El tratamiento estándar de las azoospermias es la recuperación espermática del testículo para inyección intracitoplásmica. El objetivo de este estudio es identificar factores predictivos de recuperación espermática.
Material y métodosIntentamos recuperar espermatozoides mediante extracción espermática del testículo (TESE) en 74 pacientes azoospérmicos. Se estudiaron los niveles séricos de FSH e inhibina B (INHB), la histología testicular, la genética, la criptozoospermia y el tamaño testicular.
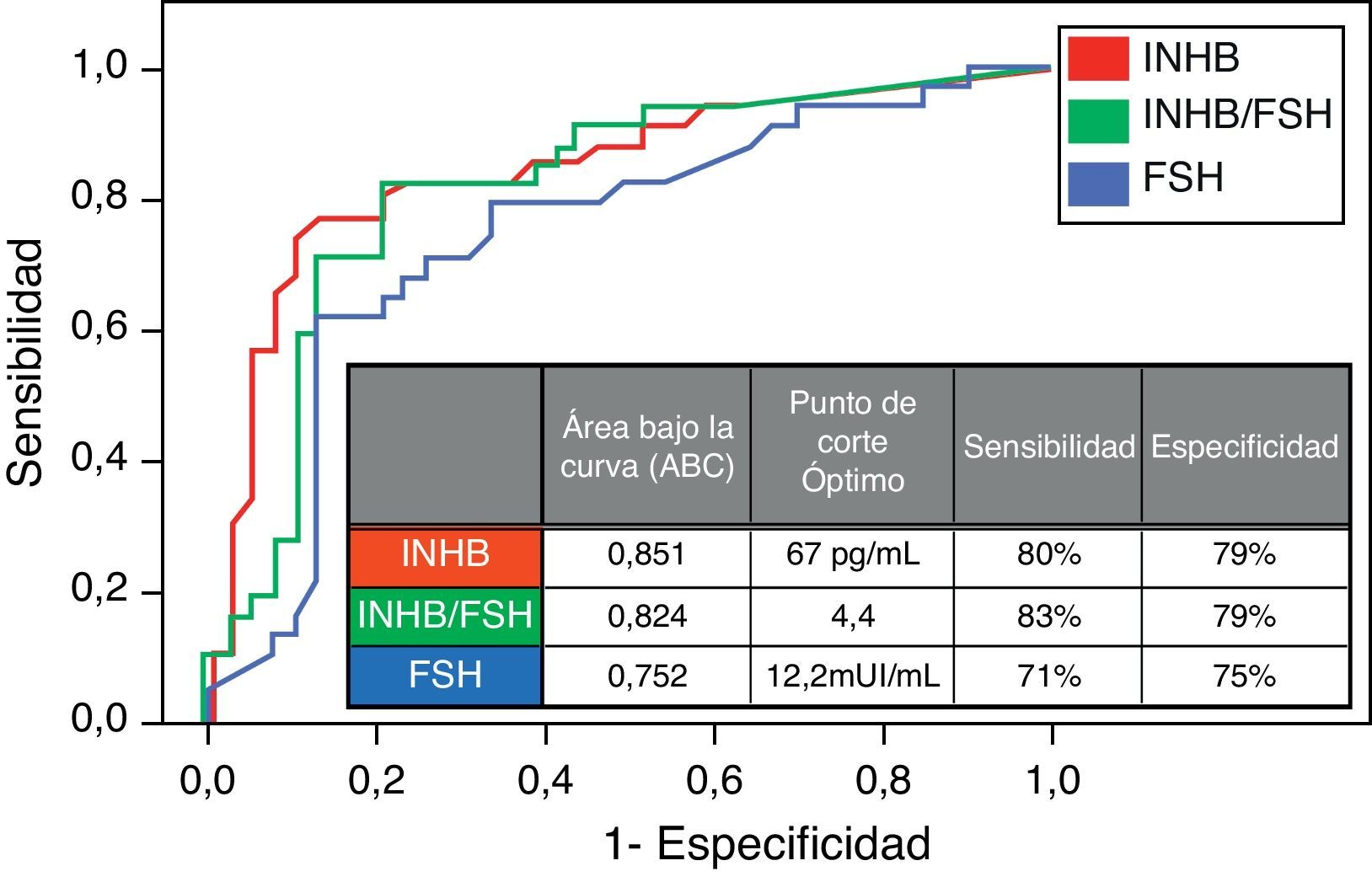
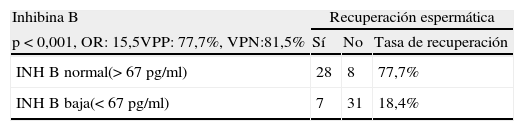
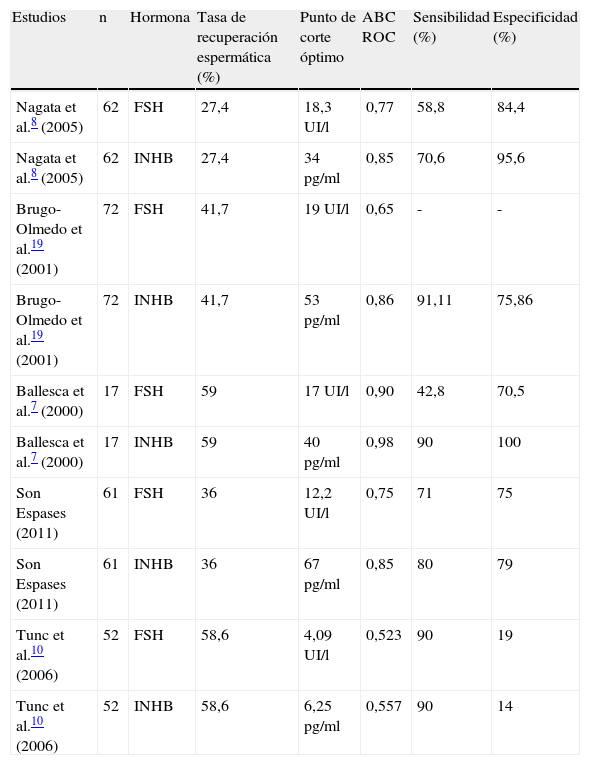
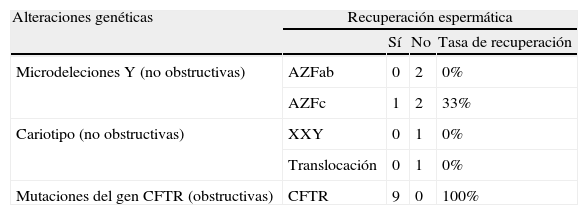
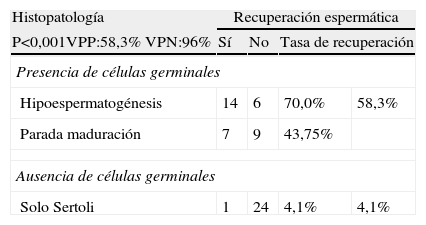
ResultadosLa recuperación espermática fue del 47,2% para el total de pacientes, del 36% para las azoospermias no obstructivas y del 100% para las obstructivas. La INHB baja y la FSH alta se correlacionaron con el fracaso en la recuperación espermática. Los puntos de corte obtenidos mediante curvas ROC fueron de 67 pg/ml para la INHB y de 12,2 mUI/ml para la FSH. En ningún paciente con microdeleción Y en AZFa,b se recuperaron espermatozoides. En el 100% de los pacientes con mutaciones CFTR se obtuvieron espermatozoides. La mayor tasa de recuperación espermática fue para las hipoespermatogénesis, seguidas de los bloqueos madurativos y de los solo Sertoli. En todos los pacientes con criptozoospermia se recuperaron espermatozoides. Se encontró una relación entre el tamaño testicular y la recuperación espermática, pero no resultó estadísticamente significativa.
ConclusionesSalvo las microdeleciones en AZFa,b ningún factor predictor descarta a un paciente para TESE. La INHB baja se relaciona mejor que la FSH alta con el fracaso en la recuperación espermática. La recuperación es posible en todos los casos de mutaciones CFTR. La ausencia de células germinales se correlaciona con una alta probabilidad de fracaso en la recuperación espermática. La presencia de criptozoospermia se vincula a una alta probabilidad de éxito en la recuperación espermática. No encontramos relación significativa entre el tamaño testicular y la recuperación espermática.
Testicular sperm extraction with intracytoplasmic sperm injection is the standard treatment for azoospermia. The objective of this study is to identify predictive factors of successful sperm retrieval.
Materials and methodsBetween June 2003 and May 2011, we tried testicular sperm extraction (TESE) in 74 azoospermic patients in the Reproductive Medicine Unit of Son Espases Hospital (Palma de Mallorca). Serum follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and inhibin B levels, testicular histology, genetic study, presence or not of cryptozoospermia and testicular volume were examined.
ResultsSpermatozoa were successfully recovered in 47.2% of the total patients, in 36% of non-obstructive azoospermic patients and in 100% of obstructive azoospermic patients. Low inhibin B and high FSH were correlated to sperm retrieval failure. The cutoff points were determined using ROC curves that were 67 pg/mL for inhibin B and 12.2 mUI/mL for FSH. Spermatozoa were not successfully retrieved in any patient with Y microdeletions in AZFa,b regions. Spermatozoa were successfully retrieved in 100% of the patients with CFTR mutations. The highest sperm retrieval rate was for hypospermatogenesis, followed by maturation arrest and Sertoli-cell-only. Spermatozoa were successfully retrieved in all cryptozoospermic patients. Although using a non-significant test, there seems to be a correlation between higher testicular volume and a higher probability of successful sperm retrieval.
ConclusionsExcept for Y microdeletions in AZFa,b regions, there is no predictive factor of testicular sperm retrieval to rule out a patient for TESE. Lower inhibin B is more related to sperm retrieval failure than higher FSH. Sperm retrieval is possible for all cases of CFTR mutations but in any case of microdeletion Y in AZFa,b. The lack of germ cells is correlated with a high probability of sperm retrieval failure. The presence of cryptozoospermia is correlated with a high probability of sperm retrieval success. We do not find a statistically significant relation between testicular volume and successful sperm retrieval.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora