INTRODUCTION
Recurrent fever is frequent during the childhood and it usually has an infectious aetiology. Periodic fever, much less frequent, refers to predictable episodes, due to its regular appearance, of recurrent fever with no apparent infectious cause. PFAPA syndrome appears as one of the causes of periodic fever in paediatrics.
Marshall et al1 describe in 1987 a new syndrome characterised by periodic episodes of high fever, aphtous stomatitis, pharyngitis and cervical adenitis in 12 children. In 1989, after the appearance of new cases in the literature2-3, the acronym PFAPA (periodic fever, aphtas, pharyngitis and cervical adenopathies) was created to define this entity4.
Later on, new cases have been described, being the revisions by Thomas et al5 and Padeh et al6 the most remarkable ones, with the combined collection of more than 120 patients. The long-term monitoring of a great number of them shows a favourable evolution with no sequels.
Nevertheless, nowadays it is probably an infradiagnosed syndrome due to the difficulty of its recognition. The ignorance of its benign nature gives rise to unnecessary complementary exams and unsuccessful treatments, with the consequent concern of the family that these cases provoke.
We present the case of a patient diagnosed of PFAPA syndrome after excluding other causes of periodic fever.
CASE REPORT
A 10-year-old girl, Z.A.R., who has been sent to the Immunoallergy Department of our Centre for an immune study. She does not present any familiar antecedent of interest. As personal antecedent we should highlight the practice of an adenoidectomy when she was two and a half years old due to repeated otitis with a good subsequent evolution. When she is 6 and a half years old she begins to suffer from repetitive episodes of high fever (39-40 °C) with great affliction of the general state of health, odynophagia and pain of the muscles of the neck. The clinical exploration in one of the bouts proved: pharyngitis, cervical adenopathy and oral aphtous lesions. These lesions are occasionally presented and the patient refers to them as not very annoying. These episodes have a duration of 4-7 days and they are very sporadic in the beginning but they have a monthly periodicity in the last year. The patient presents prodromes by means of cephalalgia and myalgias of inferior extremities the day before fever begins, being able to predict in most cases the appearance of fever. The patient is asymptotic between the periods and the growth and development are normal for the age. She has received various courses of antibiotics by oral and intramuscular administration (penicillin, cephalosporin, macrolides), as well as habitual antithermics with no satisfactory response. In the analytical studies carried out in five occasions, when there were febrile episodes, we should highlight: leukocitosis (between 14.000-16.000 leukos/mmcc), slight deviation to the left and increase of CRP (between 70 and 120 mg/dl), alterations that become normal when the patient is asymptomatic. Hemocultures and pharyngeal cultures have been negative, as well as serological studies carried out against CMV (cytomegalovirus), EBV (Epstein-Barr virus) and HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). In the same way, there is no alteration of the immune system after an extensive study: Ig G (7.320 mg/l) and its subclasses, Ig A (512 mg/l) e Ig A in saliva (25 mg/l), Ig M (657 mg7l), Ig D (36 U/ml), lymphoid populations (B lymphocytes 17 %, T lymphocytes 59 %, T4 lymphocytes 34 %, T8 lymphocytes 25 %, natural killer cells 6 %, T4/T8 rate 1,36, T4 absolute lymphocytes 1.156/mm3), negative ANA and complement (C3 1.300 mg/l, C4 304 mg/l, CH50 31,2 U/ml). The patient has a satisfactory response to a unique dose of oral prednisone (2 mg/kg) with remission of the fever in less than two hours and being free of symptoms in twenty-four hours, with the same response in the following episodes, of current quarterly periodicity, in the fourth year from its beginning.
DISCUSSION
PFAPA syndrome is a not very known entity. It should be included in the differential diagnostic of repetitive episodes of fever that follow a cyclical pattern, allowing thus the prediction of the following bout. In literature, no more than about hundred cases have been documented. The real incidence is probably higher as it is an entity with a difficult recognition due to the unspecific nature of its clinic. On the other hand, the presence of repetitive episodes of high fever that not responds to the conventional treatments implies a family worry that usually leads to a kind of pilgrimage to various centres and specialists in search of an etiology, what makes it difficult the clinical monitoring of the patient, being it crucial for the diagnostical suspicion.
The etiopathogeny of this set of symptoms is still unknown. Is it an infectious disease or an immunity dysregulation? The clinical resolution after a unique dose of corticoids in a great number of patients suggests that the symptoms can be caused by inflammatory cytokines. Preliminary studies in this field show the increase of some cytokines during the febrile episodes, fundamentally g -interferon, TNF and IL-65. On the other hand, any infectious agent can't have been isolated. No familiar patterns have been observed.
The clinic usually begins before the age of 5. It is characterized by episodes of high fever (> 39 °C) of with an unexpected set up and at least one of the following findings: pharyngitis, cervical adenopathy or oral aphtas; they are present between the 65 % and 80 % of the cases. In the case that has been described, pharyngitis and adenopathies are steady in all the bouts, whereas the aphtas are occasionally present. Other described symptoms or signs are chills (80 %), headache (65 %) and digestive symptoms (nauseas, abdominalgia, diarrhoea) in a minor proportion and cutaneous exanthema5,6. There are prodromal symptoms 24 hours before the beginning of fever in 75 % of patients and they are usually headache, irritability or unspecific mialgia.
These bouts have a duration of 4-6 days and they are solved regardless of the antibiotic or antipyretic treatment indicated. They are present with a periodicity of 3-6 weeks, with an average of 11-12 per year. Between the crises, patients remain asymptomatic, with a normal psychomotor growth and development. The average duration of episodes is 4,5 years, with a decrease of its frequency and intensity in a progressive way. In the long-term monitoring of more than 80 children with PFAPA syndrome5, no development of autoimmune diseases, cancer or chronic infectious has been observed.
The good general state of the patient between the episodes, the capacity of the family to predict the beginning of the fever and repetitive failure of antibiotics and analgesics to control it alerted about the PFAPA syndrome.
The data of the laboratory is unspecific with leukocytosis and the only important finding is the moderate increase of GSR (globular sedimentation rate) during the episodes. The inmunologic and serologic studies are negative. In some children an increase of Ig D is observed but it does not reach the values that are observed in the hyper-Ig D syndrome6.
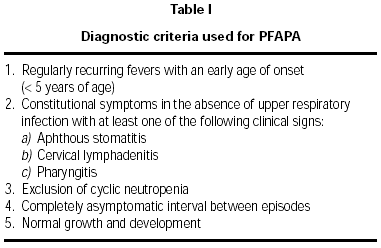
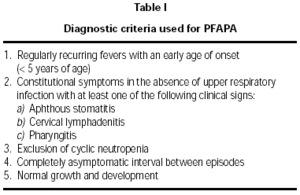
The diagnosis of this syndrome is clinical and it is based on the criteria established by Marshall in 19894. Later on we have the need to put aside the cyclical neutropenia and criteria such as leukocytosis and the increase of GSR are excluded due to its unspecification (table I).
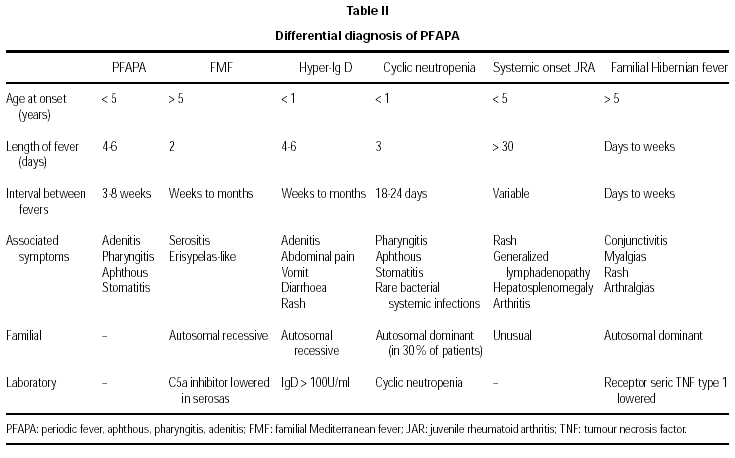
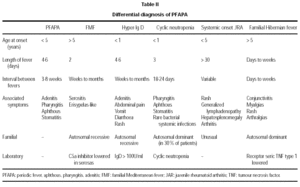
The differential diagnosis should include those entities that appear with episodes of periodic fever. Mainly they are: familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), cyclical neutropenia, hyper-Ig D syndrome, juvenile rheumatic arthritis of systemic presentation and syndrome associated to TNF receptor or also called Hibernian fever. Normally, a detailed anamnesis and physical exploration, together with certain analytical findings, are enough to direct the etiology of such episodes5,8-9 (table II). The cyclical neutropenia is put aside in our case after the serial count of leukocytes, in which the characteristic pattern of periodic neutropenia that defines it is not observed10. The normal values of Ig D in several determinations exclude the syndrome of hyper Ig D. The familial Mediterranean fever, as well as the other mentioned entities, seem unlikely in our patient with regards to its clinical characteristics and the hereditary pattern of some of them9,12.
The lack of response of the clinic to antibiotics and antipyretic is characteristic eventhough the patients have generally taken some of them before being diagnosed. NSAI (Non-steroideal anti-inflammatory) are also ineffective.
The treatment of election of PFAPA syndrome are corticoids: one or two doses of prednisone or oral prednisone (1 mg/kg) usually produces the prompt recovery of fever and the resolution of the rest of symptomatology in less than 24 hours5-6,13. This drastic response supports in a good way the diagnosis. Its specificity has lead to several authors to propose this therapeutical measure as a diagnostical criterion6. The administration of corticoids does not manage to decrease the number of bouts, but it maintains its efficacy in successive bouts. Other proposed treatments have been cimetidine (29 % of efficacy) and tonsillectomy (65 % of efficacy). The isolated adenoidectomy has not obtained favourable results5. This data should be taken with caution because such therapeutical alternatives have been applied to a very limited number of patients.
The decrease of number of episodes after more than four years from the first one makes us think of the quick resolution of the set of symptoms of our patient.
Finally, we should highlight the importance of the recognition of this clinical entity because it will avoid unnecessary complementary studies, the therapeutical approach will be improved and the anxiety of the family will be reduced when offering them an effective treatment and informing them of the benignity of syndrome and the absence of sequels.