Abstracts Asociación Mexicana del Hígado (AMH) 2023
Más datosMetabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is currently the most common chronic liver disease in children and adolescents. In Mexico, there are no studies that demonstrate its incidence and prevalence, nor its clinical and biochemical characteristics; we don't have a clinical practice guideline, nor guidelines for screening, treatment, and follow-up. Our objective is to identify the clinical and biochemical features of MAFLD in overweight and obese pediatric patients.
Materials and methodsObservational, descriptive, ambispective and cross-sectional study. Patients were recruited from the Pediatric Gastroenterology outpatient clinic of the University Hospital of Puebla for a period from 2019 to 2022, selecting those with overweight and obesity, who were confirmed with a diagnosis of MAFLD through biochemical and imaging tests.
Results38 patients met criteria; 63.2% (n=24, ±4.03) correspond to the male sex, compared to 36.8% (n=14, ±3.56) of the female sex. It was more frequent in adolescents (78.9%) and with a higher proportion of patients with obesity (76.3%); no school patient was diagnosed as overweight; all patients in this age group presented obesity at the time of diagnosis.
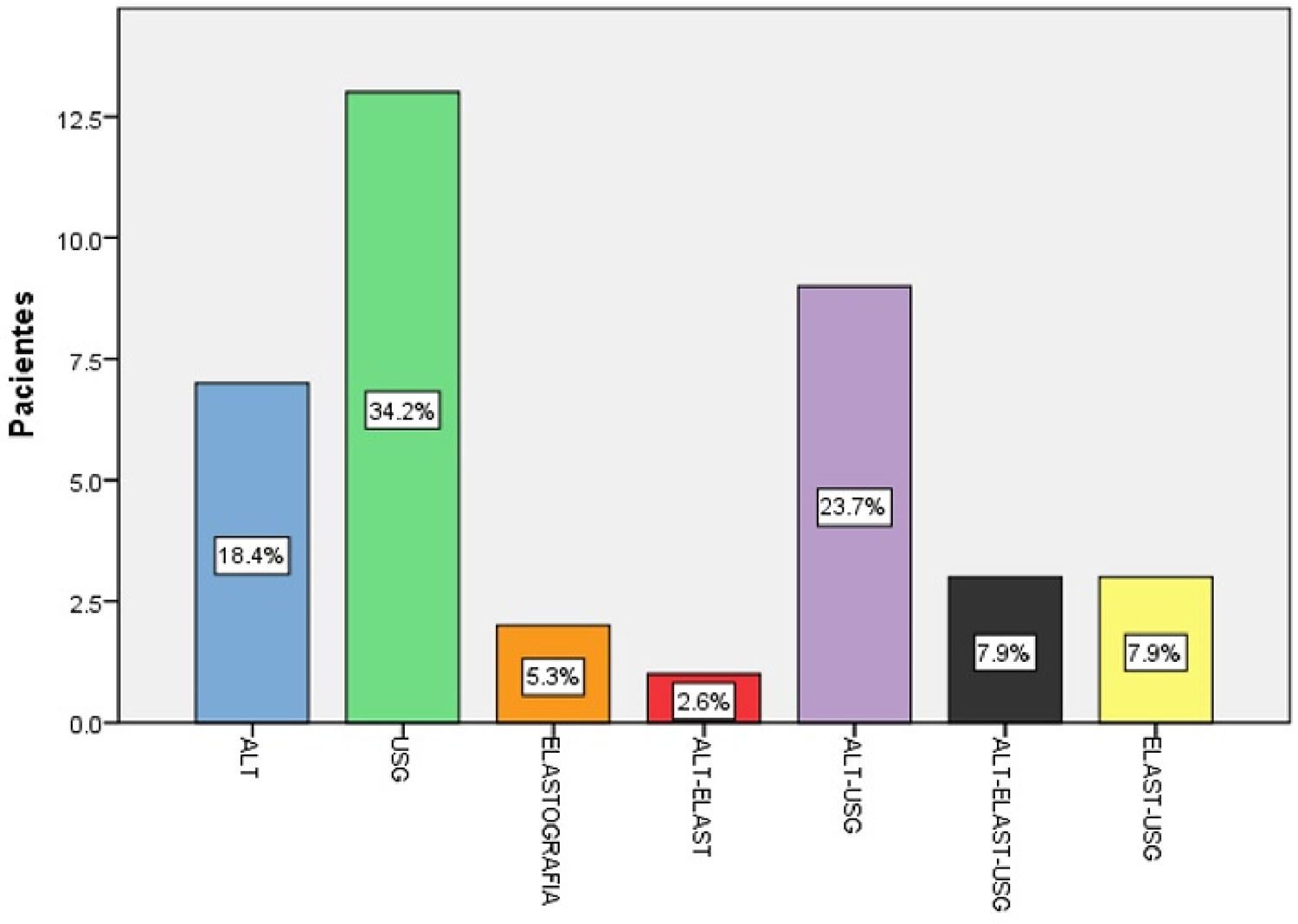
The total number of patients who presented ALT elevation in diagnostic criteria was 52.6%. Regarding metabolic alterations, the following were found more frequently: Hypoalphalipoproteinemia (50%), Hypertriglyceridemia (42.1%) and elevation of HOMA-IR (91.9%). When evaluating Vitamin D levels, all were altered in insufficiency (42.9%) and deficiency (57.1%). NonHDLC/HDLC index levels have a statistically significant correlation (p0.039) with ALT levels.
ConclusionsMAFLD development is more frequent in male adolescents who are overweight and obese. Using ALT levels as criteria for hepatic steatosis by biochemical marker in the absence of an imaging study may facilitate diagnosis in the MAFLD algorithm. The indices associated with lipid levels (TG/HDLC and nonHDLC/HDLC) may indicate an increased risk for developing MAFLD.
Ethical statement
The protocol was registered and approved by the Ethics Committee. The identity of the patients is protected. Consentment was obtained.
Declaration of interests
None
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
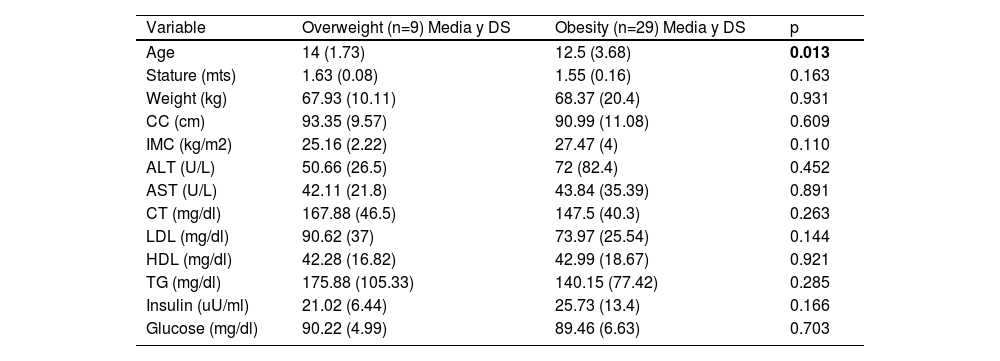
Anthropometric and biochemical data for overweight and obesity
| Variable | Overweight (n=9) Media y DS | Obesity (n=29) Media y DS | p |
| Age | 14 (1.73) | 12.5 (3.68) | 0.013 |
| Stature (mts) | 1.63 (0.08) | 1.55 (0.16) | 0.163 |
| Weight (kg) | 67.93 (10.11) | 68.37 (20.4) | 0.931 |
| CC (cm) | 93.35 (9.57) | 90.99 (11.08) | 0.609 |
| IMC (kg/m2) | 25.16 (2.22) | 27.47 (4) | 0.110 |
| ALT (U/L) | 50.66 (26.5) | 72 (82.4) | 0.452 |
| AST (U/L) | 42.11 (21.8) | 43.84 (35.39) | 0.891 |
| CT (mg/dl) | 167.88 (46.5) | 147.5 (40.3) | 0.263 |
| LDL (mg/dl) | 90.62 (37) | 73.97 (25.54) | 0.144 |
| HDL (mg/dl) | 42.28 (16.82) | 42.99 (18.67) | 0.921 |
| TG (mg/dl) | 175.88 (105.33) | 140.15 (77.42) | 0.285 |
| Insulin (uU/ml) | 21.02 (6.44) | 25.73 (13.4) | 0.166 |
| Glucose (mg/dl) | 90.22 (4.99) | 89.46 (6.63) | 0.703 |
Statistically significant p values were underlined. mts: meters, kg: kilograms, cm: centimeters, mg/dl: milligrams/deciliters, uU/ml: microunits per milliliter.
Figure 1. Type of diagnosis