The active ingredients of sunscreens protect against the harmful effects of solar radiation. According to their mechanism of action, sunscreens can be classified as physical and chemical. Despite their clear benefits, chemical sunscreens can cause allergic contact dermatitis and photoallergy. The filter octocrylene belongs to the cinnamate family. Until recently, it was regarded as a stable molecule, which was neither allergenic nor irritant.1 The dibenzoylmethane derivative azobenzone (Parsol 1789) has the capacity to absorb ultraviolet light over a wider range of wavelengths than many sunscreens and has been used in many preparations.2
We report two cases; in the first case, a one-year-old boy experienced an erythematous pruriginous eruption on the face that spread to the rest of his body 3h after application of Isdin® cream (SPF 15) without exposure to sunlight. No other symptoms were observed. The eruption disappeared in five days without treatment. A month later, he developed a new eruption in the contact area after application of La Roche-Posay cream (SPF 50)®, which also resolved without treatment in a few days. In the second case, a one-year-old child developed an erythematous maculopapular eruption with intense pruritus in the contact area 2h after application of Isdin®, which disappeared without treatment in seven days. No other clinical symptoms were observed.
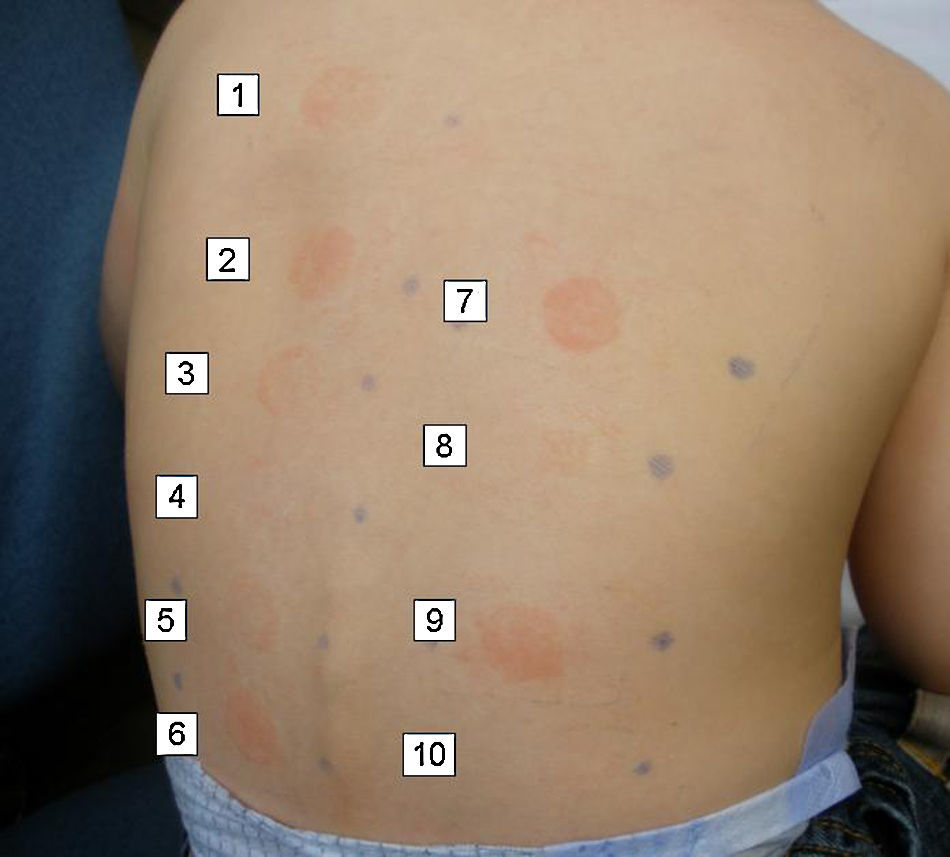
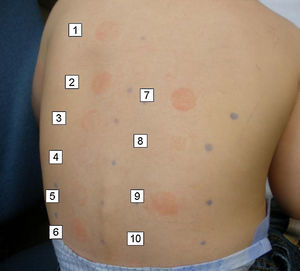
In the allergy study, a standard patch testing was applied (True Test®). The results were negative at 48 and 96h. Patch testing with the two sunscreens involved in the reactions gave a positive reading (+++) at 48 and 96h in both cases. Patch testing with a battery of sunscreens gave a positive reading (++) at 48 and 96h to butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane 2% (Parsol 1789) in both cases (Fig. 1).
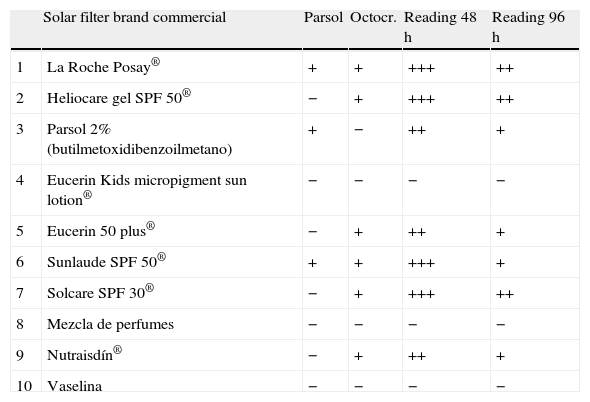
Since only one of the sunscreens contained parsol, we decided to test with other sunscreens. The results are shown in Table 1. All sunscreens that gave a positive patch test reaction contained octocrylene, which is included in some sunscreen series only. In order to confirm the positivity of octocrylene, we requested this component from the laboratory Chemotechnique for patch testing. Readings were positive (+++) in both cases at 48 and 96h.
Results of patch testing with other sunscreens.
| Solar filter brand commercial | Parsol | Octocr. | Reading 48h | Reading 96h | |
| 1 | La Roche Posay® | + | + | +++ | ++ |
| 2 | Heliocare gel SPF 50® | − | + | +++ | ++ |
| 3 | Parsol 2% (butilmetoxidibenzoilmetano) | + | − | ++ | + |
| 4 | Eucerin Kids micropigment sun lotion® | − | − | − | − |
| 5 | Eucerin 50 plus® | − | + | ++ | + |
| 6 | Sunlaude SPF 50® | + | + | +++ | + |
| 7 | Solcare SPF 30® | − | + | +++ | ++ |
| 8 | Mezcla de perfumes | − | − | − | − |
| 9 | Nutraisdín® | − | + | ++ | + |
| 10 | Vaselina | − | − | − | − |
Of the sunscreens tested, the only one with a negative result was the physical sunscreen Eucerin Kids Sun Micropigment Lotion®, which has no chemical components.
We report two cases of allergic contact dermatitis in infants who were sensitised to sunscreen (Parsol 1789 and octocrylene). Although these compounds have traditionally been considered safe, reports of allergic reactions are increasingly frequent.3 Octocrylene is an emergent allergen, which appears to cause direct allergic contact dermatitis in children, and allergic photocontact dermatitis in adults, often in patients previously diagnosed with photocontact allergy to topical ketoprofen.4 Therefore, we recommend patch testing with a comprehensive series of sunscreen ingredients, as well as with the actual commercially available sunscreens responsible for patient dermatitis, and awareness of the risk of applying chemical filters in infants. Only physical sunscreen should be used in this age group.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human subjects and animals in researchThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans for this investigation.
Confidentiality of Data. The authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consent. The authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.