Abstracts of the 2022 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
Más datosSevere alcoholic hepatitis (AH) has a high mortality rate, and currently, it is still a challenge to be able to establish the prognosis of these patients and their risk of death at admission in order to be able to offer better therapeutic alternatives that save a life in a timely manner. This study aimed to compare several prognostic scores to verify which of them has the best performance in predicting 28-day mortality at admission in patients with AH.
Materials and MethodsObservational, cohort study. Data were collected from patients with severe AH who were hospitalized between January 2010 to May 2022. MELD, MELDNa, MELD3.0, ABIC, Maddrey, Glasgow scale for AH were calculated with admission parameters, and their outcome was verified at 28 days. ROC curves were constructed to compare the different prognostic scales.
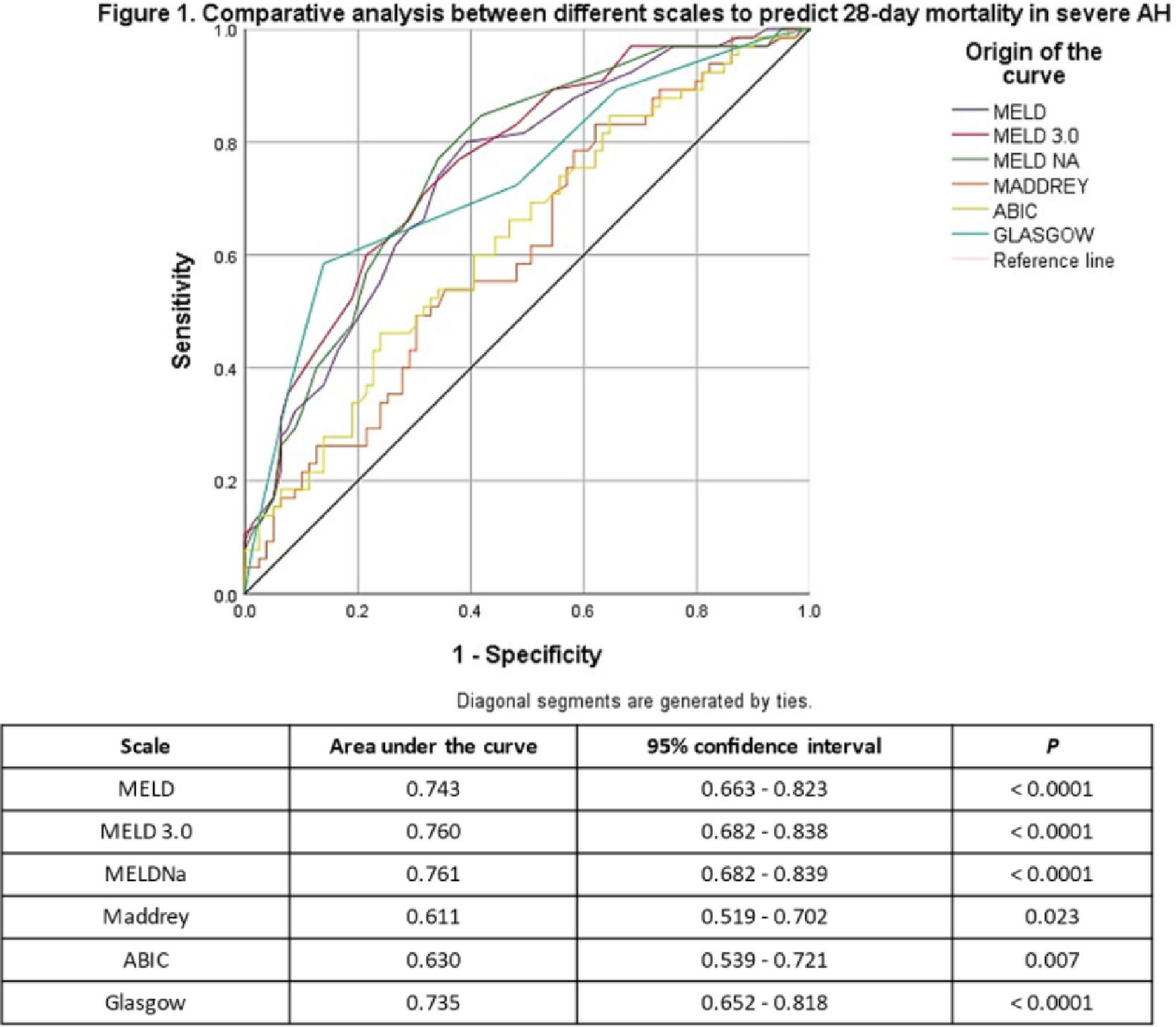
Results144 patients were included, 129 (89.6%) men, mean age 43.3±9.3 years, median grams of alcohol consumed/day were 320 (range: 60-1526). 65 (45.1%) died. The mean of MELD, MELDNa and MELD3.0 were higher among the deceased vs. survivors (33.5±7.5 vs. 27.1±6.2; 34.6±5.7 vs. 29.1±5.7; and 35.8±6.0 vs. 30.1±5.5 respectively; p<0.0001). The ROC curve analysis comparing the prognostic scales is shown in Figure 1.
ConclusionsAH mortality is high. MELDNa and MELD3.0 have the best performance for predicting on admission which patients with AH are at risk of dying in the next 28 days and can be useful tools for prioritizing patients who will require life-saving strategies, such as liver transplantation.