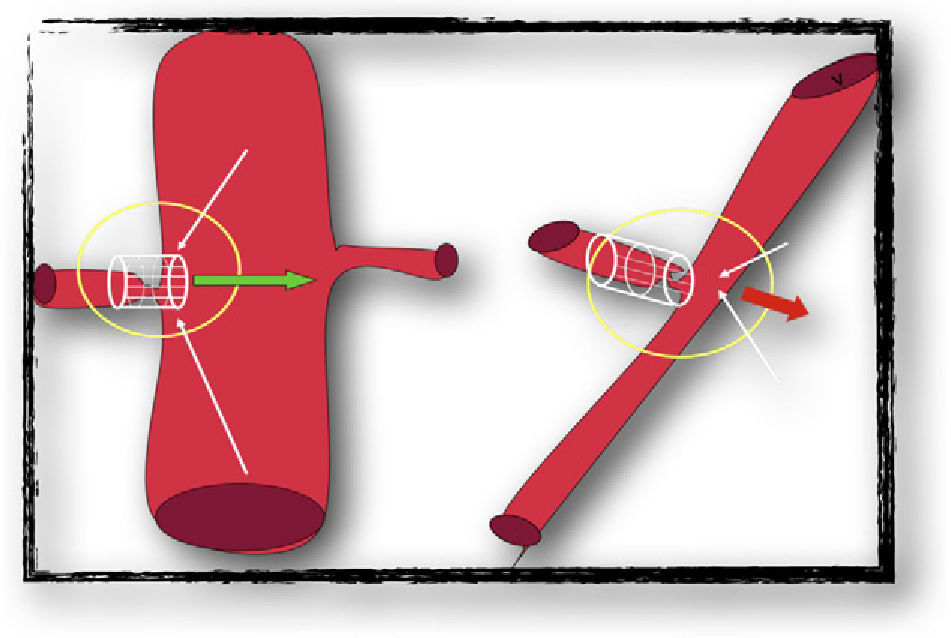
The incidence of renal artery stenosis in the transplanted kidney (TRAS) varies between 2 and 23%, being the most frequent vascular complication following renal trasplantation. The delay in diagnosis and treatment can lead to functional graft loss. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty with stent (PTAS) is the treatment of choice to restore kidney perfusion.
Materials and methodsRetrospective review of renal transplant casuistic in our institution between September 2005 and August 2009 was included in patients with greater than 70% TRAS and impaired graft function, treated with PTAS. Follow-up at 3, 12 and 36 months was done with creatinine, glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and Doppler ultrasonography (DUS). Technical success was defined as correct stent placement associated with decreased flow, and clinical success as improved renal function during follow-up.
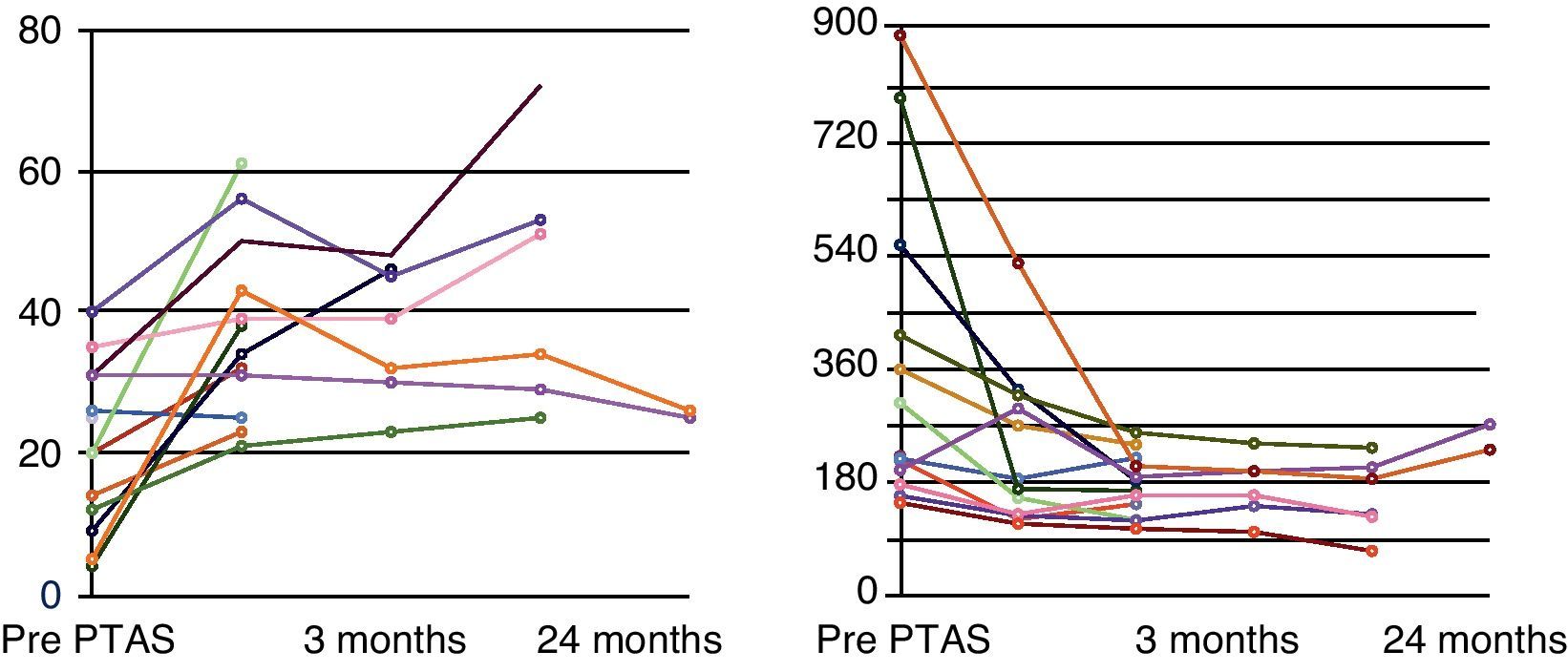
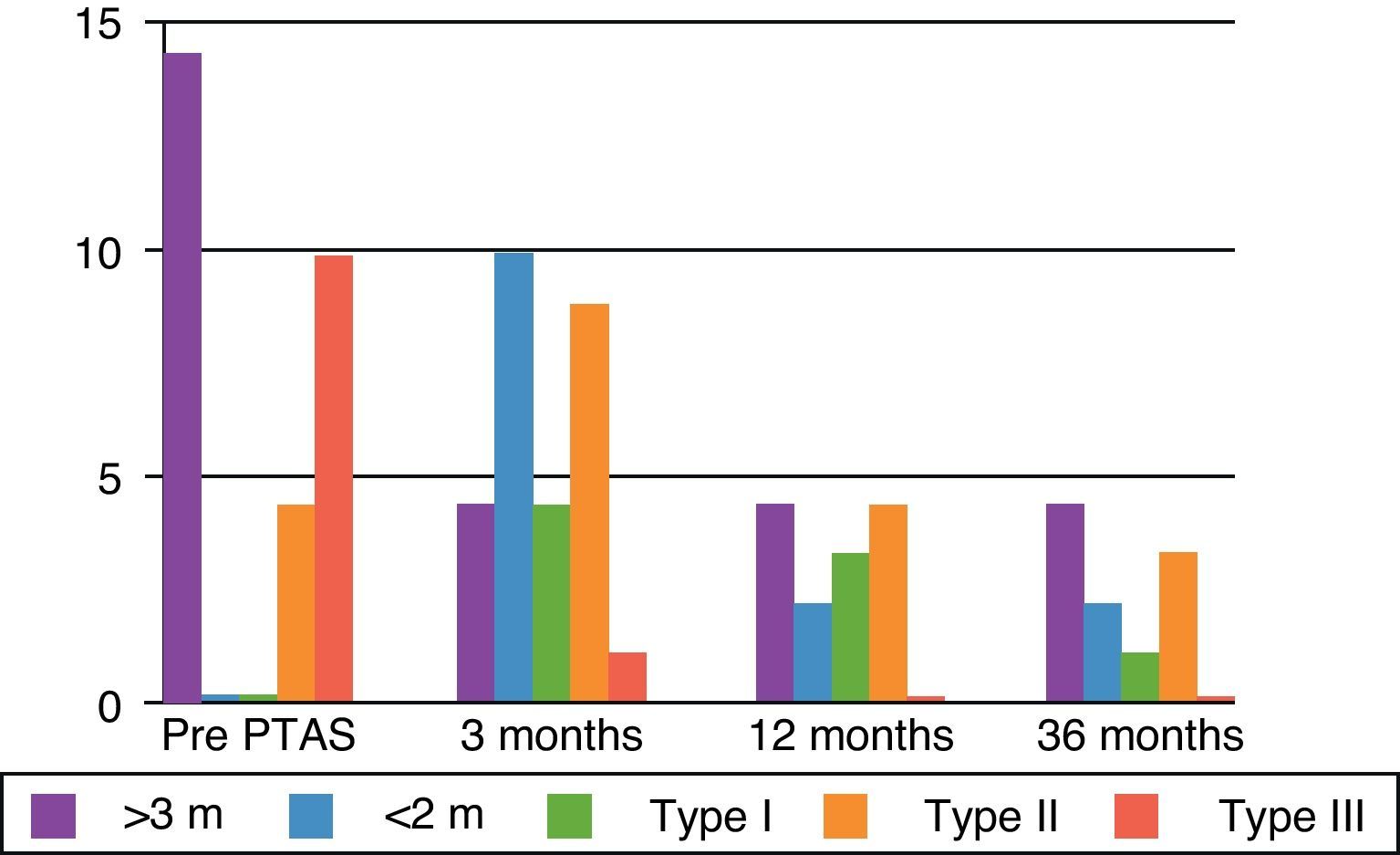
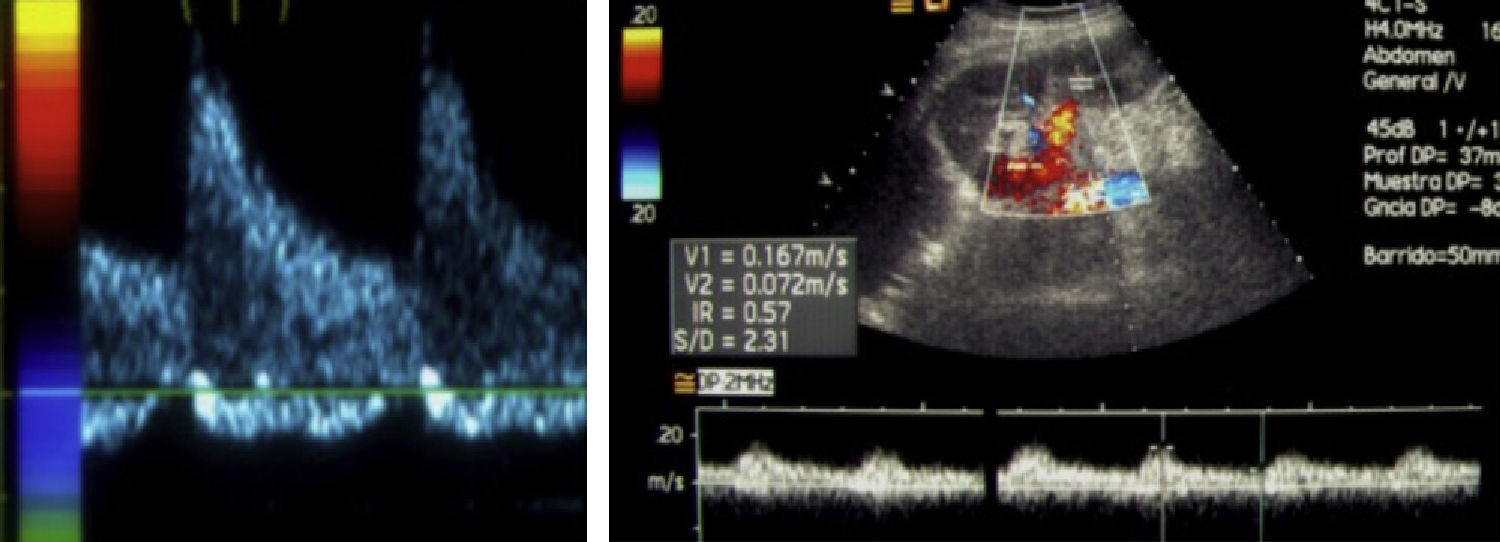
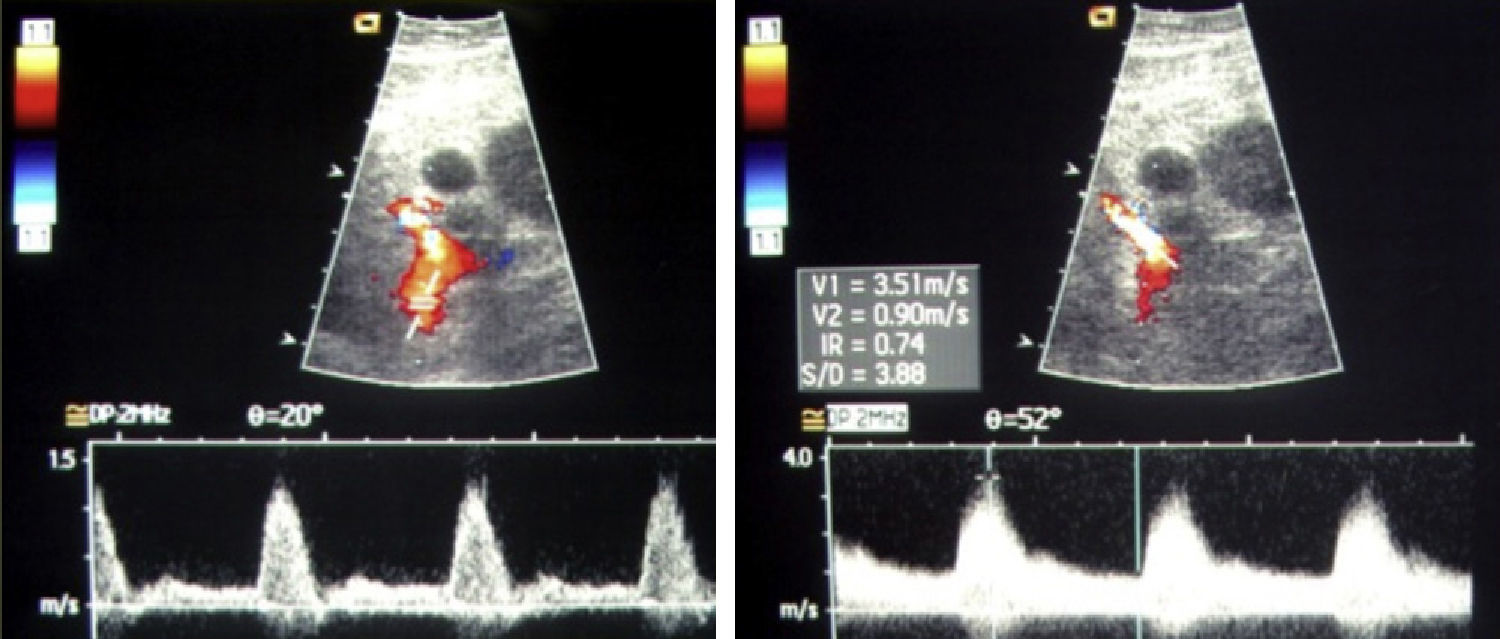
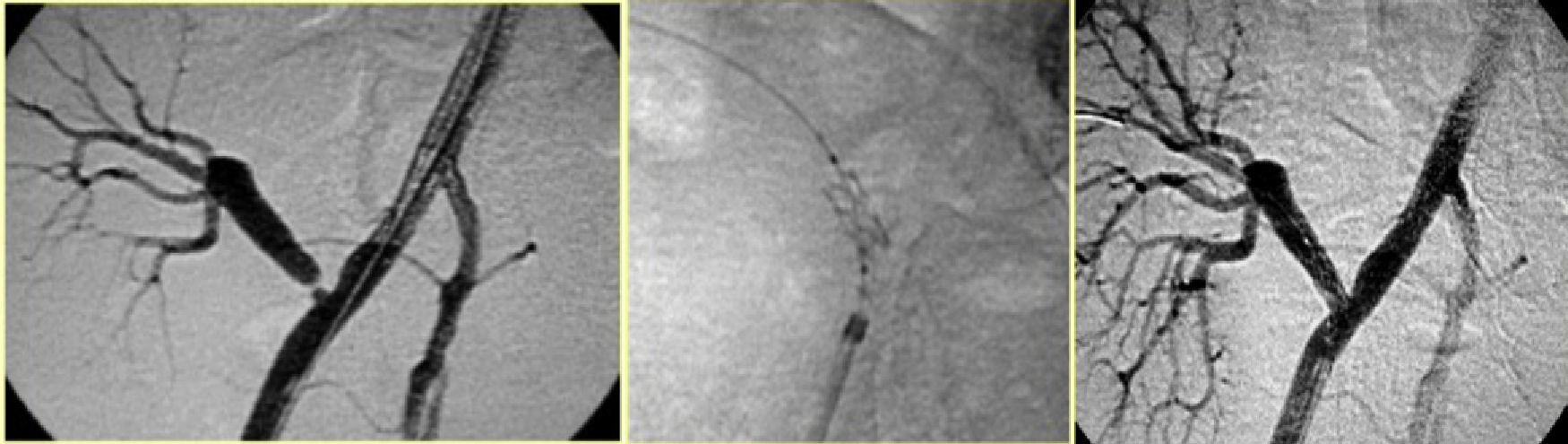
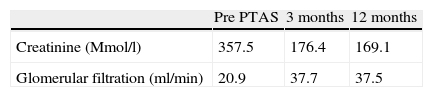
ResultsIncidence of TRAS was 7.3% (22/298), 60% PTAS subsidiary. 100% technical success and 84.6% clinical success, 15.4% without changes in renal function. 84% decreases flow rate greater than 70% by DUS, and 26% up to 60%. Wave changes from type III to type II were recorded in 69% and to type I in 33%.
ConclusionsThe PTAS is a safe and effective procedure for the treatment of selected TRAS patients, as it preserves vascular permeability in the short and medium term, ensuring the functionality of the graft. DUS is the method of choice for diagnosis and monitoring TRAS.
La incidencia de estenosis de la arteria renal en el ri¿nón trasplantado (EART) varía entre el 2 y el 23%, siendo la complicación vascular más frecuente del trasplante renal. Retrasar el diagnóstico y tratamiento puede llevar a la pérdida funcional del injerto. La angio-plastia transluminal percutánea con stent (ATPRS) es el tratamiento de elección en pacientes seleccionados.
Material y métodosRevisión retrospectiva de la casuística de trasplante renal de nuestro cen-tro entre septiembre de 2005 y agosto de 2009, incluyendo EART mayores al 70% con alteración funcional del injerto tratados con ATPRS. Seguimiento a los 3, 12 y 36 meses con valores de creatinina, filtrado glomerular (FG) y ultrasonografía doppler (USGD). Se consideró éxito téc-nico el correcto emplazamiento del stent y éxito clínico la mejoría de la función renal durante el seguimiento.
ResultadosLa incidencia de EART fue del 7,3% (22/298), 13 pacientes con EART mayor al 70% fueron subsidiarios de ATPRS. Hubo un éxito técnico del 100% y un éxito clínico del 84,6% (11 casos); Un 15,4% (dos casos) permanecieron sin cambios en la función renal. La disminución en la velocidad flujo mayor al 70% se controló con USGD; 10 casos (84%) y 3 (26%) disminuciones hasta del 60%. Se registraron cambios de ondas tipo III a tipo II en 9 casos (69%) y a tipo I en 4 (33%).
ConclusionesLa ATRPS es una técnica segura y efectiva para el tratamiento de la EART en pacientes seleccionados, ya que mantiene una buena permeabilidad vascular a corto y mediano plazo, garantizando la funcionalidad del injerto. La USGD es la herramienta de elección para el diagnóstico y seguimiento de la EART.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora