This was the first study conducted to determine the influence of home-based treadmill training on seminal quality in adults with type 2 diabetes.
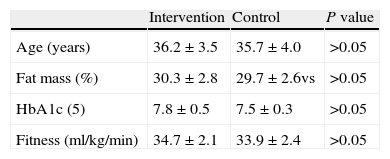
Materials and methodsSixty sedentary adults with type 2 diabetes volunteered for the current study. Thirty were randomly allocated to the intervention group and performed a 14-week, home-based, treadmill training program, 3 sessions per week, consisting of a warm-up (10–15min), 40min treadmill exercise at a work intensity of 55–70% of peak heart rate (increasing by 2.5% each two weeks) measured during a maximal treadmill test, and cooling-down (5–10min). The control group included the age of 30, and BMI matched adults with type 2 diabetes who did not take part in any training program. Seminal quality analysis included semen volume, sperm concentration, motility and normal morphologic features. Furthermore, total antioxidant status (TAS) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX) activity were assessed in seminal plasma. This protocol was approved by an Institutional Ethics Committee.
ResultsThe home-based treadmill training significantly increased sperm concentration as well as percentages of total sperm motility and normal spermatozoa. Furthermore, TAS and GPX activity were increased after the completion of the training program. No significant changes in any of the measured variables were found in the control group.
ConclusionsHome-based treadmill training improved seminal quality in adults with type 2 diabetes. A secondary finding was that seminal antioxidant defense system was significantly increased after being exercised.
El presente estudio se diseñó para determinar la influencia de un programa de entrenamiento domiciliario en la calidad seminal de adultos con diabetes tipo 2.
Material y métodoParticiparon un total de 60 adultos varones con diagnóstico de diabetes tipo 2 distribuidos aleatoriamente en un grupo intervención (n=30) y otro control (n=30). Los participantes incluidos en el grupo de intervención desarrollaron un programa de entrenamiento domiciliario en tapiz rodante de 14 semanas, 3 sesiones/semana de 40min a una intensidad del 55-70% FCmáx (incrementando un 2,5% cada 2 semanas). Los parámetros de calidad seminal ensayados fueron: volumen, concentración y porcentaje de movilidad y morfología normal. Asimismo se estudió el nivel de defensas antioxidantes en plasma seminal. Nuestro protocolo fue aprobado por un comité de ética institucional.
ResultadosTras completar el programa de entrenamiento se observó un incremento significativo de la concentración espermática, así como de los porcentajes de movilidad y de morfología normal. Paralelamente, se observó un incremento del estatus total antioxidante en el plasma seminal. No se observaron cambios significativos en ninguna de las variables ensayadas en el grupo control.
ConclusionesEl programa de entrenamiento mejoró la calidad seminal en pacientes con diabetes tipo 2. Este hallazgo podría explicarse por una mejora de las defensas antioxidantes seminales inducida por el ejercicio.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora