With the advanced laparoscopic and robotic surgery, thromboembolic prophy-laxis in urologic procedures has traditionally been based on the experience of other surgicalspecialties. This paper aims to analyze the current recommendations, through a detailed studyof the European clinical guidelines and bibliography, applying the recommendations of throm-boprophylaxis to the daily urological practice.
ObjectivesTo elaborate general recommendations to surgical patients in Urology, avoidingthe risk of perioperative thromboembolic events. Optimize medication in chronic patients andaccurately classify who are eligible for bridge therapy.
Material and methodsA review of the available literature and the European clinical guidelineswas carried out. We analyzed the most recent consensus articles by studying the availablebibliography, trials and reviews on which the European guidelines for thromboprophylaxis inurology are based.
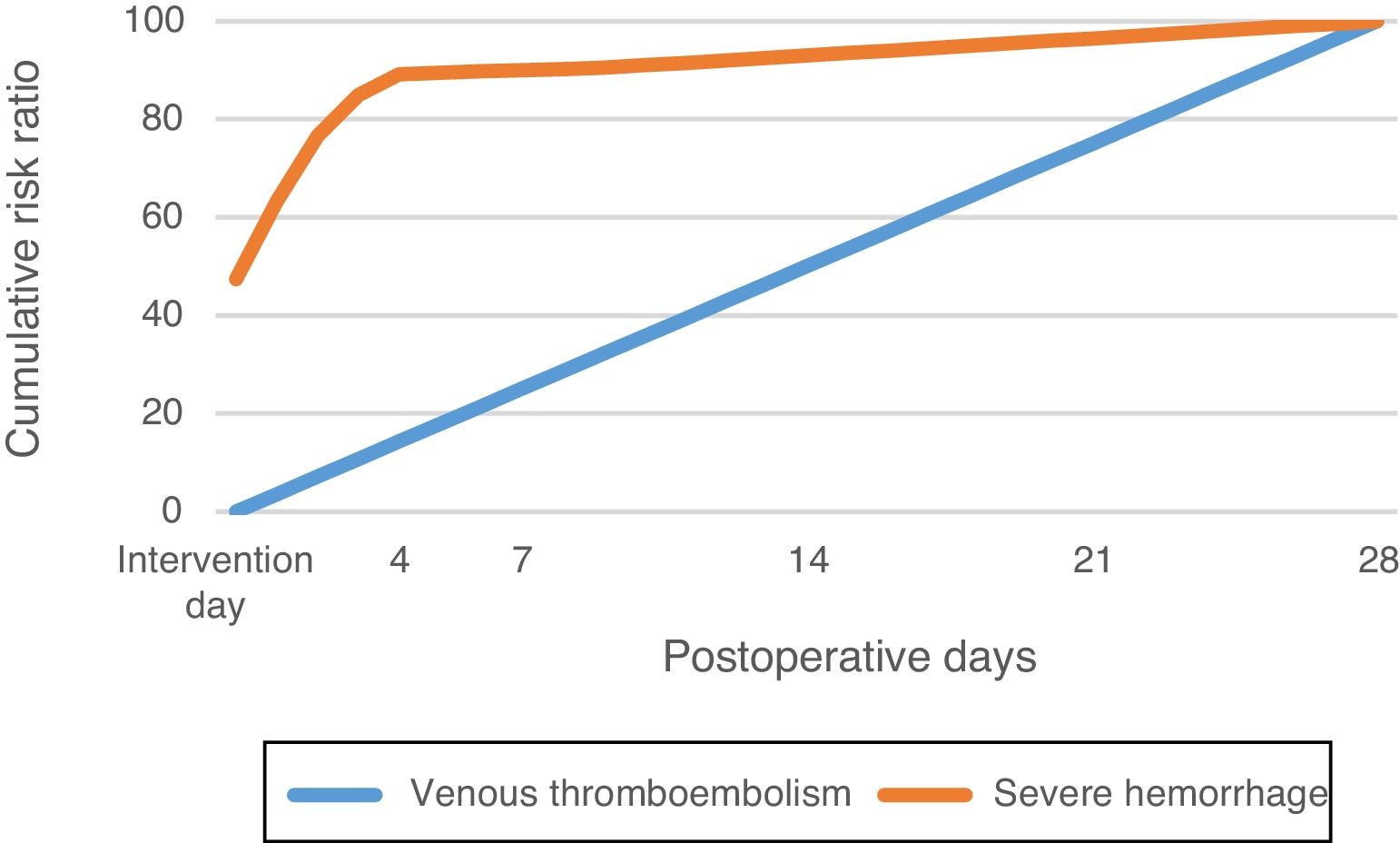
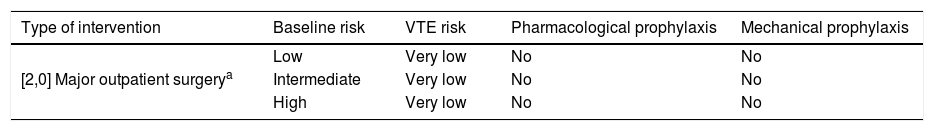
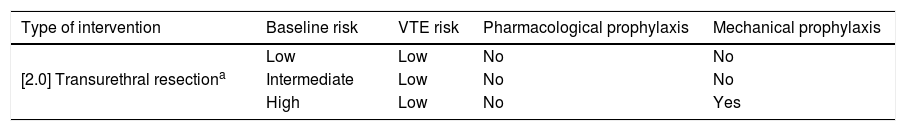
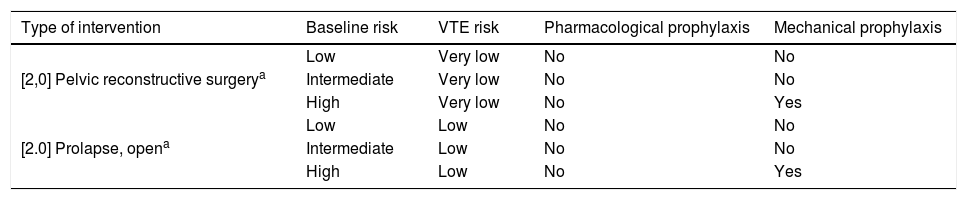
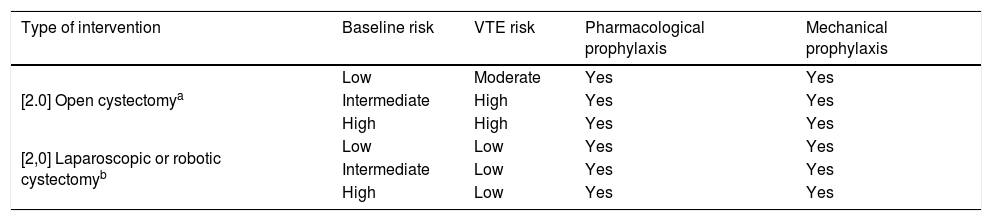
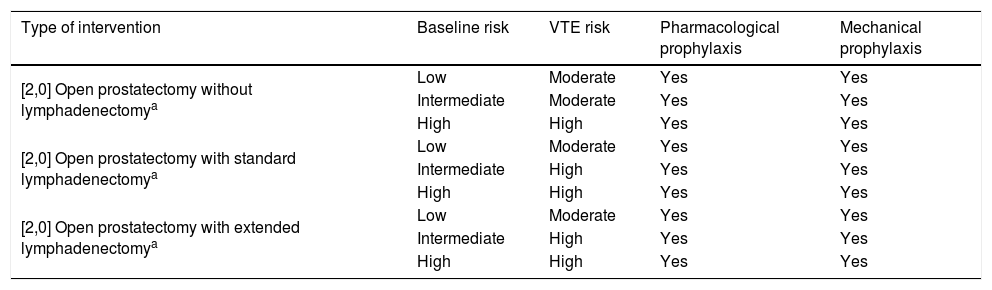
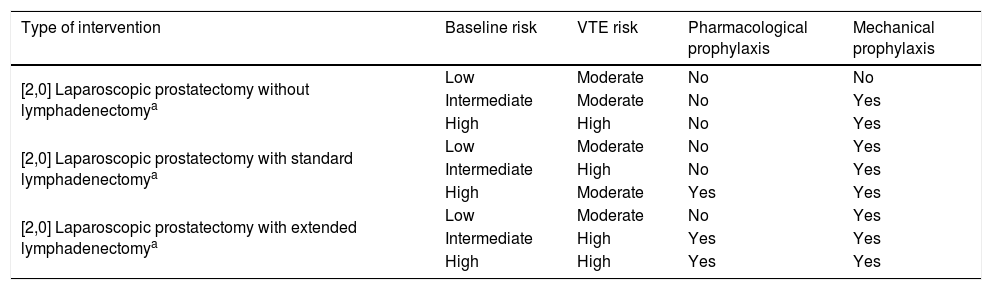
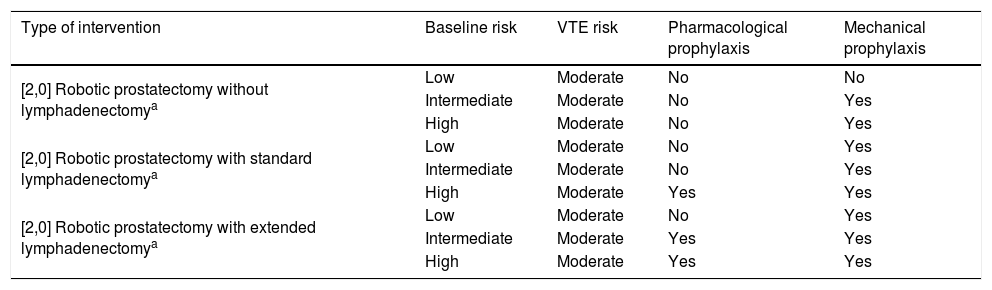
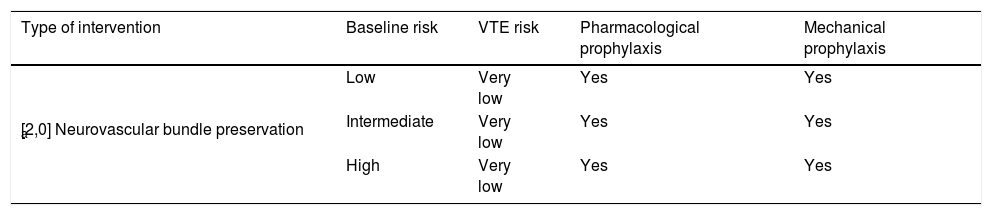
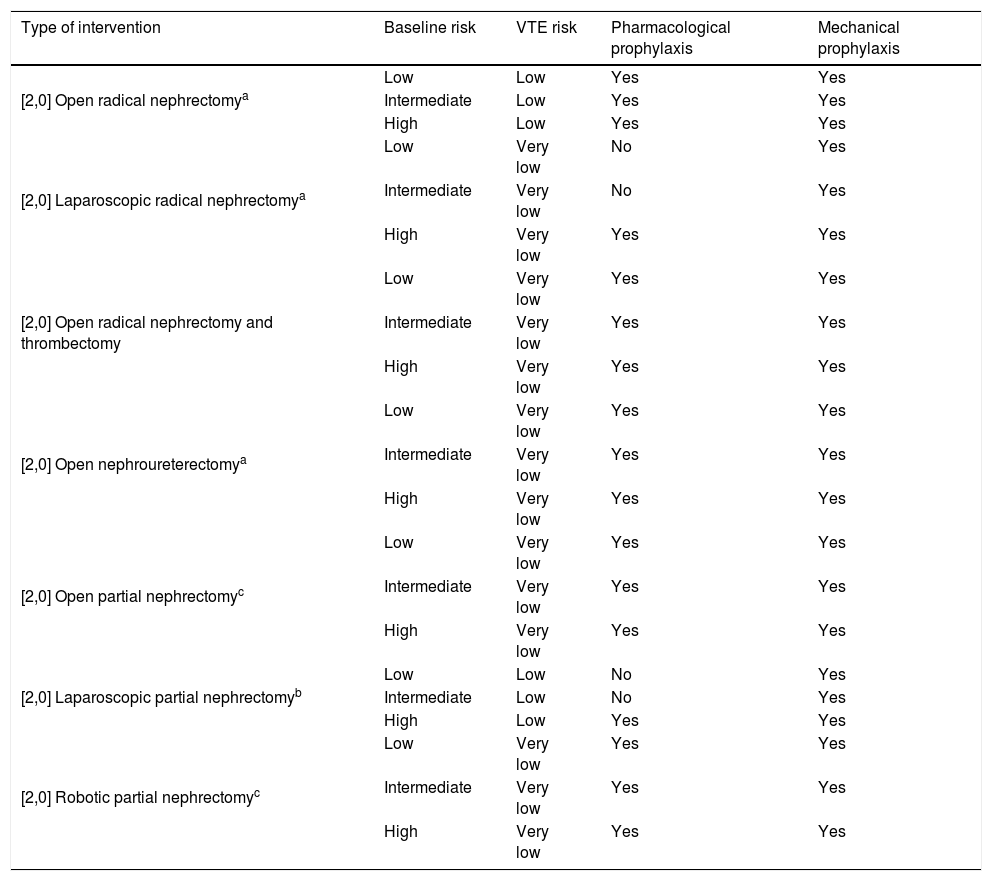
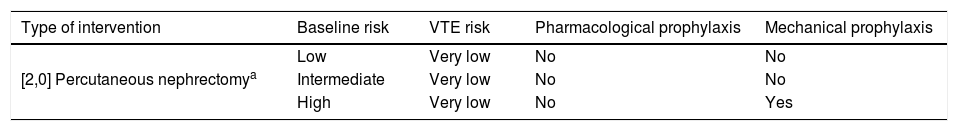
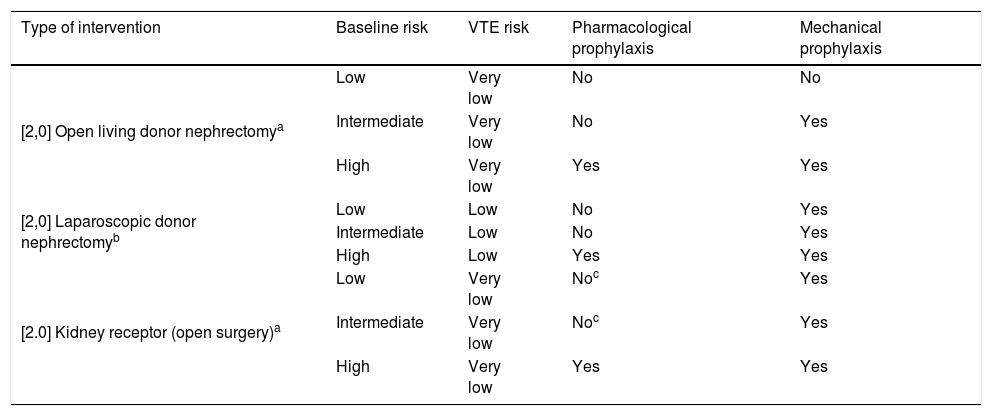
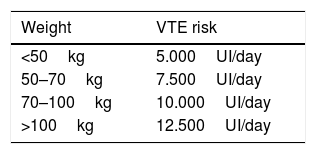
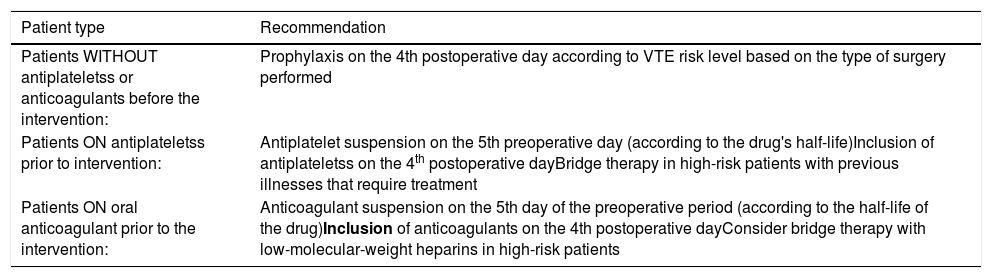
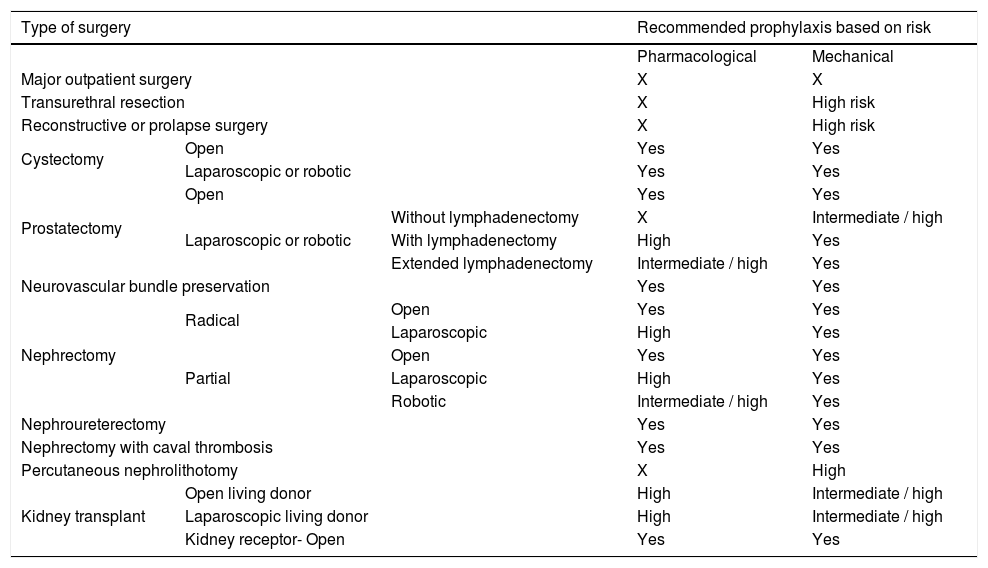
ResultsThromboembolic prophylaxis should be targeted towards surgeries that require abdo-minal approaches, prolonged bed rest or oncological pathologies. Bridge therapies with lowmolecular weight heparins should be limited. Patients undergoing treatment for chronic condi-tions can benefit from bridge therapies in specific cases.
ConclusionsAccording to the current guidelines, there might be an overuse of heparins in thedaily clinical practice. The development of -direct oral- anticoagulants have shown to reducethe time to reintroduction of medication for chronic conditions as well as a more effectivebleeding management.
Con el avance de la cirugía laparoscópica y robótica, la profilaxis tromboembó-lica en los procedimientos urológicos se han basado clásicamente en la experiencia de otrasespecialidades quirúrgicas. En este trabajo se realiza un análisis de la actualidad de las recomen-daciones, basado en un estudio pormenorizado de las guías clínicas europeas y en la bibliografía,aplicando las recomendaciones de tromboprofilaxis a la práctica urológica diaria.
ObjetivosElaborar unas recomendaciones generales aplicables a los pacientes quirúrgicos enurología, evitando la aparición de eventos tromboembólicos en el periodo perioperatorio. Opti-mizar la medicación y el ajuste en pacientes crónicos y conocer qué pacientes son candidatosa terapias puente.
Material y métodosSe ha realizado una revisión de la literatura disponible y de las guías clí-nicas europeas. Se analizan los artículos de consenso más recientes realizando una revisión dela bibliografía disponible y los estudios y revisiones en los que se basan las guías europeas detromboprofilaxis en urología.
ResultadosLa profilaxis tromboembólica se debe emplear en aquellas cirugías que requieranabordajes abdominales, encamamiento prolongado o enfermedades oncológicas. Las terapiaspuente con heparinas de bajo peso molecular deben ser reducidas. Los pacientes en tratamientocrónico se pueden beneficiar de terapias puente en casos concretos.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora