Abstracts of the 2024 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
Más datosYes, Fondecyt # 1241450
Introduction and ObjectivesBackground: There is limited information on features of lean MASLD patients in Latino subjects. We aimed to analyze the features of MASLD in Chilean patients with normal body mass index (BMI), the frequency of the rs738409 risk polymorphism (PNPLA3 I148M variant) and metabolomic profiles in Chilean individuals with MASLD.
Patients / Materials and MethodsA cross-sectional study involving 181 randomly-selected participants diagnosed with MASLD from the prospective Maule Cohort (BMC Public Health. 2016;16:122). Participants were categorized into lean, overweight, and obese groups based on their BMI. The presence of the rs738409 polymorphism was examined using Sanger sequencing. Metabolomics was assessed using UHPLC-MS in a separate group of biopsy-proven MASLD patients. Statistical analyses of clinical data and genotypes encompassed Fisher's exact test, Chi-square test, Kruskal-Wallis test.
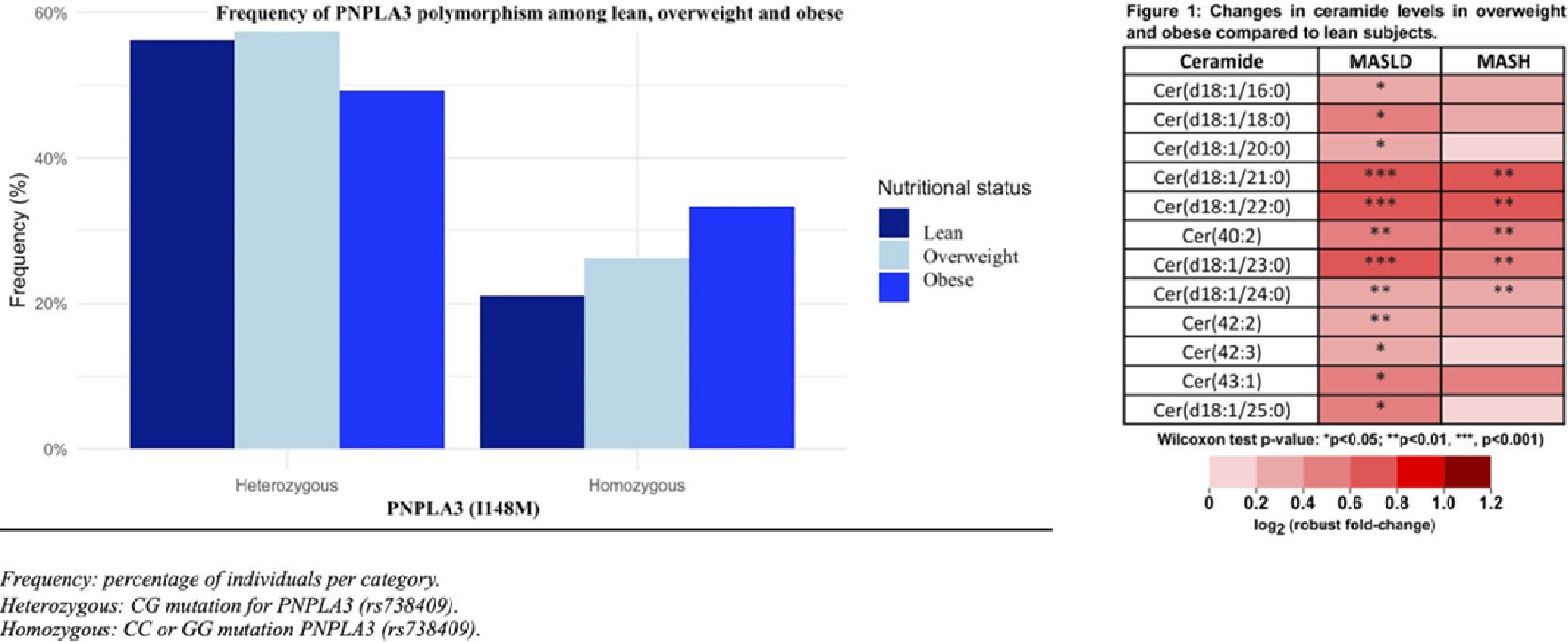
Results and Discussion31.49% (57) were classified as thin, 36.3% (61) as overweight and 39.8% (67) as obese. Higher ALT levels (p=0.004) and body fat percentage in obese subjects were the only significant differences found among the groups. The allelic frequency of rs738409 was similar among groups 77.1%, 83.6% and 82.5% in lean, overweight, and obese subjects, respectively (n.s.). Circulating metabolome showed increased levels of ceramides in overweight and obese patients compared to lean subjects (p<0.001 for five different species). The increment is higher if all the MASLD patients were considered (Figure). Serum bile acids, particularly chenodeoxycholic acid (p<0.001) and glycochenodeoxycholic acid (p=0.024), were also increased. Lipidomic analysis also showed an increase of polyunsaturated diglyceride and triglyceride species in overweight and obese compared to lean subjects. Among them, most of the species included linoleic acid or alpha-linoleic acid in their esterified chains.
ConclusionsPNPLA3 risk allele was equally frequent in lean and non-lean Chilean MASLD patients. Metabolomic differences were found with non-lean subjects exhibiting higher levels of ceramides and bile acid species compared with lean patients. (Supported by Fondecyt # 1241450)