The functional symptoms of the filling phase and detrusor overactivity are two inter-related dysfunctions of the lower urinary tract. We have aimed to study the participation of the lesion of the pudendal nerve in both urinary dysfunctions.
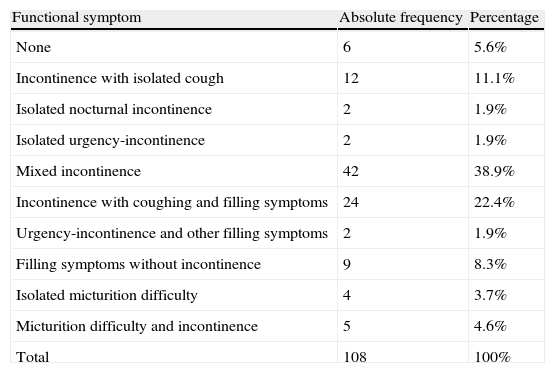
Material and methodsA cross-sectional cutoff study in a series of 108 women was carried out. The study consisted in the questioning on the presence of functional symptoms of the lower urinary tract, cystomanometry and determination of peripheral pudendal nerve latency time, selective electromyography of the external anal sphincter and determination of the sacral reflex latency time.
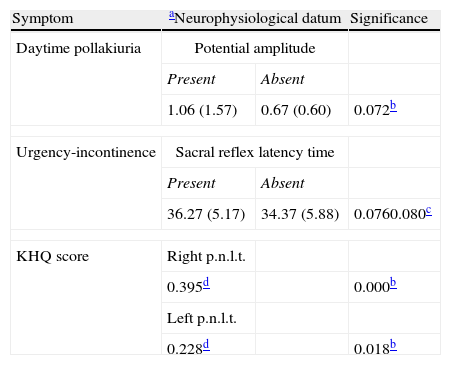
ResultsA tendency was observed toward significance between the presence of pollakiuria amplitude of motor unit potentials (greater in presence of pollakiuria) and the presence of urgency-incontinence and time of sacral latency (greater in the presence of urge incontinence) and a significant relation between the score on the King's Health Questionnaire and peripheral pudendal nerve latency time. Regarding detrusor hyperactivity, greater sacral latency time was observed in patients with overactivity with tendency toward significance.
ConclusionsThere is a relation between pudendal innervation alterations and presence of symptoms in the filling phase and detrusor overactivity. This relation would explain the therapeutic action of the perineal rehabilitation on these dysfunctions.
La presencia de los síntomas funcionales de la fase de llenado y la hiperactividad del detrusor son dos disfunciones del tracto urinario inferior relacionadas entre sí. Pretendemos estudiar la participación de la lesión del nervio pudendo en ambas disfunciones urinarias.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio transversal de corte en una serie de 108 mujeres. El estudio consistió en un interrogatorio sobre la presencia de síntomas funcionales del tracto urinario inferior, cistomanometría y determinación del tiempo de latencia periférico del nervio pudendo, electromiografía selectiva del esfínter anal externo y determinación del tiempo de latencia del reflejo sacro.
ResultadosSe observó una tendencia hacia la significación entre la presencia de polaquiuria y la amplitud de los potenciales de unidad motora (mayores en presencia de polaquiuria) y de la presencia de urgencia-incontinencia y el tiempo de latencia sacro (mayor en presencia de urgencia incontinencia), y una relación significativa entre la puntuación del King's Health Questionnaire y el tiempo de latencia periférico del nervio pudendo. Respecto de la hiperactividad del detrusor se observó un mayor tiempo de latencia sacro en pacientes con hiperactividad con tendencia hacia la significación.
ConclusionesExiste una relación entre las alteraciones de la inervación pudenda y la presencia de síntomas de la fase de llenado e hiperactividad del detrusor. Esta relación explicaría la acción terapéutica de la rehabilitación perineal sobre estas disfunciones.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora