Determine the degree of completion, agreement and diagnostic performance of various instruments for assessing the presence and intensity of urgency and other symptoms of idiopathic overactive bladder (OAB) and determine which is the best diagnostic combination.
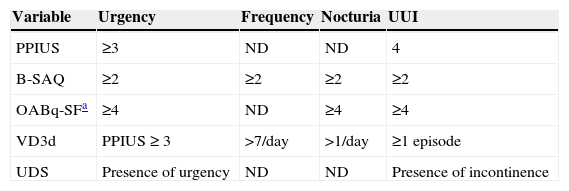
Material and methodsObservational, noninterventional, cross-sectional multicentre study on 247 women aged 18 years or older, with a clinical diagnosis of OAB, evaluated in 55 functional urology and urodynamic units. The women completed the Patient Perception of Intensity of Urgency Scale questionnaire, an independent bladder control self-assessment questionnaire (B-SAQ), the Overactive Bladder Questionnaire Short-Form and a 3-day voiding diary (VD3d), and they underwent a urodynamic study (UDS). The degree of completion and agreement among the instruments was assessed using the Kappa index (95% CI) and Cramér's V. The diagnostic performance of each tool and their combination was studied using absolute frequencies of positive cases for each OAB symptom.
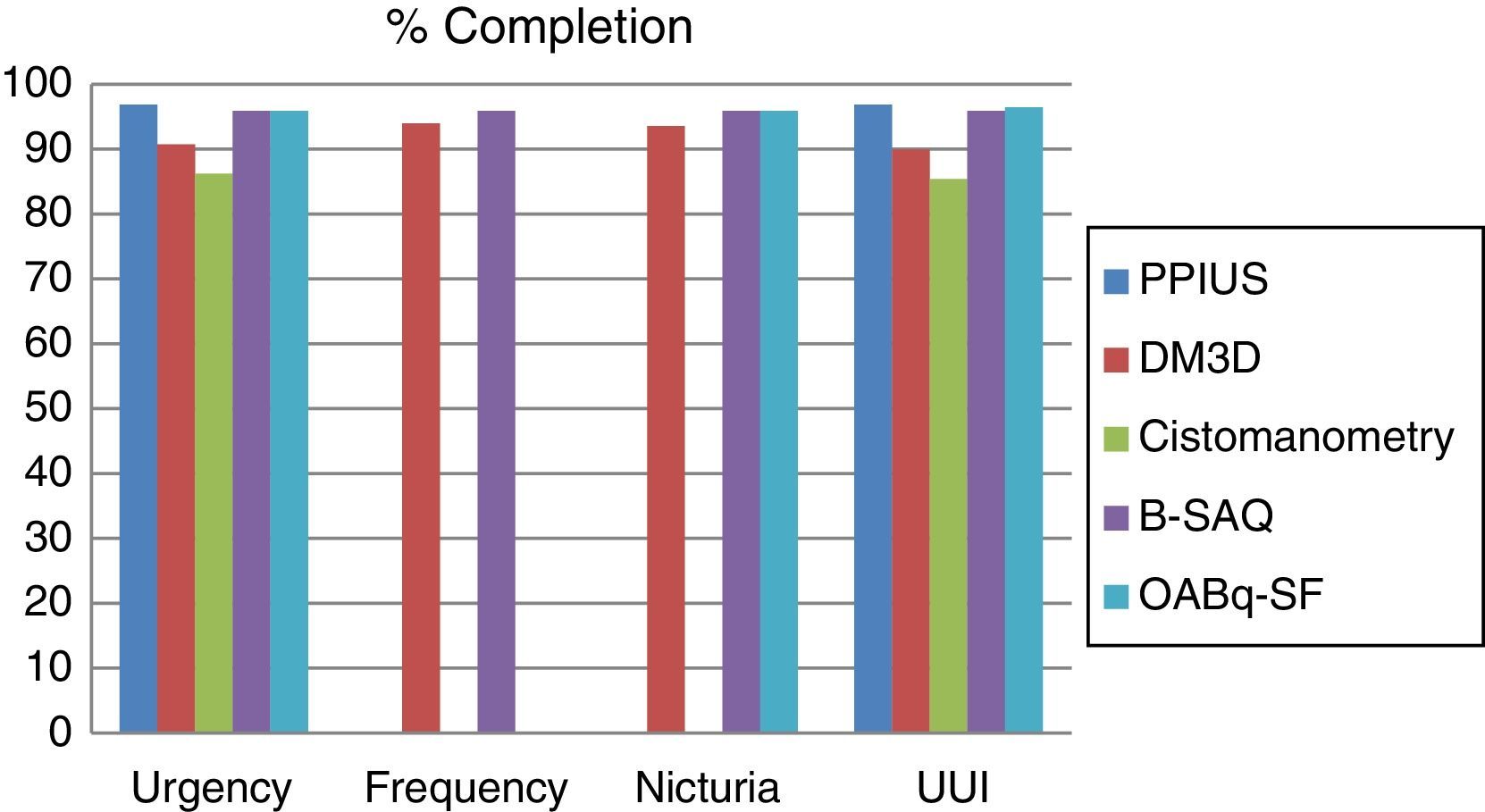
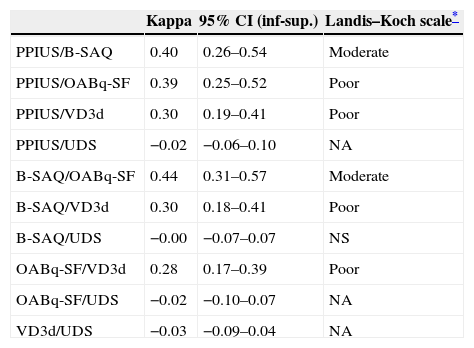
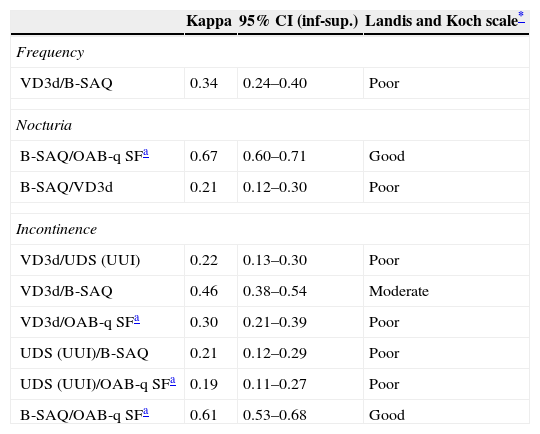
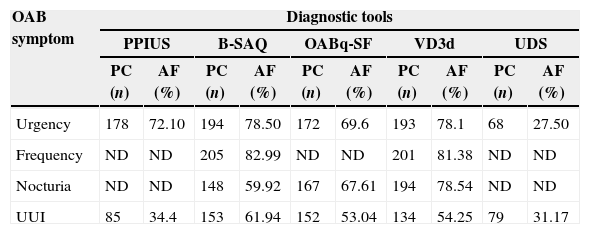
ResultsThe patients mean age was 57.66 years (SD, 13.43). There was a high degree of completion (>85%). The agreement among the instruments was poor or moderate, and there was no agreement with the UDS. The best combination of tools for the diagnosis of OAB in women was the B-SAQ and VD3d.
ConclusionsThe degree of completion of all instruments was high, the agreement between them was poor-moderate and not significant for the UDS. The instruments that had the best diagnostic performance for assessing urgency and other OAB symptoms, providing data on their severity and discomfort, were the B-SAQ and the VD3d.
Determinar el grado de cumplimentación, concordancia y redimiendo diagnóstico de diferentes instrumentos para evaluar la presencia e intensidad de la urgencia y el resto de síntomas de la vejiga hiperactiva idiopática (VH) y determinar cuál es la mejor combinación diagnóstica.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional no intervencionista, transversal y multicéntrico de 247 mujeres ≥18 años con diagnóstico clínico de VH, estudiadas en 55 unidades de urología funcional y urodinámica que cumplimentaron los cuestionarios Patient Perception of Intensity of Urgency Scale como un cuestionario independiente, Cuestionario de autoevaluación del control de la vejiga (CACV), Overactive Bladder Questionnaire Short-Form y un diario miccional de 3 días (DM3d) y sometidas a estudio urodinámico (EUD). Se evaluó el grado de cumplimentación y grado de acuerdo entre instrumentos utilizando el índice Kappa (IC 95%) y V de Cramer. Se estudió el rendimiento diagnóstico de cada herramienta y la combinación de ellas, mediante las frecuencias absolutas de casos positivos para cada síntoma de VH.
ResultadosEdad media (DE): 57,66 (13,43) años. El grado de cumplimentación es elevado (>85%). El grado de acuerdo entre instrumentos es pobre o moderado, y sin acuerdo para el EUD. La mejor combinación de herramientas para el diagnóstico de la VH en la mujer es el CACV y DM3d.
ConclusionesEl grado de cumplimentación de todos los instrumentos fue elevado, la concordancia fue pobre-moderada entre sí y sin significación para el EUD. Los instrumentos que presentan mayor rendimiento diagnóstico para evaluar la urgencia y resto de síntomas de VH aportando datos sobre su severidad y molestia son el CACV y el DM3d.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora