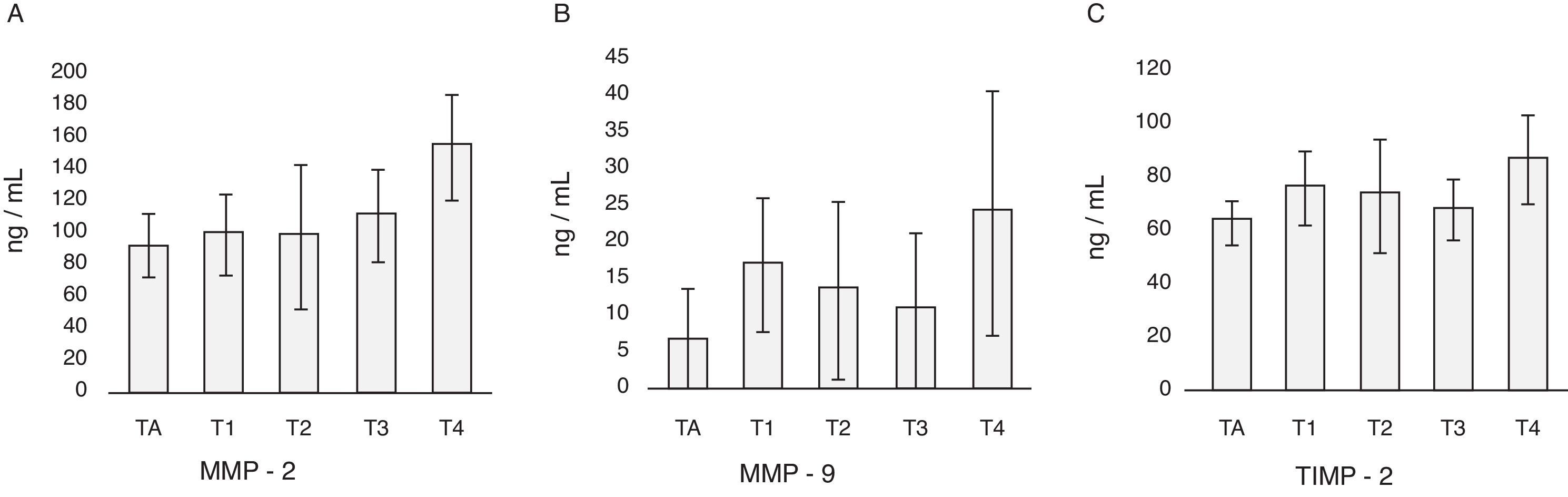
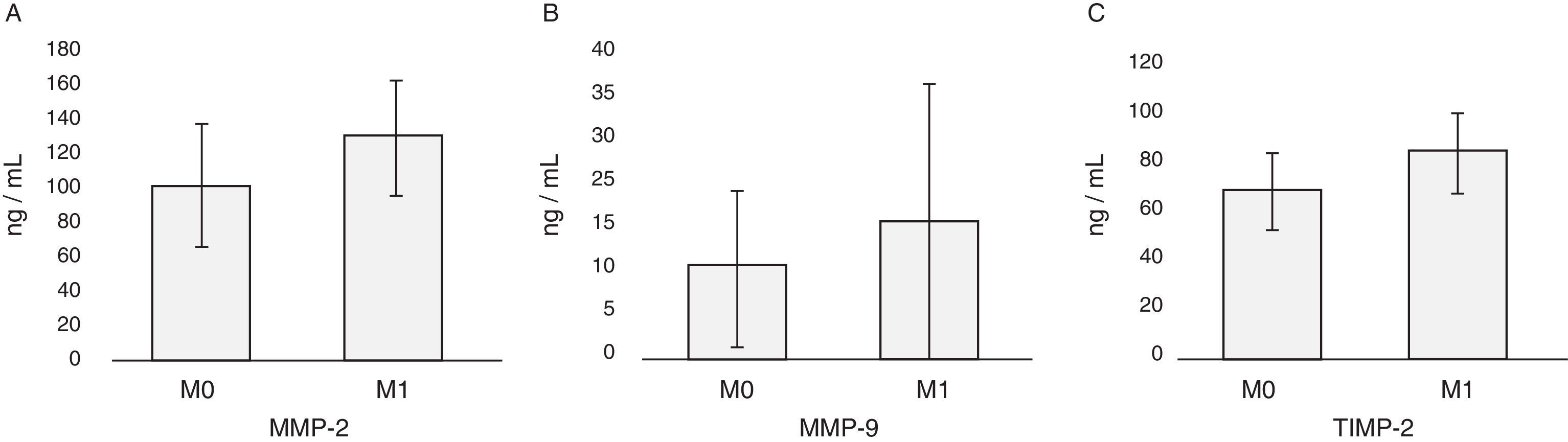
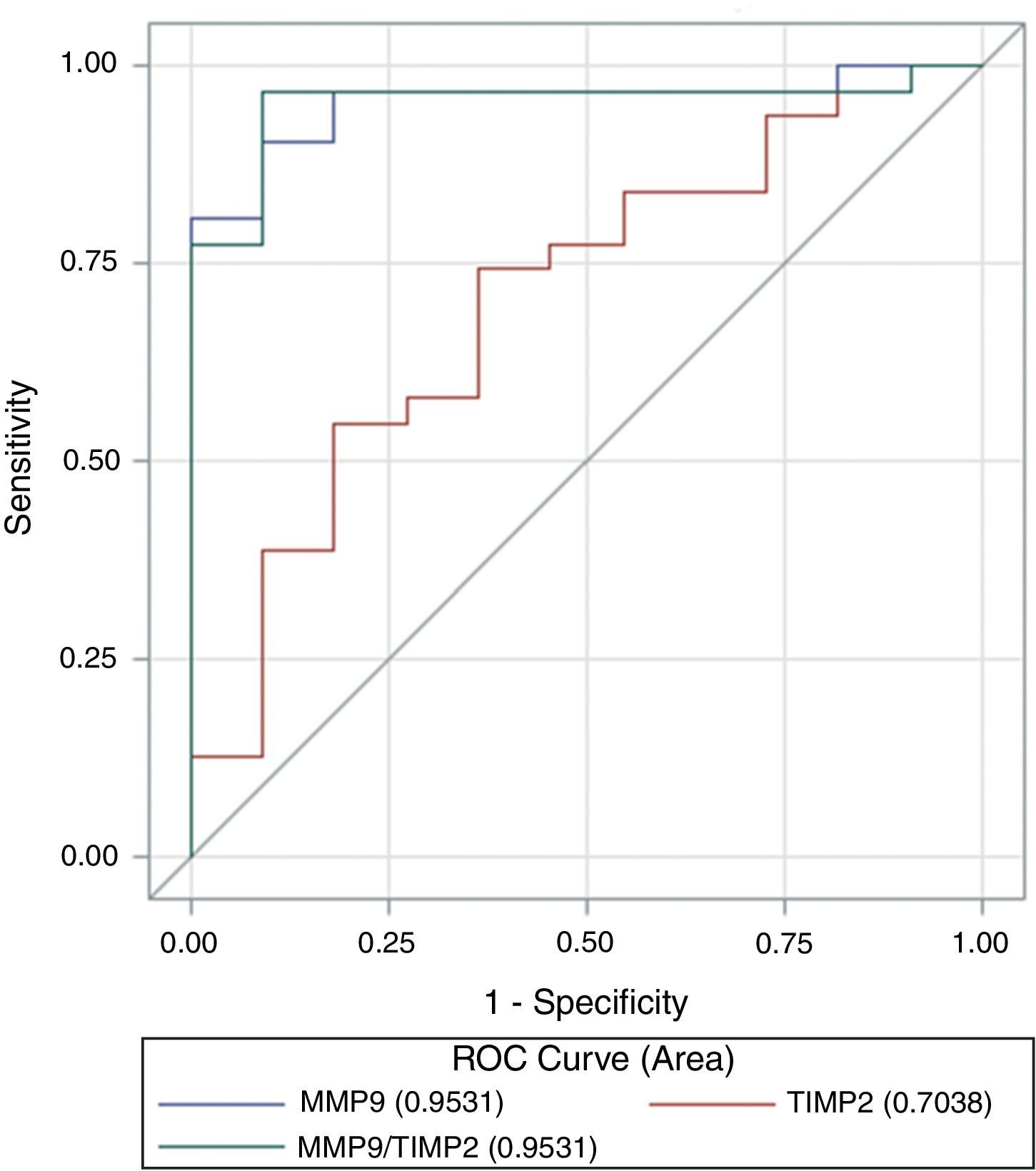
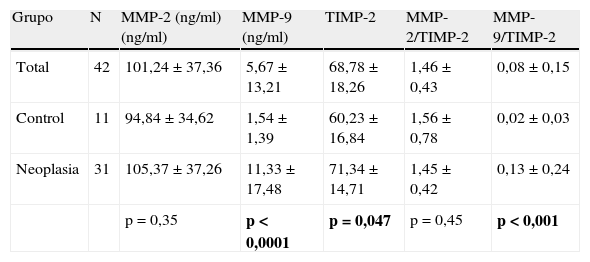
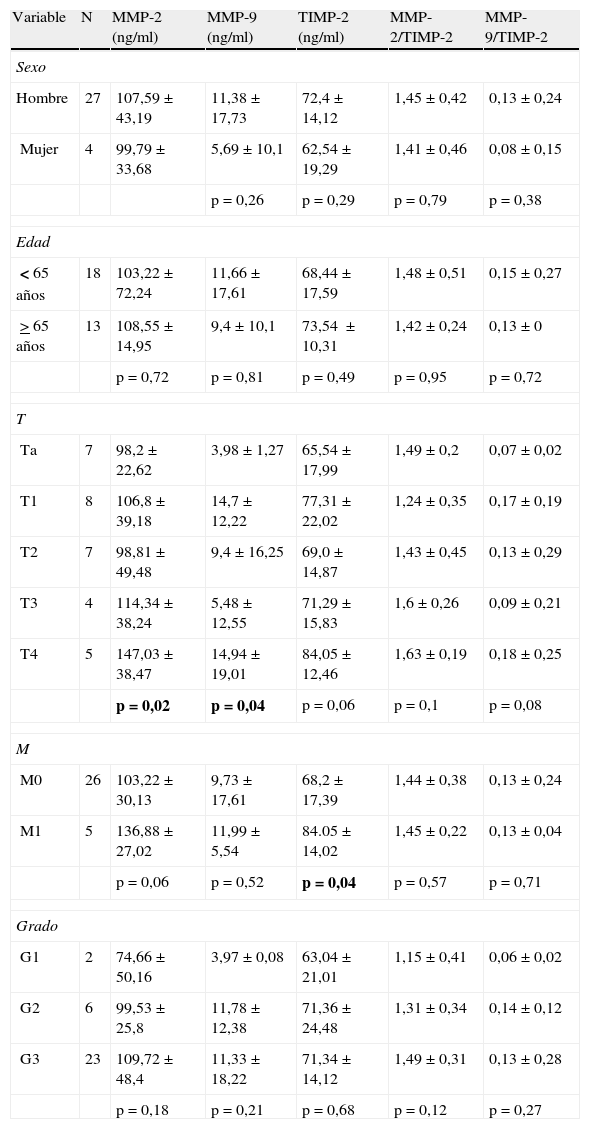
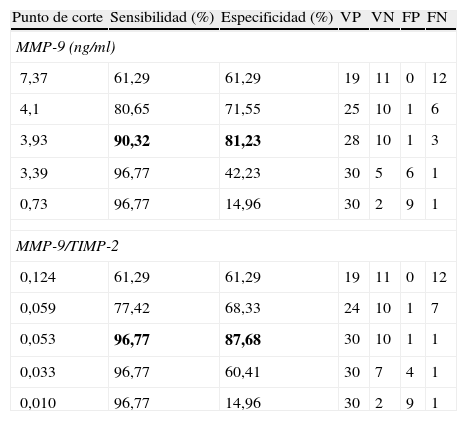
ResultadosExiste correlación entre las determinaciones de MMP-2 y TIMP-2 (R=0,699; p>0,0001) y de MMP-9 y TIMP-2 (R=0,305; p=0,049). Los pacientes con cáncer de vejiga presentan niveles más elevados de MMP-9 (p<0,0001) y TIMP-2 (p=0,047) que los controles. Así mismo, el cociente MMP-9/TIMP-2 también es superior en pacientes con cáncer (p<0,001). No se detectan diferencias entre cáncer y control respecto a edad (p=0,64) o sexo (p=0,64). Tampoco se detectan diferencias con respecto a MMP-2 (p=0,35) ni al cociente MMP-2/TIMP-2 (p=0,45). Dentro de la población de pacientes con cáncer los valores de MMP-2 y MMP-9 difieren según categoría T (p=0,022 y p=0,038, respectivamente) y los de TIMP-2 según categoría M (p=0,036). El análisis de curvas ROC mostró que tanto MMP-9 como el cociente MMP-9/TIMP-2 discriminan pacientes con cáncer y controles, con equivalente exactitud diagnóstica (ABC 0,953) y unos puntos de corte de 3,93 ng/ml (S 90%; E 81%) y de 0,053 ng/ml (S 96%; E 84%), respectivamente.
ConclusionesLos resultados obtenidos sugieren que tanto MMP-9 como TIMP-2 séricos podrían tener una aplicación en la predicción del desarrollo y progresión del cáncer vesical, y potencial utilidad como marcadores clínicos de la enfermedad. Se requieren estudios multicéntricos prospectivos que confirmen estos resultados preliminares.
The diagnosis and molecular staging of bladder cancer based on the detection of gelatinases mRNA (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in peripheral blood circulating and mononuclear cells have shown promising results. We analyze if the determination of the corresponding protein synthesis products makes it possible to diagnose and characterize patients with bladder cancer.
Material and methodQuantification of the serum levels of MMP-2, MMP-9 and TIMP-2 in a series of 42 individuals (31 patients with bladder cancer in different stages and 11 healthy controls) using the ELISA technique was carried out. The determinations were compared between cases and controls (Mann-Whitney U) and between different groups of tumors (Mann-Whitney U or Kruskal-Wallis), according to the clinical-pathological characteristics (age, gender, T category, M category or grade). Diagnostic yield of these markers was evaluated by analysis of the ROC curves.
ResultsThere is a correlation between the determinations of MMP-2 and TIMP-2 (R=.699; P>.0001) and MMP-9 and TIMP-2 (R=.305; P=.049). Patients with bladder cancer have higher levels of MMP-9 (p<0.0001) and TIMP-2 (P=.047) than the controls. Furthermore, the MMP-9/TIMP-2 ratio is also superior in cancer patients (P<.001). Differences were not detected between cancer and controls regarding age (P=.64) or gender (P=.64). Differences were also not detected regarding MMP-2 (P=.35) or MMP-2/TIMP-2 rate (P=.45). Within the cancer patient population, the MMP-2 and MMP-9 values differ according to T category (P=.022 and P=.038, respectively) and those of the TIMP-2 according to M category (P=.036). ROC curve analysis showed that both MMP-9 and the MMP-9/TIMP-2 ratio discriminate patients with cancer and controls, with equivalent diagnostic accuracy (ABC 0.953) and cut offs of 3.93 ng/mL (S 90%; Sp 81%) and 0.053 ng/mL (S 96%; Sp 84%), respectively.
ConclusionsThe results obtained suggest that both serum MMP-9 and TIMP-2 would have an application in the prediction of the development and progression of bladder cancer, and a potential utility as clinical markers of the disease. Multicenter, prospective studies that confirm their preliminary results are necessary.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora