To determine the current state of kidney transplantation (KT) training in a country that is leader in organ donation and transplantation.
Material and methodsWe conducted an online survey by e-mail to 138 urology residents. The survey contained 5 sections: affiliation, training in KT, interest in KT, residents of transplant centers and residents of nontransplant centers.
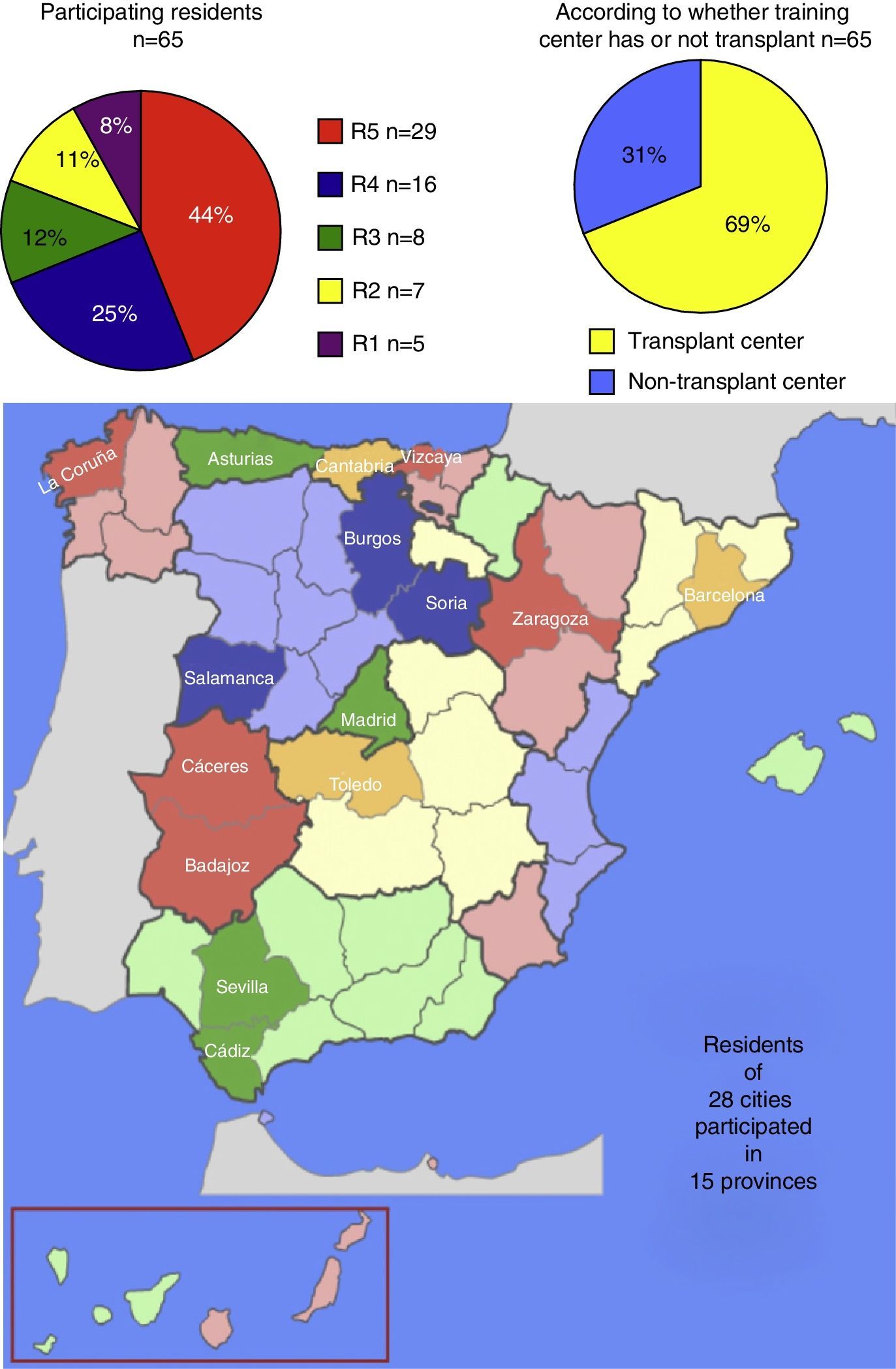
ResultsSixty-five residents responded, 47.1% of the urologists in training surveyed, representing 28 cities and 15 provinces.
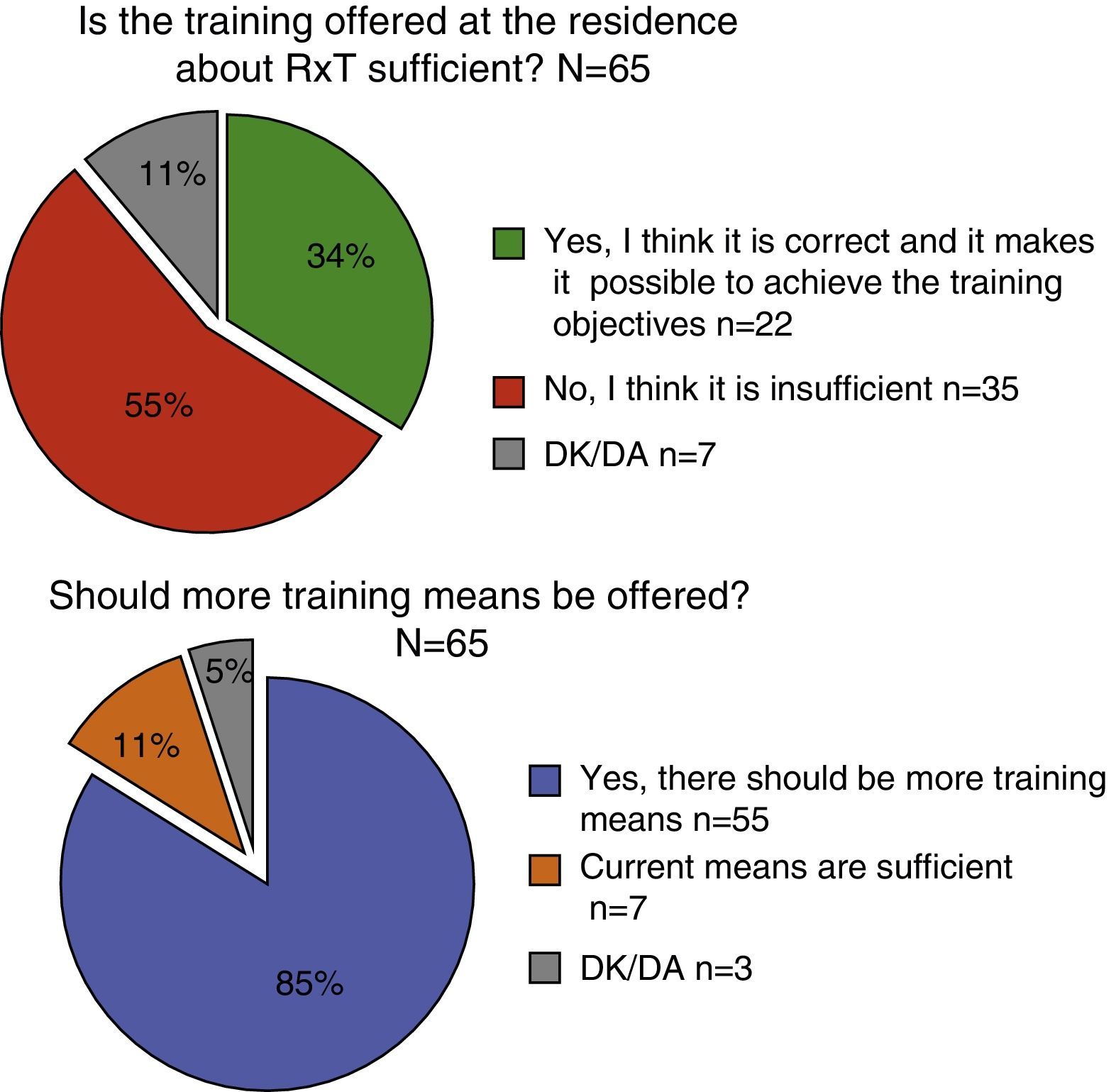
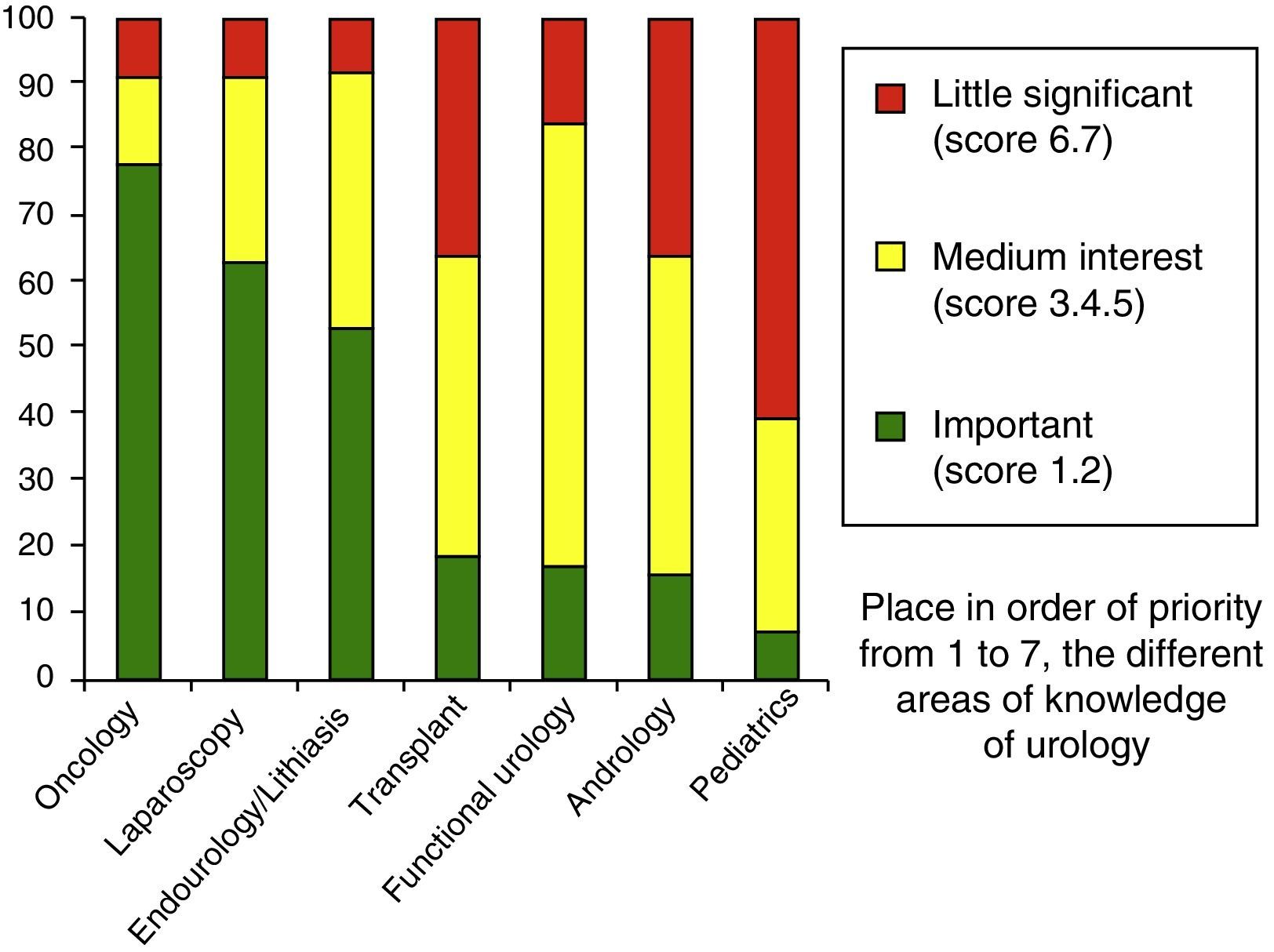
Fifty-five percent (n=36) of the respondents deemed the KT training offered during their residency as insufficient, and 85% (n=55) demanded more resources. More than half were not confident in their abilities to perform transplantation surgery over the course of their residency (n=35). Nineteen percent of the residents considered KT an important discipline in their residency, with a mean score of 56.2 (1–100).
Among the residents of the transplant centers (69.2%, n=45), 73% (n=33) considered KT when choosing a center for their residency. Of the surveyed residents from nontransplant centers (30.7%, n=20), 45% (n=9) do not perform an external rotation in KT.
ConclusionsThe surveyed residents demand more training in KT. The most common situation is to end a residency without having performed a complete KT.
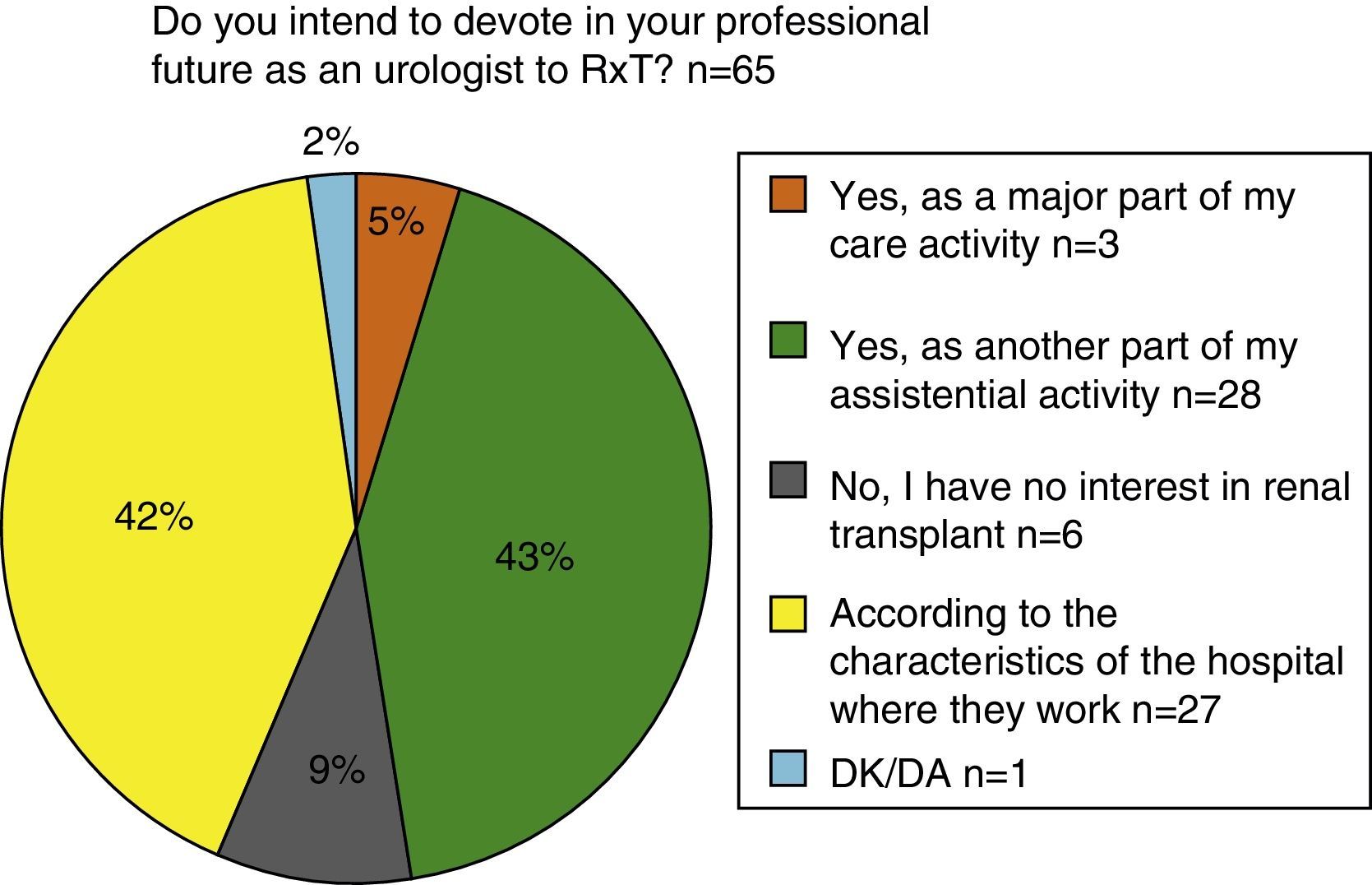
KT is considered an asset when selecting a resident medical intern position and commonly they are part of the transplantation team. The majority of residents are trained in centers with less than 75 transplants/year. External rotations in KT are not the rule in centers where transplantation is not performed.
Conocer la situación actual sobre el adiestramiento en trasplante renal (TxR) en un país líder en donación y trasplante.
Material y métodosRealizamos una encuesta on-line vía correo electrónico a 138 residentes de urología con 5 apartados: filiación, formación en TxR, interés por el TxR, residentes de centros trasplantadores y de centros no trasplantadores.
ResultadosRespondieron 65 residentes, un 47,1% de los urólogos en formación encuestados, desde 28 ciudades en 15 provincias.
Para un 55% (n=36) la formación que se ofrece sobre el TxR les parece insuficiente y el 85% (n=55) demanda más medios. Más de la mitad no confía en realizar una cirugía de trasplante a lo largo de su residencia (n=35). El 19% lo considera una disciplina importante, otorgándole una puntación media de 56,2 (1-100).
Entre los residentes de centros trasplantadores—69,2% (n=45)—: el 73% (n=33) consideraron el TxR a la hora de elegir centro para hacer la residencia. Los residentes encuestados de centros no trasplantadores—30,7% (n=20)—: un 45% (n=9) no realiza rotación externa en TxR.
ConclusionesLos residentes encuestados demandan más formación en TxR. La situación más habitual es terminar la residencia sin haber realizado un TxR de forma completa.
Se contempla el TxR como un activo a la hora de elegir plaza MIR. El residente forma habitualmente parte del equipo de trasplante. La mayoría se forma en centros con menos de 75 trasplantes/año. La rotación externa en TxR no es la norma en los centros donde no se realiza trasplante.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora