To analyze the management of patients newly diagnosed with overactive bladder (OAB) and to assess the impact of treatment on associated comorbidities.
Methods1434 patients over 60 years with newly diagnosed OAB and at least one associated comorbidity (Urinary tract infections, genital skin infections, sleep disturbances, depression, and hypertension) were recruited in 300 urology/gynecology surgeries in Spain. During the first visit sociodemographic and clinic data were recorded, and treatment for OAB following usual practice was prescribed. Symptoms were reevaluated 4–6 months later. A descriptive statistical analysis was performed, variables were compared by gender (Chi2/Mann–Whitney) and between visits (McNemar).
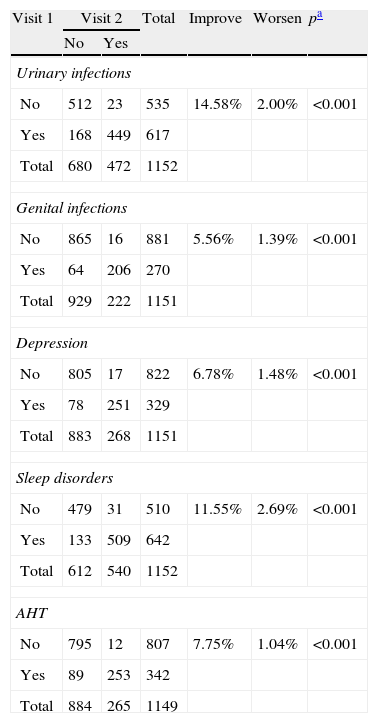
ResultsData for 1274 valid patients in visit 1 and 1153 in visit 2 are presented. Mean age in the sample was 68.17 (6.19) years, 71.51% were women. 66.41% presented urgency, with or without urge urinary incontinence, and 33.59% presented urgency related to stress urinary incontinence. The most frequent associated pathologies were sleep disturbances (56.44%) and urinary tract infections (53.14%). Urinary tract infections and genital skin infections and treatment for depression were more frequent in women; sleep disturbances and hypertension in men. Treatments more frequently prescribed were anticholinergics (95.45%) and guidance for lifestyle changes (85.32%). Statistically significant improvement in symptoms of associated comorbidities was detected in visit 2.
ConclusionsDetection and treatment of OAB symptoms are relevant to reduce both the impact of the affection and of associated pathologies.
Analizar el manejo de pacientes con Vejiga Hiperactiva (VH) de nuevo diagnóstico y el impacto del tratamiento en las comorbilidades asociadas.
Material y MétodosSe reclutaron 1.434 pacientes mayores de 60 años con VH de nuevo diagnóstico y al menos una patología asociada (infecciones urinarias o de piel del área genital, trastornos del sueño, depresión, hipertensión) en 300 consultas de urología/ginecología de España. Inicialmente se recogieron datos socio-demográficos y clínicos y se pautó tratamiento para VH según práctica clínica habitual; 4-6 meses después se reevaluó la sintomatología. Se realizó un análisis estadístico descriptivo, contrastes por sexos (chi2/Mann–Whitney) y para la evolución entre visitas (McNemar).
ResultadosSe presentan datos de 1.274 pacientes válidos en visita 1 y 1.153 en visita 2. La edad media fue 68,17(6,19) años, el 71,51% de la muestra fueron mujeres. El 66,41% presentó urgencia miccional, con o sin incontinencia urinaria (IU) de urgencia y el 33,59% urgencia asociada a IU de esfuerzo. Las patologías asociadas más frecuentes fueron trastornos de sueño (56,44%) e infecciones urinarias (53,14%). Las infecciones urinarias y genitales y el tratamiento para la depresión fueron más frecuentes en mujeres; los trastornos del sueño e hipertensión, en varones. Los tratamientos más frecuentemente indicados fueron anti-colinérgicos (95,45%) y recomendaciones sobre pautas de estilo de vida (85,32%). En la segunda visita se detectó mejora significativa en los síntomas de las comorbilidades asociadas.
ConclusionesLa identificación y tratamiento de los síntomas de VH es importante para reducir el impacto de la enfermedad y de las patologías asociadas.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora