To analyze the diagnostic accuracy of the VI-RADS® system in the differentiation of non-muscle-invasive bladder tumors (NMIBT) from muscle-invasive bladder tumors (MIBT) in suspicious cystoscopic findings without prior transurethral resection (TUR) evaluated by radiologists with no prior experience in its use.
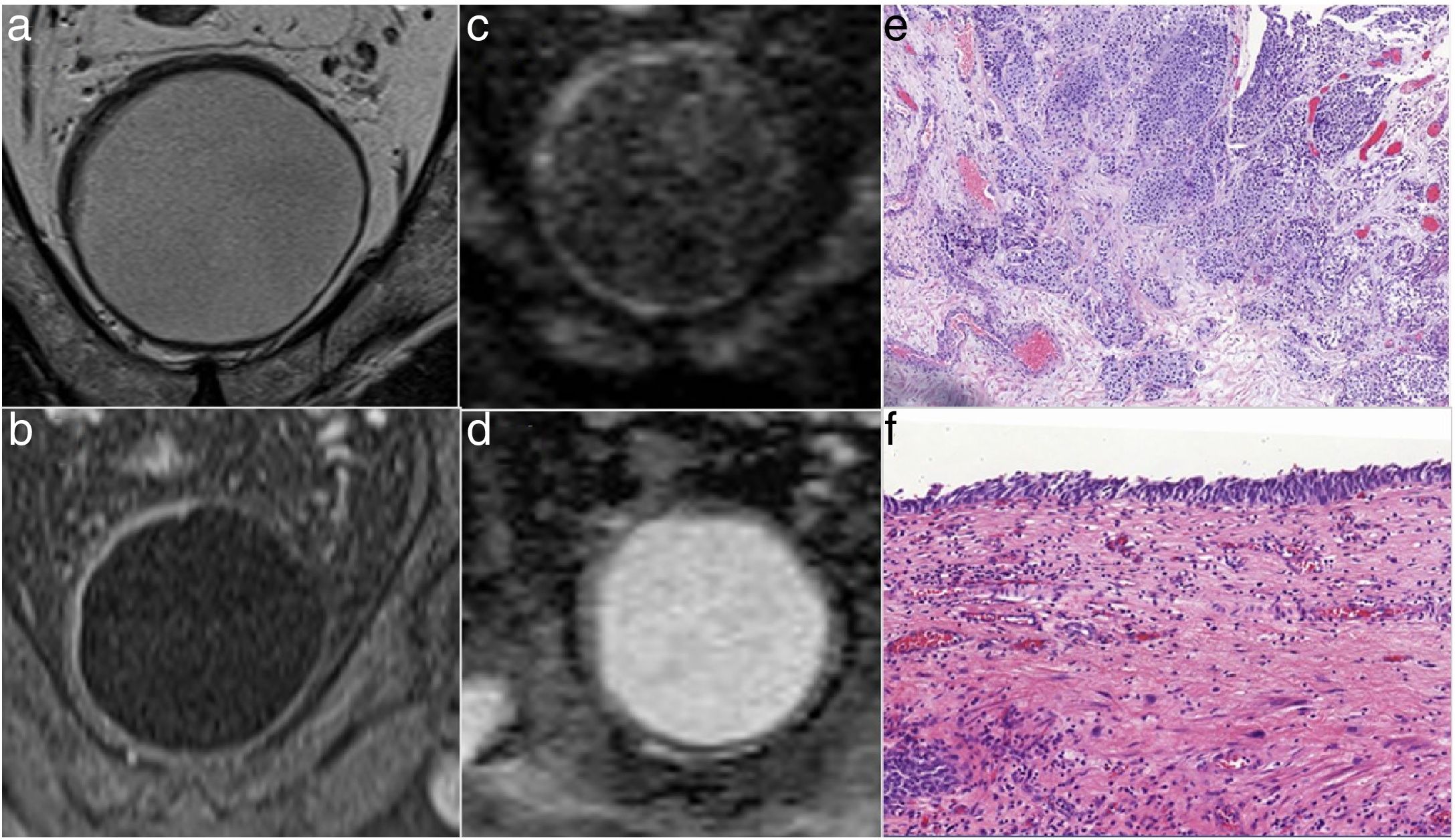
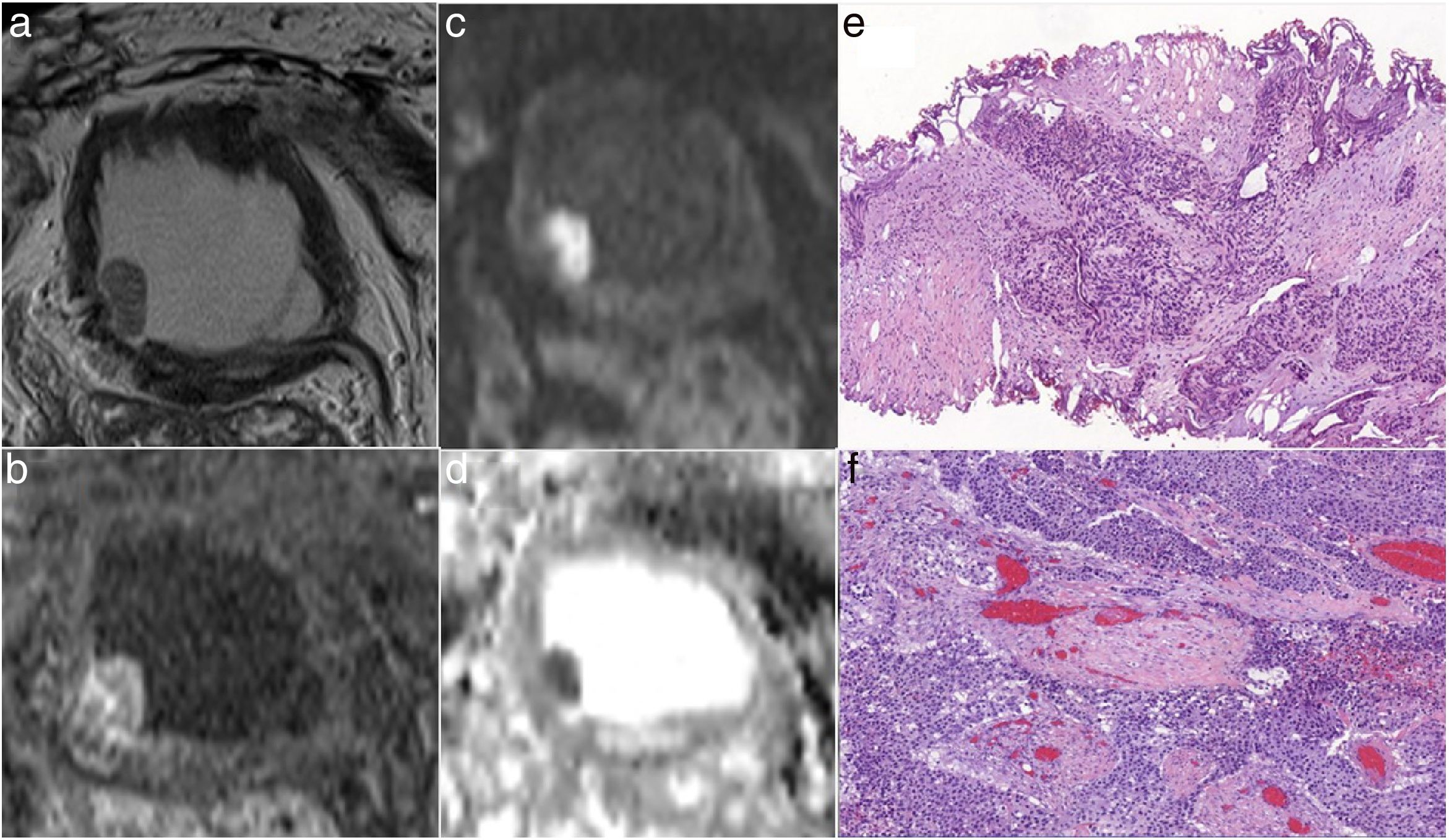
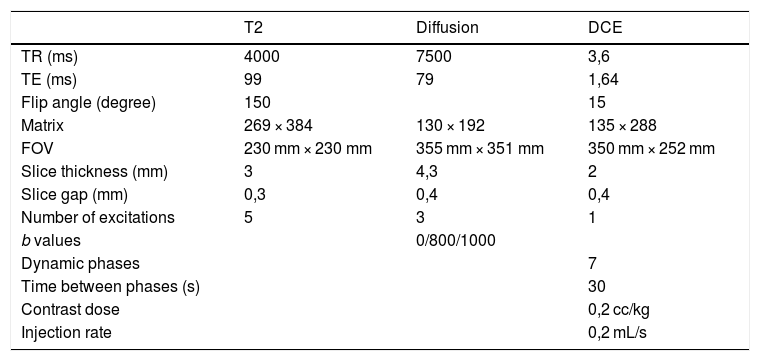
Material and methodsRetrospective study carried out with 18 patients with suspicious lesions in cystoscopy. All of them underwent MRI of the bladder. Two radiologists with no prior experience in the use of the VI-RADS® system evaluated the results. All patients underwent TUR of the suspicious lesions after MRI. The sensitivity and specificity of the system were analyzed for VI-RADS® values ≥3 or VI-RADS® ≥4, as well as the Cohen’s kappa coefficient between both radiologists.
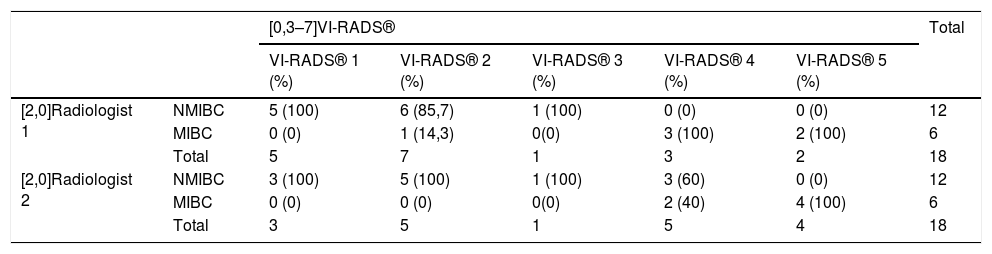
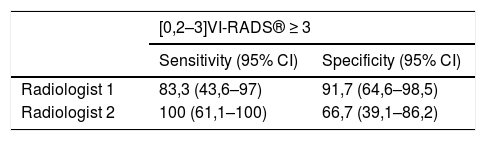
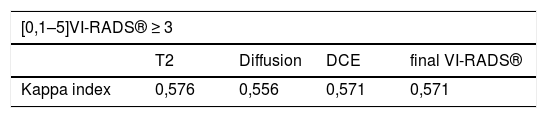
ResultsThe mean values of sensitivity and specificity of both radiologists considering both the VI-RADS® ≥3 or VI-RADS® ≥4 values were 91.7% and 87.5%, respectively. The kappa coefficient considering the VI-RADS® ≥3 as positive, was 0.551 (P < .05), while considering the VI-RADS® ≥4 as positive, it was 0.571 (P < .05).
ConclusionThe VI-RADS® system presents excellent sensitivity (91.7%) and specificity (87.5%) values in the classification of MIBT performed by radiologists with no prior experience in its use, with a moderate interobserver agreement.
Analizar la precisión diagnóstica del sistema VI-RADS® en radiólogos sin experiencia previa en su uso para diferenciar tumores de vejiga no músculo-infiltrantes (TVNMI) de tumores de vejiga músculo-infiltrantes (TVMI) en lesiones sospechosas de malignidad en cistoscopia sin resección transuretral previa (RTU).
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo en el que se incluyeron 18 pacientes con lesiones sospechosas en cistoscopia a los que se les realizó una RM de vejiga. Dos radiólogos sin experiencia previa en el sistema VI-RADS® evaluaron los estudios. Tras la RM, a los pacientes se les realizo una RTU de las lesiones sospechosas. Se analizó la sensibilidad y especificidad del sistema para valores VI-RADS® ≥3 o VI-RADS® ≥4, así como el índice kappa de cohen entre ambos radiólogos.
ResultadosLos valores medios de sensibilidad y especificidad de ambos radiólogos considerando tanto a los estudios VI-RADS® ≥3 o VI-RADS® ≥4 fueron 91,7% y 87,5% respectivamente. El índice kappa considerando los estudios VI-RADS® ≥3 positivos fue de 0,551 (P < ,05) y considerando positivos los estudios VI-RADS® ≥4 de 0,571 (P < ,05).
ConclusiónEl sistema VI-RADS® presenta unos excelentes valores de sensibilidad (91,7%) y especificidad (87,5%) en la clasificación de los TVMI cuando lo utilizan radiólogos sin experiencia previa en su uso con una moderada concordancia interobservador.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora