The role of renal mass (RM) biopsy is currently under discussion. As a result of the progressive increase in the incidental diagnosis of RMs (which have a higher percentage of benignity and well-differentiated cancers), new approaches have emerged such as observation, especially with elderly patients or those with significant comorbidity. RM biopsy (RMB) should provide sufficient information for making this decision, but so far this has not been the case. We examine our prospective series of in-bench RMBs after surgery and compare them with the anatomy of the removed specimen.
Material and methodsWe obtained (prospectively, in-bench and with a 16-gauge needle) 4 biopsies of RMs operated on in our department from October 2008 to December 2009. These RMs were analyzed by 2 uropathologists and compared with the results of the specimen.
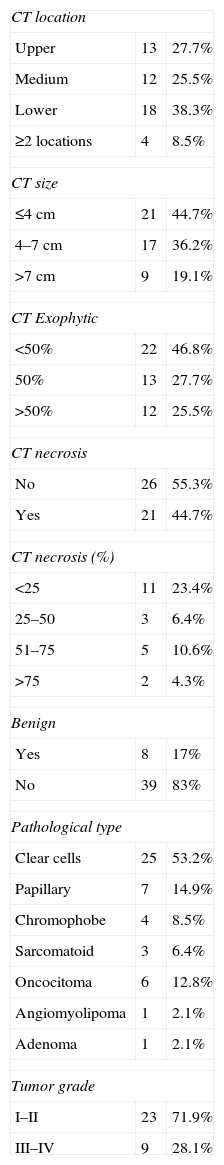
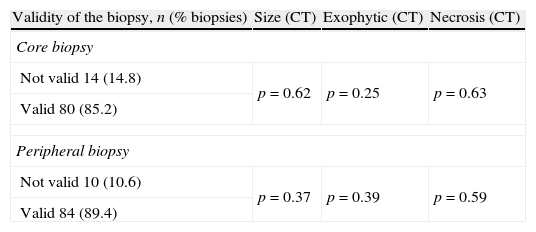
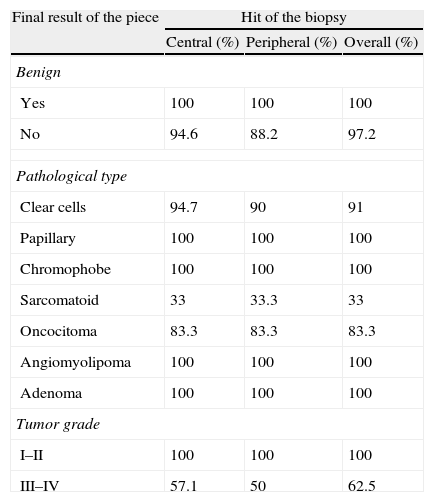
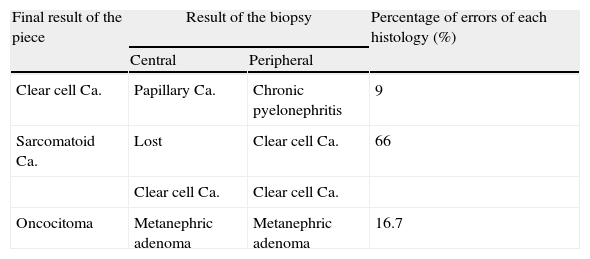
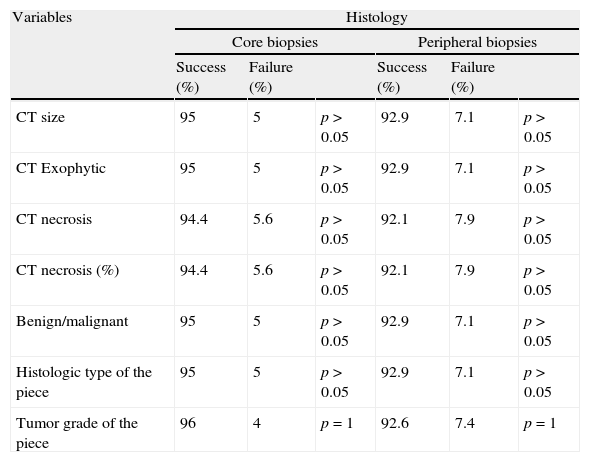
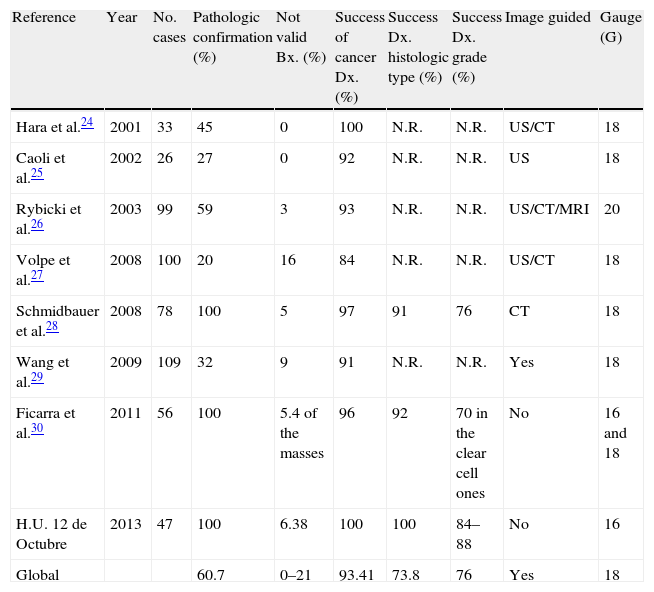
ResultsWe analyzed 188 biopsies (47 RMs); 12.75% were “not valid”. The ability of biopsy to diagnose malignancy or benignity was 100%, and the coincidence in the histological type was 95%. The success in determining the tumor grade was 100% when the cancer was low-grade and 62% when high-grade. None of the analyzed data (necrosis, size, etc.) influenced the results in a statistically significant manner.
ConclusionRMB with a 16-G needle enables the differentiation between malignancy and benignity in 100% of cases, with a very similar diagnostic accuracy in the tumor type. Tumor grade is still the pending issue with renal mass biopsy.
El papel de la biopsia de masa renal (MR) está actualmente en discusión. Ante el aumento progresivo en el diagnóstico incidental de MR (que tienen un mayor porcentaje de benignidad y cánceres bien diferenciados) surgen nuevos planteamientos como la observación, especialmente en pacientes añosos o con importante comorbilidad. La biopsia de la MR (BMR) debería proporcionar datos suficientes para tomar esa decisión, pero hasta ahora no ha sido así. Estudiamos nuestra serie prospectiva de BMR tomadas en banco tras la cirugía, comparándola con la anatomía de la pieza extirpada.
Material y métodosSe obtuvieron, prospectivamente y en banco, 4 biopsias con aguja 16 Gauge (G) de las MR operadas en nuestro servicio desde octubre de 2008 a diciembre de 2009. Estas fueron analizadas por 2 uropatólogos y comparadas con el resultado de la pieza.
ResultadosSe analizaron 188 biopsias (47 MR): 12,75% «no validas». La capacidad de la biopsia para diagnosticar la malignidad o benignidad fue del 100%, y la coincidencia en el tipo histológico del 95%. El acierto en el grado tumoral fue del 100% si el tumor era de bajo grado y del 62% si era de alto grado. Ninguno de los datos estudiados (necrosis, tamaño…) influyeron de manera estadísticamente significativa en los resultados.
ConclusiónLa BMR con aguja 16G permite diferenciar entre malignidad y benignidad en 100% de los casos, con una exactitud diagnóstica en el tipo tumoral muy similar. El grado tumoral sigue siendo la asignatura pendiente de la BMR.